|
Transamazonian Orogeny
The Transamazonian orogeny was a mountain building event in the Paleoproterozoic, affecting what is now the São Francisco Craton and Guyana Shield. During the orogeny from 2.14 to 1.94 billion years ago two small Archean proto-continents—including the greenstone belt-dominated Gavião Block and the calc-alkaline charnockite and enderbite-dominated Jequié Block—collided. The Contendas-Jacobina Lineament represents a suture zone where the collision occurred and the Gavião Block partially subducted under the Jequié Block. At the same time, another small continental fragment, the Serrinha Block, may have collided as well and was extensively reworked and metamorphosed, with orthogneiss and migmatite reaching amphibolite-grade on the sequence of metamorphic facies. The Serrinha Block is the basement rock of the Rio Itapicuru granite-greenstone belt. Several magmatic arcs formed between the colliding proto-continent blocks, including the Salvador-Curaçá Belt, Contendas-Mirante Bel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orogeny
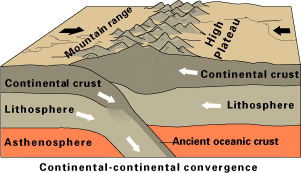
Orogeny is a mountain building process. An orogeny is an event that takes place at a convergent plate margin when plate motion compresses the margin. An ''orogenic belt'' or ''orogen'' develops as the compressed plate crumples and is uplifted to form one or more mountain ranges. This involves a series of geological processes collectively called orogenesis. These include both structural deformation of existing continental crust and the creation of new continental crust through volcanism. Magma rising in the orogen carries less dense material upwards while leaving more dense material behind, resulting in compositional differentiation of Earth's lithosphere ( crust and uppermost mantle). A synorogenic process or event is one that occurs during an orogeny. The word "orogeny" () comes from Ancient Greek (, , + , , ). Although it was used before him, the term was employed by the American geologist G. K. Gilbert in 1890 to describe the process of mountain-building as distinguished f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neoproterozoic
The Neoproterozoic Era is the unit of geologic time from 1 billion to 538.8 million years ago. It is the last era of the Precambrian Supereon and the Proterozoic Eon; it is subdivided into the Tonian, Cryogenian, and Ediacaran periods. It is preceded by the Mesoproterozoic Era and succeeded by the Paleozoic Era of the Phanerozoic Eon. The most severe glaciation known in the geologic record occurred during the Cryogenian, when ice sheets may have reached the equator and formed a " Snowball Earth". The earliest fossils of complex multicellular life are found in the Ediacaran Period. These organisms make up the Ediacaran biota, including the oldest definitive animals in the fossil record. According to Rino and co-workers, the sum of the continental crust formed in the Pan-African orogeny and the Grenville orogeny makes the Neoproterozoic the period of Earth's history that has produced most continental crust. Geology At the onset of the Neoproterozoic the supercontine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orogenies Of South America
Orogeny is a mountain building process. An orogeny is an event that takes place at a convergent plate margin when plate motion compresses the margin. An ''orogenic belt'' or ''orogen'' develops as the compressed plate crumples and is uplifted to form one or more mountain ranges. This involves a series of geological processes collectively called orogenesis. These include both structural deformation of existing continental crust and the creation of new continental crust through volcanism. Magma rising in the orogen carries less dense material upwards while leaving more dense material behind, resulting in compositional differentiation of Earth's lithosphere ( crust and uppermost mantle). A synorogenic process or event is one that occurs during an orogeny. The word "orogeny" () comes from Ancient Greek (, , + , , ). Although it was used before him, the term was employed by the American geologist G. K. Gilbert in 1890 to describe the process of mountain-building as distinguished f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Orogenies
The following is a list of known orogenies organised by continent, starting with the oldest at the top. The organization of this article is along present-day continents that do not necessarily reflect the geography contemporary to the orogenies. Note that some orogenies encompass more than one continent and might have different names in each continent. Likewise some very large orogenies include a number of sub-orogenies. As with other geological phenomena orogenies are often subject to different and changing interpretations regarding to their age, type and associated paleogeography. In some interpretations, especially in the older literature, the term orogeny is equivalent to a long "Episode" of basin formation and deposition of sediments (with durations of hundreds of millions of years), ending with deformation (sometimes including metamorphism) of these deposits. Some workers use the term only for the final mountain building deformation "Event" with a small duration of tens of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geology Of Guyana
Guyana occurs within the northern part of the Guiana Shield. The Guiana Shield forms the northern part of the Amazonian Craton, the core of the South American continent. Most of the geology of northern Guyana consists of Palaeoproterozoic Orosirian greenstone belts (Barama-Mazaruni Supergroup) intruded by granites. These are overlain unconformably by the Statherian Burro-Burro Group, which consist of the Muruwa Formation sandstones and Iwokrama Formation felsic volcanics. Both are intruded by granites associated with the Iwokrama Formation. Some folding occurred before these were overlain by the locally unconformable almost flat lying Roraima Group.Gibbs, A.K & Barron, C.N (1993). ''The Geology of the Guiana Shield''. Oxford University Press. Major mafic sills and dykes of the Avanavero Suite intrude all of the older rocks, and are part of a Large Igneous Province (LIP). Numerous mafic dykes intruded the basement in the late Permian and Early Jurassic, associated with the start of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geology Of Brazil
