|
Guriense Orogeny
The Guriense orogeny was a mountain building event in the Archean 2.8 to 2.7 billion years ago, preserved in the Guyana Shield rocks of Venezuela, Guyana and Suriname. See also *Geology of Venezuela *Geology of Guyana * Geology of Suriname *List of orogenies The following is a list of known orogenies organised by continent, starting with the oldest at the top. The organization of this article is along present-day continents that do not necessarily reflect the geography contemporary to the orogenies. ... References {{South America topic, Geology of Orogenies of South America Archean orogenies Geology of Venezuela Geology of Guyana Geology of Suriname ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
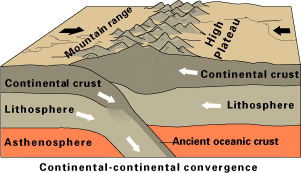
Orogeny
Orogeny is a mountain building process. An orogeny is an event that takes place at a convergent plate margin when plate motion compresses the margin. An ''orogenic belt'' or ''orogen'' develops as the compressed plate crumples and is uplifted to form one or more mountain ranges. This involves a series of geological processes collectively called orogenesis. These include both structural deformation of existing continental crust and the creation of new continental crust through volcanism. Magma rising in the orogen carries less dense material upwards while leaving more dense material behind, resulting in compositional differentiation of Earth's lithosphere ( crust and uppermost mantle). A synorogenic process or event is one that occurs during an orogeny. The word "orogeny" () comes from Ancient Greek (, , + , , ). Although it was used before him, the term was employed by the American geologist G. K. Gilbert in 1890 to describe the process of mountain-building as distinguished f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archean
The Archean Eon ( , also spelled Archaean or Archæan) is the second of four geologic eons of Earth's history, representing the time from . The Archean was preceded by the Hadean Eon and followed by the Proterozoic. The Earth Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surfa ... during the Archean was mostly a water world: there was continental crust, but much of it was under an ocean deeper than today's ocean. Except for some trace minerals, today's oldest continental crust dates back to the Archean. Much of the geological detail of the Archean has been destroyed by subsequent activity. The Earliest known life forms, earliest known life started in the Archean. Life was simple throughout the Archean, mostly represented by shallow-water microbial mats called stromatolites, and the a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geology Of Venezuela
The geology of Venezuela includes ancient Precambrian igneous and metamorphic basement rocks, layered with sedimentary rocks from the Paleozoic and Mesozoic and thick geologically recent Cenozoic sediments with extensive oil and gas. Geologic History, Stratigraphy & Tectonics The oldest rocks in Venezuela formed during the Precambrian and occupy the Guiana shield in the southern tier of the country near Guyana and Brazil, east of the El BaUl swell. In the western Guiana Shield, within the Amazonas Territory, Precambrian Roraima Formation zircon grains have been dated with uranium-lead dating and rubidium-strontium dating. Metamorphism and intrusive activity formed gneiss with sedimentary and igneous protoliths around 1.8 billion years ago. Plutons emplaced granite and tonalite after inferred collision and subduction tectonics until around 1.55 billion years ago. The formation's volcanic rocks were produced 1.74 billion years ago. Metamorphism was driven in places by the Transamazo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geology Of Guyana
Guyana occurs within the northern part of the Guiana Shield. The Guiana Shield forms the northern part of the Amazonian Craton, the core of the South American continent. Most of the geology of northern Guyana consists of Palaeoproterozoic Orosirian greenstone belts (Barama-Mazaruni Supergroup) intruded by granites. These are overlain unconformably by the Statherian Burro-Burro Group, which consist of the Muruwa Formation sandstones and Iwokrama Formation felsic volcanics. Both are intruded by granites associated with the Iwokrama Formation. Some folding occurred before these were overlain by the locally unconformable almost flat lying Roraima Group.Gibbs, A.K & Barron, C.N (1993). ''The Geology of the Guiana Shield''. Oxford University Press. Major mafic sills and dykes of the Avanavero Suite intrude all of the older rocks, and are part of a Large Igneous Province (LIP). Numerous mafic dykes intruded the basement in the late Permian and Early Jurassic, associated with the start of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geology Of Suriname
The geology of Suriname is predominantly formed by the Guyana Shield, which spans 90% of its land area. Coastal plains account for the remaining ten percent. Most rocks in Suriname date to the Precambrian. These crystalline basement rocks consists of granitoid and acid volcanic rocks with enclaves of predominantly low-grade metamorphic, geosynclinal rocks in the Marowijne area and of probably considerably older rocks in the Falawatra group of the Bakhuisgebirge and the Coronie area. There are also small, scattered bodies of gabbro and ultramafitite. These are about the same age as the granite and volcanics. It has been found that the construction of the basement was largely created during the final phase of the Trans-Amazonian Orogeny Cycle, about 1.9 billion years ago. This cycle has had a significant influence on the geology of Suriname, characterized by sedimentation, metamorphosis, corrugation and magmatism. Young sediments cover the northern 20% of the country. They exist from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Orogenies
The following is a list of known orogenies organised by continent, starting with the oldest at the top. The organization of this article is along present-day continents that do not necessarily reflect the geography contemporary to the orogenies. Note that some orogenies encompass more than one continent and might have different names in each continent. Likewise some very large orogenies include a number of sub-orogenies. As with other geological phenomena orogenies are often subject to different and changing interpretations regarding to their age, type and associated paleogeography. In some interpretations, especially in the older literature, the term orogeny is equivalent to a long "Episode" of basin formation and deposition of sediments (with durations of hundreds of millions of years), ending with deformation (sometimes including metamorphism) of these deposits. Some workers use the term only for the final mountain building deformation "Event" with a small duration of tens of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orogenies Of South America
Orogeny is a mountain building process. An orogeny is an event that takes place at a convergent plate margin when plate motion compresses the margin. An ''orogenic belt'' or ''orogen'' develops as the compressed plate crumples and is uplifted to form one or more mountain ranges. This involves a series of geological processes collectively called orogenesis. These include both structural deformation of existing continental crust and the creation of new continental crust through volcanism. Magma rising in the orogen carries less dense material upwards while leaving more dense material behind, resulting in compositional differentiation of Earth's lithosphere ( crust and uppermost mantle). A synorogenic process or event is one that occurs during an orogeny. The word "orogeny" () comes from Ancient Greek (, , + , , ). Although it was used before him, the term was employed by the American geologist G. K. Gilbert in 1890 to describe the process of mountain-building as distinguished f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archean Orogenies
The Archean Eon ( , also spelled Archaean or Archæan) is the second of four geologic eons of Earth's history, representing the time from . The Archean was preceded by the Hadean Eon and followed by the Proterozoic. The Earth during the Archean was mostly a water world: there was continental crust, but much of it was under an ocean deeper than today's ocean. Except for some trace minerals, today's oldest continental crust dates back to the Archean. Much of the geological detail of the Archean has been destroyed by subsequent activity. The earliest known life started in the Archean. Life was simple throughout the Archean, mostly represented by shallow-water microbial mats called stromatolites, and the atmosphere lacked free oxygen. Etymology and changes in classification The word ''Archean'' comes from the Greek word (), meaning 'beginning, origin'. It was first used in 1872, when it meant 'of the earliest geological age'. Before the Hadean Eon was recognized, the Archean sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |