|
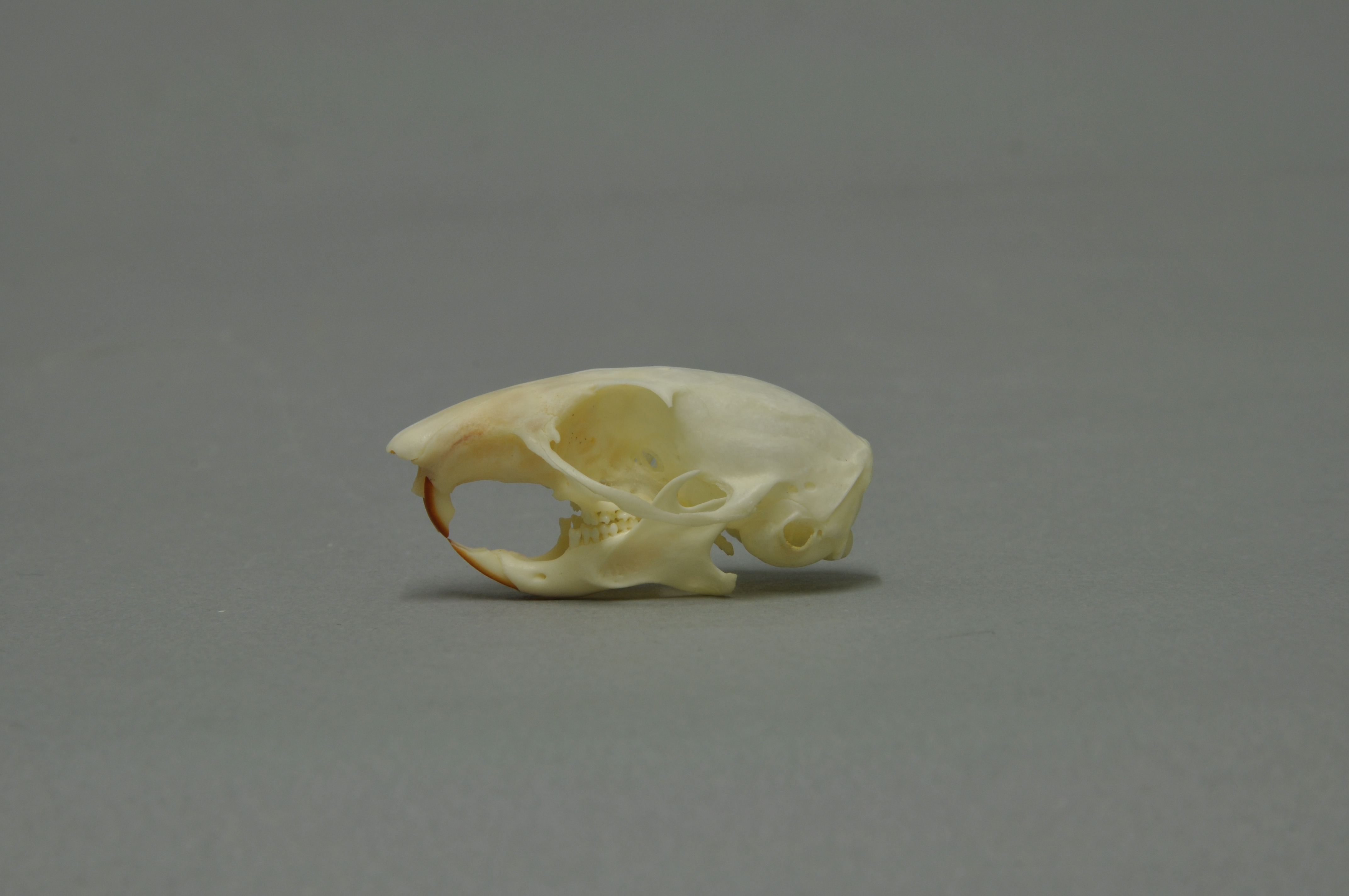
Townsend's Chipmunk
Townsend's chipmunk (''Neotamias townsendii'') is a species of rodent in the squirrel family, Sciuridae. It lives in the forests of the Pacific Northwest of North America, from extreme southwestern British Columbia through western Washington and western Oregon. Townsend's chipmunk is named after John Kirk Townsend, an early 19th-century ornithologist. Description A large chipmunk, adults can be from nose to the tip of its tail. In much of its range, it is the only chipmunk; it can be identified by its tail which is grayish above and reddish below, and by its brown coloration with indistinct tawny stripes. Biology Townsend's chipmunk hibernates in regions where the winter is harsh, but in other parts of its range that have a more mild climate it can be active year-round. It is omnivorous, eating a variety of plants and insects and even birds' eggs. Townsend's chipmunks in the Oregon Coast Range have higher population densities in areas with dense shrubbery, especially salal (' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Bachman
John Bachman (February 4, 1790 – February 24, 1874) was an American Lutheran minister, social activist and naturalist who collaborated with John James Audubon to produce ''Viviparous Quadrupeds of North America'' and whose writings, particularly ''Unity of the Human Race'', were influential in the development of the theory of evolution. He was married to the painter Maria Martin. Several species of animals are named in his honor. Life Bachman served the same Charleston, South Carolina church as pastor for 56 years but still found time to conduct natural history studies that caught the attention of noted bird artist John James Audubon and eminent scientists in England, Europe, and beyond. He was a proponent of secular and religious education and helped found Newberry College and the Lutheran Theological Southern Seminary, as well as the South Carolina Lutheran Synod. He was elected an Associate Fellow of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences in 1845. Bachman was a so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Omnivore
An omnivore () is an animal that has the ability to eat and survive on both plant and animal matter. Obtaining energy and nutrients from plant and animal matter, omnivores digest carbohydrates, protein, fat, and fiber, and metabolize the nutrients and energy of the sources absorbed. Often, they have the ability to incorporate food sources such as algae, fungi, and bacteria into their diet. Omnivores come from diverse backgrounds that often independently evolved sophisticated consumption capabilities. For instance, dogs evolved from primarily carnivorous organisms ( Carnivora) while pigs evolved from primarily herbivorous organisms ( Artiodactyla). Despite this, physical characteristics such as tooth morphology may be reliable indicators of diet in mammals, with such morphological adaptation having been observed in bears. The variety of different animals that are classified as omnivores can be placed into further sub-categories depending on their feeding behaviors. Frugivo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammals Of The United States
About 490 species of mammals are recorded in the United States. Unincorporated territories like for example Puerto Rico, Guam or Northern Mariana Islands are not covered. Mammals introduced and extinct in the Holocene except Pleistocene/Holocene boundary are included. According to the IUCN Red List 3 of these species are critically endangered, 20 endangered, 15 vulnerable, 20 near threatened and 4 extinct. Some species are identified as indicated below: *(A) - Accidental *(E) - Extinct *(Ex) - Extirpated (extinct in the US, but exists elsewhere in the world) *(I) - Introduced The following tags are used to highlight each species' conservation status as assessed by the International Union for Conservation of Nature: (v. 2013.2, the data are current as of March 5, 2014) and the Endangered Species Act: (the data are current as of March 28, 2014) Subclass: Theria Infraclass: Metatheria Order: Didelphimorphia (common opossums) ---- Didelphimorphia is the order ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxa Named By John Bachman