The geology of Brazil includes very ancient craton basement rock from the Precambrian overlain by sedimentary rocks and intruded by igneous activity, as well as impacted by the rifting of the Atlantic Ocean. Geologic history, stratigraphy, and tectonics Much of the rock underlying Brazil formed during the Precambrian, including the São Francisco Craton which outcrops in Minas Gerais and Bahia. In the Mesoproterozoic, the Rio de la Plata Craton (beneath southern Brazil), the vast Amazonia Craton, and the small São Luis Craton and sections of the Congo Craton which form the basement rock of much of Brazil were joined with Africa. Earlier, during the Archean, the São Francisco Craton developed between 3.2 and 2.6 billion years ago and grew as microcontinents collided with it, forming a series of mobile belts. The rocks became a craton, a section of stable continental crust by the end of the Trans-amazonian orogeny 1.8 billion years ago. The Borborema Province is benea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhyolite
Rhyolite ( ) is the most silica-rich of volcanic rocks. It is generally glassy or fine-grained (aphanitic) in texture, but may be porphyritic, containing larger mineral crystals (phenocrysts) in an otherwise fine-grained groundmass. The mineral assemblage is predominantly quartz, sanidine, and plagioclase. It is the extrusive equivalent to granite. Rhyolitic magma is extremely viscous, due to its high silica content. This favors explosive eruptions over effusive eruptions, so this type of magma is more often erupted as pyroclastic rock than as lava flows. Rhyolitic ash-flow tuffs are among the most voluminous of continental igneous rock formations. Rhyolitic tuff has been extensively used for construction. Obsidian, which is rhyolitic volcanic glass, has been used for tools from prehistoric times to the present day because it can be shaped to an extremely sharp edge. Rhyolitic pumice finds use as an abrasive, in concrete, and as a soil amendment. Description Rhyolite i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ignimbrite
Ignimbrite is a type of volcanic rock, consisting of hardened tuff. Ignimbrites form from the deposits of pyroclastic flows, which are a hot suspension of particles and gases flowing rapidly from a volcano, driven by being denser than the surrounding atmosphere. New Zealand geologist Patrick Marshall (1869-1950) coined the term ''ignimbrite'' from the Latin ''igni-'' [fire] and ''imbri-'' [rain]. Ignimbrites are made of a very poorly sorted mixture of volcanic ash (or tuff when Lithification, lithified) and pumice lapilli, commonly with scattered lithic fragments. The ash is composed of glass shards and crystal fragments. Ignimbrites may be loose and unconsolidated, or lithified (solidified) rock called lapilli-tuff. Near the volcanic source, ignimbrites often contain thick accumulations of lithic blocks, and distally, many show meter-thick accumulations of rounded cobbles of pumice. Ignimbrites may be white, grey, pink, beige, brown, or black depending on their composition and d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyroclastic
Pyroclastic rocks (derived from the el, πῦρ, links=no, meaning fire; and , meaning broken) are clastic rocks composed of rock fragments produced and ejected by explosive volcanic eruptions. The individual rock fragments are known as pyroclasts. Pyroclastic rocks are a type of volcaniclastic deposit, which are deposits made predominantly of volcanic particles. 'Phreatic' pyroclastic deposits are a variety of pyroclastic rock that forms from volcanic steam explosions and they are entirely made of accidental clasts. 'Phreatomagmatic' pyroclastic deposits are formed from explosive interaction of magma with groundwater. Unconsolidated accumulations of pyroclasts are described as tephra. Tephra may become lithified to a pyroclastic rock by cementation or chemical reactions as the result of the passage of hot gases (fumarolic alteration) or groundwater (e.g. hydrothermal alteration and diagenesis) and burial, or, if it is emplaced at temperatures so hot that the soft glassy pyroc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horst And Graben
In geology, horst and graben (or range and valley) refers to topography consisting of alternating raised and lowered fault blocks known as horsts and grabens. The features are created by normal faulting and rifting caused by crustal extension. Horst and graben are formed when normal faults of opposite dip occur in pairs with parallel strike, and are always formed together. Each feature can range in size from a few centimeters up to tens of kilometers, and the vertical displacement can be up to several thousand meters. The movement on either side of each block is typically equal, resulting in little tilting. Features Horst A horst is a section of crust that has been lifted relative to the blocks on either side, which is a result of its bounding faults dipping away from each other. Horsts can form features such as plateaus, mountain ranges or ridges on either side of the valleys. Graben A graben is a section of crust that has lowered relative to the blocks on either ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guriense Orogeny
The Guriense orogeny was a mountain building event in the Archean 2.8 to 2.7 billion years ago, preserved in the Guyana Shield rocks of Venezuela, Guyana and Suriname. See also *Geology of Venezuela *Geology of Guyana * Geology of Suriname *List of orogenies The following is a list of known orogenies organised by continent, starting with the oldest at the top. The organization of this article is along present-day continents that do not necessarily reflect the geography contemporary to the orogenies. ... References {{South America topic, Geology of Orogenies of South America Archean orogenies Geology of Venezuela Geology of Guyana Geology of Suriname ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syenite
Syenite is a coarse-grained intrusive igneous rock with a general composition similar to that of granite, but deficient in quartz, which, if present at all, occurs in relatively small concentrations (< 5%). Some syenites contain larger proportions of components and smaller amounts of felsic material than most granites; those are classed as being of . The equivalent of syenite is |