|
Toric Code
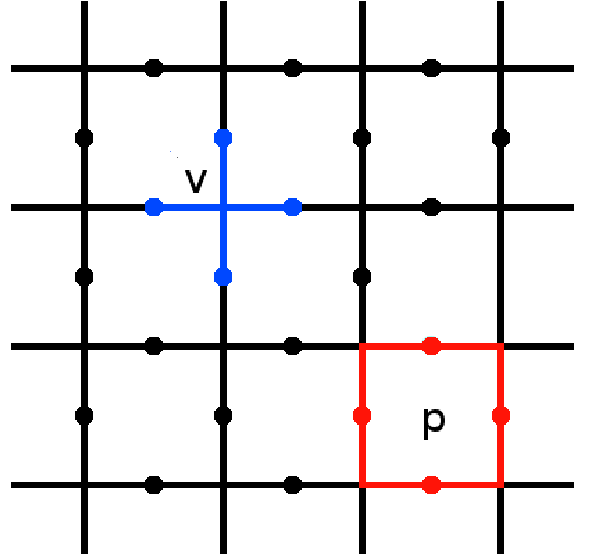
The toric code is a topological quantum error correcting code, and an example of a stabilizer code, defined on a two-dimensional spin lattice. It is the simplest and most well studied of the quantum double models. It is also the simplest example of topological order—''Z''2 topological order (first studied in the context of ''Z''2 spin liquid in 1991). The toric code can also be considered to be a ''Z''2 lattice gauge theory in a particular limit. It was introduced by Alexei Kitaev. The toric code gets its name from its periodic boundary conditions, giving it the shape of a torus. These conditions give the model translational invariance, which is useful for analytic study. However, some experimental realizations require open boundary conditions, allowing the system to be embedded on a 2D surface. The resulting code is typically known as the planar code. This has identical behaviour to the toric code in most, but not all, cases. Error correction and computation The toric code is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topological Order
In physics, topological order is a kind of order in the zero-temperature phase of matter (also known as quantum matter). Macroscopically, topological order is defined and described by robust ground state degeneracy and quantized non-Abelian geometric phases of degenerate ground states. Microscopically, topological orders correspond to patterns of long-range quantum entanglement. States with different topological orders (or different patterns of long range entanglements) cannot change into each other without a phase transition. Various topologically ordered states have interesting properties, such as (1) topological degeneracy and fractional statistics or non-abelian statistics that can be used to realize a topological quantum computer; (2) perfect conducting edge states that may have important device applications; (3) emergent gauge field and Fermi statistics that suggest a quantum information origin of elementary particles; See also (4) topological entanglement entropy that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quasiparticles
In physics, quasiparticles and collective excitations are closely related emergent phenomena arising when a microscopically complicated system such as a solid behaves as if it contained different weakly interacting particles in vacuum. For example, as an electron travels through a semiconductor, its motion is disturbed in a complex way by its interactions with other electrons and with atomic nuclei. The electron behaves as though it has a different effective mass travelling unperturbed in vacuum. Such an electron is called an ''electron quasiparticle''. In another example, the aggregate motion of electrons in the valence band of a semiconductor or a hole band in a metal behave as though the material instead contained positively charged quasiparticles called ''electron holes''. Other quasiparticles or collective excitations include the ''phonon'', a quasiparticle derived from the vibrations of atoms in a solid, and the ''plasmons'', a particle derived from plasma oscillation. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topological Entanglement Entropy
The topological entanglement entropy or ''topological entropy'', usually denoted by \gamma, is a number characterizing many-body states that possess topological order. A non-zero topological entanglement entropy reflects the presence of long range quantum entanglements in a many-body quantum state. So the topological entanglement entropy links topological order with pattern of long range quantum entanglements. Given a topologically ordered state, the topological entropy can be extracted from the asymptotic behavior of the Von Neumann entropy measuring the quantum entanglement between a spatial block and the rest of the system. The entanglement entropy of a simply connected region of boundary length ''L'', within an infinite two-dimensional topologically ordered state, has the following form for large ''L'': : S_L \; \longrightarrow \; \alpha L -\gamma +\mathcal(L^) \; , \qquad \nu>0 \,\! where -\gamma is the topological entanglement entropy. The topological entanglement en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
String-net Liquid
In condensed matter physics, a string-net is an extended object whose collective behavior has been proposed as a physical mechanism for topological order by Michael A. Levin and Xiao-Gang Wen. A particular string-net model may involve only closed loops; or networks of oriented, labeled strings obeying branching rules given by some gauge group; or still more general networks. Overview The string-net model is claimed to show the derivation of photons, electrons, and U(1) gauge charge, small (relative to the Planck mass) but nonzero masses, and suggestions that the leptons, quarks, and gluons can be modeled in the same way. In other words, string-net condensation provides a unified origin for photons and electrons (or gauge bosons and fermions). It can be viewed as an origin of light and electron (or gauge interactions and Fermi statistics). However, their model does not account for the chiral coupling between the fermions and the SU(2) gauge bosons in the standard model. For s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spin–statistics Theorem
In quantum mechanics, the spin–statistics theorem relates the intrinsic spin of a particle (angular momentum not due to the orbital motion) to the particle statistics it obeys. In units of the reduced Planck constant ''ħ'', all particles that move in 3 dimensions have either integer spin or half-integer spin. Background Quantum states and indistinguishable particles In a quantum system, a physical state is described by a state vector. A pair of distinct state vectors are physically equivalent if they differ only by an overall phase factor, ignoring other interactions. A pair of indistinguishable particles such as this have only one state. This means that if the positions of the particles are exchanged (i.e., they undergo a permutation), this does not identify a new physical state, but rather one matching the original physical state. In fact, one cannot tell which particle is in which position. While the physical state does not change under the exchange of the particles' po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fermionic
In particle physics, a fermion is a particle that follows Fermi–Dirac statistics. Generally, it has a half-odd-integer spin: spin , spin , etc. In addition, these particles obey the Pauli exclusion principle. Fermions include all quarks and leptons and all composite particles made of an odd number of these, such as all baryons and many atoms and nuclei. Fermions differ from bosons, which obey Bose–Einstein statistics. Some fermions are elementary particles (such as electrons), and some are composite particles (such as protons). For example, according to the spin-statistics theorem in relativistic quantum field theory, particles with integer spin are bosons. In contrast, particles with half-integer spin are fermions. In addition to the spin characteristic, fermions have another specific property: they possess conserved baryon or lepton quantum numbers. Therefore, what is usually referred to as the spin-statistics relation is, in fact, a spin statistics-quantum number rel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bosonic
In particle physics, a boson ( ) is a subatomic particle whose spin quantum number has an integer value (0,1,2 ...). Bosons form one of the two fundamental classes of subatomic particle, the other being fermions, which have odd half-integer spin (,, ...). Every observed subatomic particle is either a boson or a fermion. Bosons are named after physicist Satyendra Nath Bose. Some bosons are elementary particles and occupy a special role in particle physics unlike that of fermions, which are sometimes described as the constituents of "ordinary matter". Some elementary bosons (for example, gluons) act as force carriers, which give rise to forces between other particles, while one (the Higgs boson) gives rise to the phenomenon of mass. Other bosons, such as mesons, are composite particles made up of smaller constituents. Outside the realm of particle physics, superfluidity arises because composite bosons (bose particles), such as low temperature helium-4 atoms, follow Bose–Einst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anyons
In physics, an anyon is a type of quasiparticle that occurs only in two-dimensional systems, with properties much less restricted than the two kinds of standard elementary particles, fermions and bosons. In general, the operation of exchanging two identical particles, although it may cause a global phase shift, cannot affect observables. Anyons are generally classified as ''abelian'' or ''non-abelian''. Abelian anyons (detected by two experiments in 2020) play a major role in the fractional quantum Hall effect. Non-abelian anyons have not been definitively detected, although this is an active area of research. Introduction The statistical mechanics of large many-body systems obeys laws described by Maxwell–Boltzmann statistics. Quantum statistics is more complicated because of the different behaviors of two different kinds of particles called fermions and bosons. Quoting a recent, simple description:In the three-dimensional world we live in, there are only two types of part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
One-way Quantum Computer
The one-way or measurement-based quantum computer (MBQC) is a method of quantum computing that first prepares an entangled ''resource state'', usually a cluster state or graph state, then performs single qubit measurements on it. It is "one-way" because the resource state is destroyed by the measurements. The outcome of each individual measurement is random, but they are related in such a way that the computation always succeeds. In general the choices of basis for later measurements need to depend on the results of earlier measurements, and hence the measurements cannot all be performed at the same time. The hardware implementation of MBQC mainly relies on photonic devices, thanks to the properties of entanglement between the photons. The process of entanglement and measurement can be described with the help of graph tools and group theory, in particular by the elements from the stabilizer group. Definition The purpose of quantum computing focuses on building an informatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Gate
In quantum computing and specifically the quantum circuit model of computation, a quantum logic gate (or simply quantum gate) is a basic quantum circuit operating on a small number of qubits. They are the building blocks of quantum circuits, like classical logic gates are for conventional digital circuits. Unlike many classical logic gates, quantum logic gates are reversible. It is possible to perform classical computing using only reversible gates. For example, the reversible Toffoli gate can implement all Boolean functions, often at the cost of having to use ancilla bits. The Toffoli gate has a direct quantum equivalent, showing that quantum circuits can perform all operations performed by classical circuits. Quantum gates are unitary operators, and are described as unitary matrices relative to some basis. Usually we use the ''computational basis'', which unless we compare it with something, just means that for a ''d''-level quantum system (such as a qubit, a quantum register ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Computation
Quantum computing is a type of computation whose operations can harness the phenomena of quantum mechanics, such as superposition, interference, and entanglement. Devices that perform quantum computations are known as quantum computers. Though current quantum computers may be too small to outperform usual (classical) computers for practical applications, larger realizations are believed to be capable of solving certain computational problems, such as integer factorization (which underlies RSA encryption), substantially faster than classical computers. The study of quantum computing is a subfield of quantum information science. There are several models of quantum computation with the most widely used being quantum circuits. Other models include the quantum Turing machine, quantum annealing, and adiabatic quantum computation. Most models are based on the quantum bit, or "qubit", which is somewhat analogous to the bit in classical computation. A qubit can be in a 1 or 0 quantum s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edmonds's Matching Algorithm
In graph theory, the blossom algorithm is an algorithm for constructing maximum matchings on graphs. The algorithm was developed by Jack Edmonds in 1961, and published in 1965. Given a general graph , the algorithm finds a matching such that each vertex in is incident with at most one edge in and is maximized. The matching is constructed by iteratively improving an initial empty matching along augmenting paths in the graph. Unlike bipartite matching, the key new idea is that an odd-length cycle in the graph (blossom) is contracted to a single vertex, with the search continuing iteratively in the contracted graph. The algorithm runs in time , where is the number of edges of the graph and is its number of vertices. A better running time of O( , E, \sqrt ) for the same task can be achieved with the much more complex algorithm of Micali and Vazirani. A major reason that the blossom algorithm is important is that it gave the first proof that a maximum-size matching could be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)