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''Taxonomy (biology), taxonomy''; plural taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and given a particular Taxonomic rank, ranking, especially if and when it is accepted or becomes established. It is very common, however, for taxonomists to remain at odds over what belongs to a taxon and the criteria used for inclusion. If a taxon is given a formal scientific name, its use is then governed by one of the nomenclature codes specifying which scientific name is correct for a particular grouping. Initial attempts at classifying and ordering organisms (plants and animals) were set forth in Carl Linnaeus's Linnaean taxonomy, system in ''Systema Naturae'', 10th edition (1758), as well as an unpublished work by Bernard de Jussieu, Bernard and Antoine Laurent de Jussieu. The idea of a unit-based system of bio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxonomy Articles Created By Polbot
Taxonomy is the practice and science of categorization or classification. A taxonomy (or taxonomical classification) is a scheme of classification, especially a hierarchical classification, in which things are organized into groups or types. Among other things, a taxonomy can be used to organize and index knowledge (stored as documents, articles, videos, etc.), such as in the form of a library classification system, or a search engine taxonomy, so that users can more easily find the information they are searching for. Many taxonomies are hierarchies (and thus, have an intrinsic tree structure), but not all are. Originally, taxonomy referred only to the categorisation of organisms or a particular categorisation of organisms. In a wider, more general sense, it may refer to a categorisation of things or concepts, as well as to the principles underlying such a categorisation. Taxonomy organizes taxonomic units known as "taxa" (singular "taxon")." Taxonomy is different from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammals Described In 1839
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur or hair, and three middle ear bones. These characteristics distinguish them from reptiles (including birds) from which they diverged in the Carboniferous, over 300 million years ago. Around 6,400 extant species of mammals have been described divided into 29 orders. The largest orders, in terms of number of species, are the rodents, bats, and Eulipotyphla (hedgehogs, moles, shrews, and others). The next three are the Primates (including humans, apes, monkeys, and others), the Artiodactyla (cetaceans and even-toed ungulates), and the Carnivora (cats, dogs, seals, and others). In terms of cladistics, which reflects evolutionary history, mammals are the only living members of the Synapsida (synapsids); this clade, together with Saur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neotamias
''Neotamias'' is a genus of chipmunks within the tribe Marmotini of the squirrel family. It contains 23 species, which mostly occur in western North America. Along with '' Eutamias'', this genus is often considered a subgenus of '' Tamias''. Species * Alpine chipmunk, ''Neotamias alpinus'' *Yellow-pine chipmunk ''Neotamias amoenus'' * Buller's chipmunk, ''Neotamias bulleri'' * Gray-footed chipmunk, ''Neotamias canipes'' *Gray-collared chipmunk, ''Neotamias cinereicollis'' *Cliff chipmunk, ''Neotamias dorsalis'' *Durango chipmunk, ''Neotamias durangae'' * Merriam's chipmunk, ''Neotamias merriami'' * Least chipmunk, ''Neotamias minimus'' * California chipmunk, ''Neotamias obscurus'' * Yellow-cheeked chipmunk, ''Neotamias ochrogenys'' * Palmer's chipmunk, ''Neotamias palmeri'' *Panamint chipmunk, ''Neotamias panamintinus'' * Long-eared chipmunk, ''Neotamias quadrimaculatus'' * Colorado chipmunk, ''Neotamias quadrivittatus'' *Red-tailed chipmunk The red-tailed chipmunk (''Neo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaultheria Shallon
''Gaultheria shallon'' is an evergreen shrub in the heather family (Ericaceae), native to western North America. In English, it is known as salal, shallon, or (mainly in Britain) gaultheria. Description ''Gaultheria shallon'' is tall, sprawling to erect. It is loosely to densely branched and often forms dense, nearly impenetrable thickets. The twigs are reddish-brown, with shredding bark. Twigs can live up to 16 years or more, but bear leaves only the first few years. Its evergreen leaves are dense, leathery, and tough, of egg-headed shape. They are shiny and dark green on the upper surface, and rough and lighter green on the lower. Each finely and sharply serrate leaf is long. Each leaf generally lives for 2 to 4 years before it is replaced. The inflorescence of flowers consists of a bracteate raceme, one-sided, with 5–15 flowers at the ends of branches. Each flower is composed of a deeply five-parted, glandular-haired calyx and an urn-shaped pink to white, glandular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oregon Coast Range
The Oregon Coast Range, often called simply the Coast Range and sometimes the Pacific Coast Range, is a mountain range, in the Pacific Coast Ranges physiographic region, in the U.S. state of Oregon along the Pacific Ocean. This north-south running range extends over from the Columbia River in the north on the border of Oregon and Washington, south to the middle fork of the Coquille River. It is wide and averages around in elevation above sea level. The coast range has three main sections, a Northern, Central, and Southern. The oldest portions of the range are over 60 million years old, with volcanics and a forearc basin as the primary mountain building processes responsible for the range. It is part of the larger grouping known as the Pacific Coast Ranges that extends over much of the western edge of North America from California to Alaska. The range creates a rain shadow effect for the Willamette Valley that lies to the east of the mountains, creating a more stable c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lone Pine Publishing
Lone Pine Publishing is an BC-based book publisher, best known across Canada and parts of the United States for its gardening books, bird guides and nature guides. Lone Pine Publishing was founded in 1980 when Canadian broadcaster and journalist Grant Kennedy set up the company in Edmonton and published the firm’s first book, entitled ''The Albertans''. Since then, Lone Pine Publishing has published over 600 titles. The company also distributes books for a number of smaller Canadian and U.S. publishers through an extensive network of independent booksellers and other retailers, marketing in all Canadian provinces except Quebec and in the U.S. Pacific Northwest, California and the Great Lakes states. Lone Pine Publishing maintains head office operations in Vancouver, British Columbia and central warehouse operations in Edmonton, Alberta, Canada, as well as a sales office and warehouse in Tukwila, Washington, USA. The company maintains a network of satellite warehouses across C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hibernation
Hibernation is a state of minimal activity and metabolic depression undergone by some animal species. Hibernation is a seasonal heterothermy characterized by low body-temperature, slow breathing and heart-rate, and low metabolic rate. It most commonly occurs during winter months. Although traditionally reserved for "deep" hibernators such as rodents, the term has been redefined to include animals such as bears and is now applied based on active metabolic suppression rather than any absolute decline in body temperature. Many experts believe that the processes of daily torpor and hibernation form a continuum and utilise similar mechanisms. The equivalent during the summer months is aestivation. Hibernation functions to conserve energy when sufficient food is not available. To achieve this energy saving, an endothermic animal decreases its metabolic rate and thereby its body temperature. Hibernation may last days, weeks, or months—depending on the species, ambient temperatu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can reproduction, produce Fertility, fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology (biology), morphology, behaviour or ecological niche. In addition, paleontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. The most recent rigorous estimate for the total number of species of eukaryotes is between 8 and 8.7 million. However, only about 14% of these had been described by 2011. All species (except viruses) are given a binomial nomenclature, two-part name, a "binomial". The first part of a binomial is the genus to which the species belongs. The second part is called the specifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |