|
Torsa Strict Nature Reserve
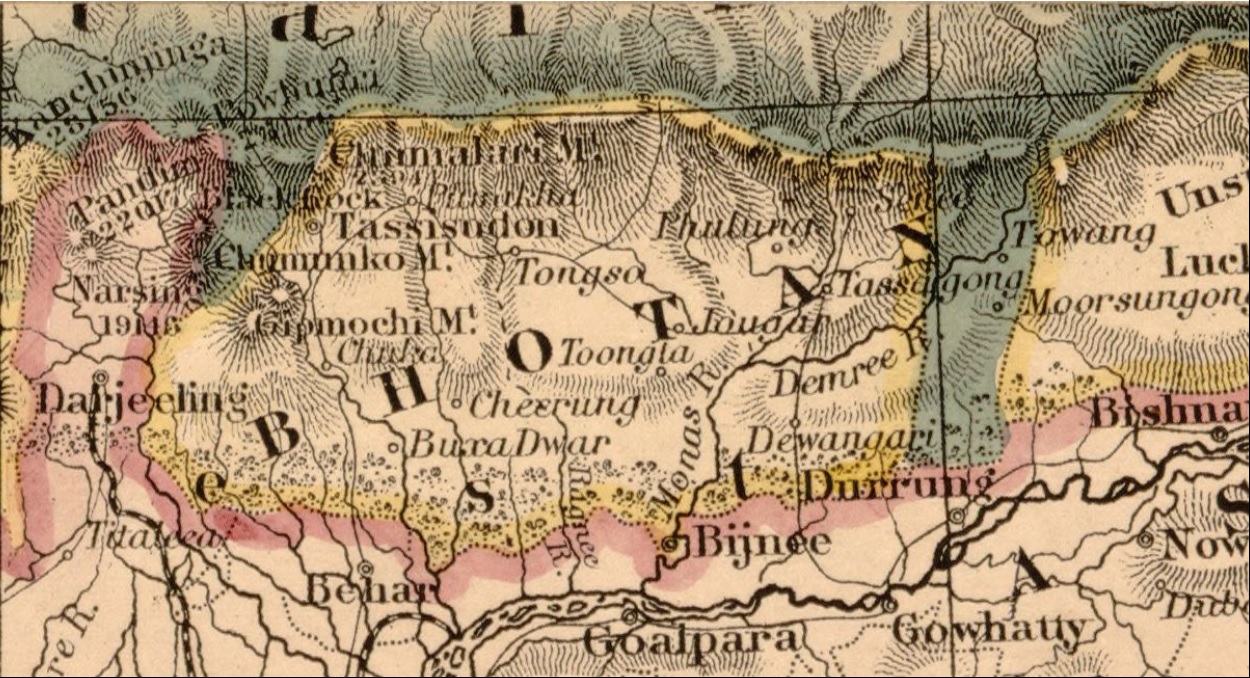
__NOTOC__ The Torsa Strict Nature Reserve (officially Jigme Khesar Strict Nature Reserve) in Bhutan covers 609.51 square kilometres in Haa District, occupying most of its area. Founded along with other national parks in 1993 by decision of the royal government, It borders Sikkim and Tibet to the west and is connected to Jigme Dorji National Park via a "biological corridor." Torsa SNR contains the westernmost temperate forests of Bhutan, from broadleaf forests to alpine meadows and the small lakes of Sinchulungpa, at altitudes ranging from to . Like Phibsoo Wildlife Sanctuary, Torsa SNR has no resident human population. Flora and fauna This diverse ecosystem, home to various endangered species such as the Tibetan Snow Cock, Red Panda, Snow Leopard and Rufous Necked Hornbills, also grows in the reserve the only endemic poppy, the White Poppy. Rivers The Amo Chu river that flows in from Tibet's Chumbi Valley is called Torsa Chu after it enters the Torsa SNR. See also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haa District
Haa District ( Dzongkha: ཧཱ་; Wylie: ''Haa''; alternative spellings include "Ha") is one of the 20 dzongkhag or districts comprising Bhutan. An alternative name for the district is "Hidden-Land Rice Valley." It the second least-populated dzongkhag in the country after Gasa.http://www.haa.gov.bt/downloads?Type=12&Sector=AlBhutan Census website The most-spoken language of the district is Dzongkha. The river Haa Chhu, originating at Jomolhari mountain, flows through the district. Mystical history of Haa The name Haa (pronounced "hah"), as well as the more ancient name ''Has'' ( Dzongkha: ཧས་; Wylie: ''Has''; pronounced "hay"), connotes esoteric hiddenness. Haa's major feature is the Haa Valley, a steep north-south valley with a narrow floor. The district is presided over by three mountains collectively referred as "Three Brothers" -- ''Jampelyang, Chana-Dorji, and Chenrezig.'' Black, White, and Haa Gonpa temples Local historians maintain that two important templ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bhutan
Bhutan (; dz, འབྲུག་ཡུལ་, Druk Yul ), officially the Kingdom of Bhutan,), is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is situated in the Eastern Himalayas, between China in the north and India in the south. A mountainous country, Bhutan is known as "Druk Yul," or "Land of the Thunder Dragon". Nepal and Bangladesh are located near Bhutan but do not share a land border. The country has a population of over 727,145 and territory of and ranks 133rd in terms of land area and 160th in population. Bhutan is a Constitutional Democratic Monarchy with King as head of state and Prime Minister as head of government. Mahayana and Vajrayana Buddhism is the state religion and the Je Khenpo is the head of state religion. The subalpine Himalayan mountains in the north rise from the country's lush subtropical plains in the south. In the Bhutanese Himalayas, there are peaks higher than above sea level. Gangkhar Puensum is Bhutan's highest peak and is the highest uncl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Druk Gyalpo
The Druk Gyalpo (; 'Dragon King') is the head of state of the Bhutan, Kingdom of Bhutan. In the Dzongkha, Dzongkha language, Bhutan is known as ''Drukyul'' which translates as "The Land of the Thunder Dragon". Thus, while kings of Bhutan are known as ''Druk Gyalpo'' ("Dragon King"), the Bhutanese people call themselves the ''Drukpa'', meaning "people of Druk (Bhutan)". The current sovereign of Bhutan is Jigme Khesar Namgyel Wangchuck, the fifth ''Druk Gyalpo''. He wears the Raven Crown, which is the official crown worn by the kings of Bhutan. He is correctly styled "''Mi'wang 'Ngada Rinpoche''" ("His Majesty") and addressed "''Ngada Rimboche''" ("Your Majesty"). King Jigme Khesar was the second-youngest reigning monarch in the world when he ascended the throne on 1 November 2008 after his father, Jigme Singye Wangchuck, abdicated the throne in his favour. Duties and powers The Constitution confirms the institution of monarchy. The Druk Gyalpo (King of Bhutan) is the head of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jigme Khesar Namgyel Wangchuck
Jigme Khesar Namgyel Wangchuck ( dz, འཇིགས་མེད་གེ་སར་རྣམ་རྒྱལ་དབང་ཕྱུག་, ; born 21 February 1980) is the Druk Gyalpo ( Dzongkha: Dragon King) of the Kingdom of Bhutan. After his father Jigme Singye Wangchuck abdicated the throne in his favor, he became the monarch on 9 December 2006. A public coronation ceremony was held on 6 November 2008, a year that marked 100 years of monarchy in Bhutan. Early life and education Khesar was born 21 February 1980 at Paropakar Maternity and Women's Hospital in Kathmandu. He is the eldest son of the fourth Dragon king of Bhutan, Jigme Singye Wangchuck, and his third wife, Queen ''Ashi'' Tshering Yangdon. He has a younger sister, Princess ''Ashi'' Dechen Yangzom, and brother, Prince ''Gyaltshab'' Jigme Dorji, as well as four half-sisters and three half-brothers. After completing his higher secondary studies at Yangchenphug High School, Khesar was educated in the United States ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sikkim
Sikkim (; ) is a state in Northeastern India. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China in the north and northeast, Bhutan in the east, Province No. 1 of Nepal in the west and West Bengal in the south. Sikkim is also close to the Siliguri Corridor, which borders Bangladesh. Sikkim is the least populous and second smallest among the Indian states. Situated in the Eastern Himalaya, Sikkim is notable for its biodiversity, including alpine and subtropical climates, as well as being a host to Kangchenjunga, the highest peak in India and third highest on Earth. Sikkim's capital and largest city is Gangtok. Almost 35% of the state is covered by Khangchendzonga National Park – a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The Kingdom of Sikkim was founded by the Namgyal dynasty in the 17th century. It was ruled by Buddhist priest-kings known as the Chogyal. It became a princely state of British India in 1890. Following Indian independence, Sikkim continued its protectorate status with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tibet
Tibet (; ''Böd''; ) is a region in East Asia, covering much of the Tibetan Plateau and spanning about . It is the traditional homeland of the Tibetan people. Also resident on the plateau are some other ethnic groups such as Monpa people, Monpa, Tamang people, Tamang, Qiang people, Qiang, Sherpa people, Sherpa and Lhoba peoples and now also considerable numbers of Han Chinese and Hui people, Hui settlers. Since Annexation of Tibet by the People's Republic of China, 1951, the entire plateau has been under the administration of the People's Republic of China, a major portion in the Tibet Autonomous Region, and other portions in the Qinghai and Sichuan provinces. Tibet is the highest region on Earth, with an average elevation of . Located in the Himalayas, the highest elevation in Tibet is Mount Everest, Earth's highest mountain, rising 8,848.86 m (29,032 ft) above sea level. The Tibetan Empire emerged in the 7th century. At its height in the 9th century, the Tibet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jigme Dorji National Park
The Jigme Dorji National Park (JDNP), named after the late Jigme Dorji Wangchuck, is the second-largest National Park of Bhutan. It occupies almost the entire Gasa District, as well as the northern areas of Thimphu District, Paro District, Punakha, and Wangdue Phodrang Districts. It was established in 1974 and stretches over an area of 4316 km², thereby spanning all three climate zones of Bhutan, ranging in elevation from 1400 to over 7000 meters. About 6,500 people in 1,000 households live within the park, from subsistence agriculture and animal husbandry. It is listed as a tentative site in Bhutan's Tentative List for UNESCO inclusion. Flora and fauna The park provides sanctuary for 37 known species of mammals including several endangered, threatened or vulnerable species, such as the Bhutan takin, snow leopard, clouded leopard, Bengal tiger, bharal or Himalayan blue sheep, black musk deer, Himalayan black bear, red panda, Ussuri dhole, and spotted linsang. It is also h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phibsoo Wildlife Sanctuary
The Phibsoo Wildlife Sanctuary is the second-smallest national park in Bhutan, covering in western Sarpang District and southeastern Dagana District along the border with West Bengal. It is connected to Jigme Singye Wangchuck National Park and Royal Manas National Park via a "biological corridor" that crosses a national highway. Its elevations range from to . It is separated from the border with India by two rivers, the Sunkosh River to the west and the Sanathang River to the east. The park is recovering from the scars of the ’90s. In those years, when the country had internal problems with the militia, that is why the park only came to life in 2009. The altitude of the terrain is from 200 to 1600 meters. Flora and fauna Phibsoo is unique in Bhutan for its chital (''Axis axis'', "spotted deer") and natural Shorea robusta, sal (''Shorea robusta'') forests. Like Royal Manas National Park, Phibsoo is inhabited by elephants, bengal tigers, gaur, three species of mahseer, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chumbi Valley
The Chumbi Valley, called Dromo or Tromo in Tibetan, is a valley in the Himalayas that projects southwards from the Tibetan plateau, intervening between Sikkim and Bhutan. It is coextensive with the administrative unit Yadong County in the Tibet Autonomous Region of China. The Chumbi Valley is connected to Sikkim to the southwest via the mountain passes of Nathu La and Jelep La. The valley is at an altitude of , and being on the south side of the Himalayas, enjoys a wetter and more temperate climate than most of Tibet. The valley supports some vegetation in the form of the Eastern Himalayan broadleaf forests and transitions to the Eastern Himalayan alpine shrub and meadows in the north. The plant ''Pedicularis chumbica'' ( 春丕马先蒿) is named after the valley. The 1904 Younghusband Expedition of British India passed through the Chumbi Vally on its way to Lhasa. At the end of the expedition, the British took control of the Chumbi Valley in lieu of a war indemnity. Chin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Protected Areas Of Bhutan
The protected areas of Bhutan are its national parks, nature preserves, and wildlife sanctuaries. Most of these protected areas were first set aside in the 1960s, originally covering most of the northern and southern regions of Bhutan. Today, protected areas cover more than 42% of the kingdom, mostly in the northern regions. Protected areas also line most of Bhutan's international borders with China and India. Background The Forest and Nature Conservation Act of Bhutan, 1995 is the primary legislation that provides a framework of protected areas for Bhutan. The Act defines a protected area as ''an area, which has been declared to be a national park, conservation area, wildlife sanctuary, wildlife reserve, nature reserve, strict nature reserve, research forest, critical watershed or other protected areas.'' The government agency responsible for the oversight of protected areas is the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry Services Division. Since 1992, protected areas have been managed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Himalayan Broadleaf Forests
The Eastern Himalayan broadleaf forests is a temperate broadleaf forest ecoregion found in the middle elevations of the eastern Himalayas, including parts of Nepal, India, and Bhutan. These forests have an outstanding richness of wildlife. Setting This ecoregion covers an area of and constitutes a band of temperate broadleaf forests lying on steep mountain slopes of the Himalayas between approximately . It extends from the Kali Gandaki River in Nepal across Sikkim and West Bengal in India, Bhutan, and the Indian state of Arunachal Pradesh. The temperate broadleaf forests transition into the Himalayan subtropical pine forests and the Himalayan subtropical broadleaf forests at lower elevations, and into the Eastern Himalayan subalpine conifer forests at higher elevations. This area receives over 2000 mm of rainfall per year, mostly falling from May to September during the monsoon. Flora The Eastern Himalayan broadleaf forests are diverse and species-rich, with a great diversity (o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |