|
Tonicella Insignis
''Tonicella insignis'', the white-lined chiton, or red chiton, also known as the hidden chiton, belongs to the Tonicellidae family in the class Polyplacophora, and the phylum of Mollusca. Its body length of T. insignis is around 5 cm. Habitat It can be found in the coastal region of Alaska to Oregon in North America. Similar to other types of chitons, T. insignis also lives on hard rocks in the Subtidal zone, sub-tidal zone and can be found at depths up to 52 meters under water. Characteristic ''Tonicella insignis'' have camouflaged eight-valve shells with white wavy lines on all valves.Lamb, Andy & Handy, Bernard P. Marine Life of the Pacific Northwest Harbour Publishing 2005 The shell protects themselves from predators by blending their body into the environment. The special white line on T. insignis is one of the most distinguish characteristic which only exist on the second to the seventh valve. ''Tonicella insignis'' mainly eats phytoplankton and algae that floating ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mollusca
Mollusca is the second-largest phylum of invertebrate animals after the Arthropoda, the members of which are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 85,000 extant species of molluscs are recognized. The number of fossil species is estimated between 60,000 and 100,000 additional species. The proportion of undescribed species is very high. Many taxa remain poorly studied. Molluscs are the largest marine phylum, comprising about 23% of all the named marine organisms. Numerous molluscs also live in freshwater and terrestrial habitats. They are highly diverse, not just in size and anatomical structure, but also in behaviour and habitat. The phylum is typically divided into 7 or 8 taxonomic classes, of which two are entirely extinct. Cephalopod molluscs, such as squid, cuttlefish, and octopuses, are among the most neurologically advanced of all invertebrates—and either the giant squid or the colossal squid is the largest known invertebrate species. The gastropod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oregon
Oregon () is a U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. The Columbia River delineates much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington (state), Washington, while the Snake River delineates much of its eastern boundary with Idaho. The 42nd parallel north, 42° north parallel delineates the southern boundary with California and Nevada. Oregon has been home to many Indigenous peoples of the Americas, indigenous nations for thousands of years. The first European traders, explorers, and settlers began exploring what is now Oregon's Pacific coast in the early-mid 16th century. As early as 1564, the Spanish expeditions to the Pacific Northwest, Spanish began sending vessels northeast from the Philippines, riding the Kuroshio Current in a sweeping circular route across the northern part of the Pacific. In 1592, Juan de Fuca undertook detailed mapping and studies of ocean currents in the Pacific Northwest, including the Oregon coast as well as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subtidal Zone
The neritic zone (or sublittoral zone) is the relatively shallow part of the ocean above the drop-off of the continental shelf, approximately in depth. From the point of view of marine biology it forms a relatively stable and well-illuminated environment for marine life, from plankton up to large fish and corals, while physical oceanography sees it as where the oceanic system interacts with the coast. Definition (marine biology), context, extra terminology In marine biology, the neritic zone, also called coastal waters, the coastal ocean or the sublittoral zone, refers to that zone of the ocean where sunlight reaches the ocean floor, that is, where the water is never so deep as to take it out of the photic zone. It extends from the low tide mark to the edge of the continental shelf, with a relatively shallow depth extending to about 200 meters (660 feet). Above the neritic zone lie the intertidal (or eulittoral) and supralittoral zones; below it the continental slope begin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
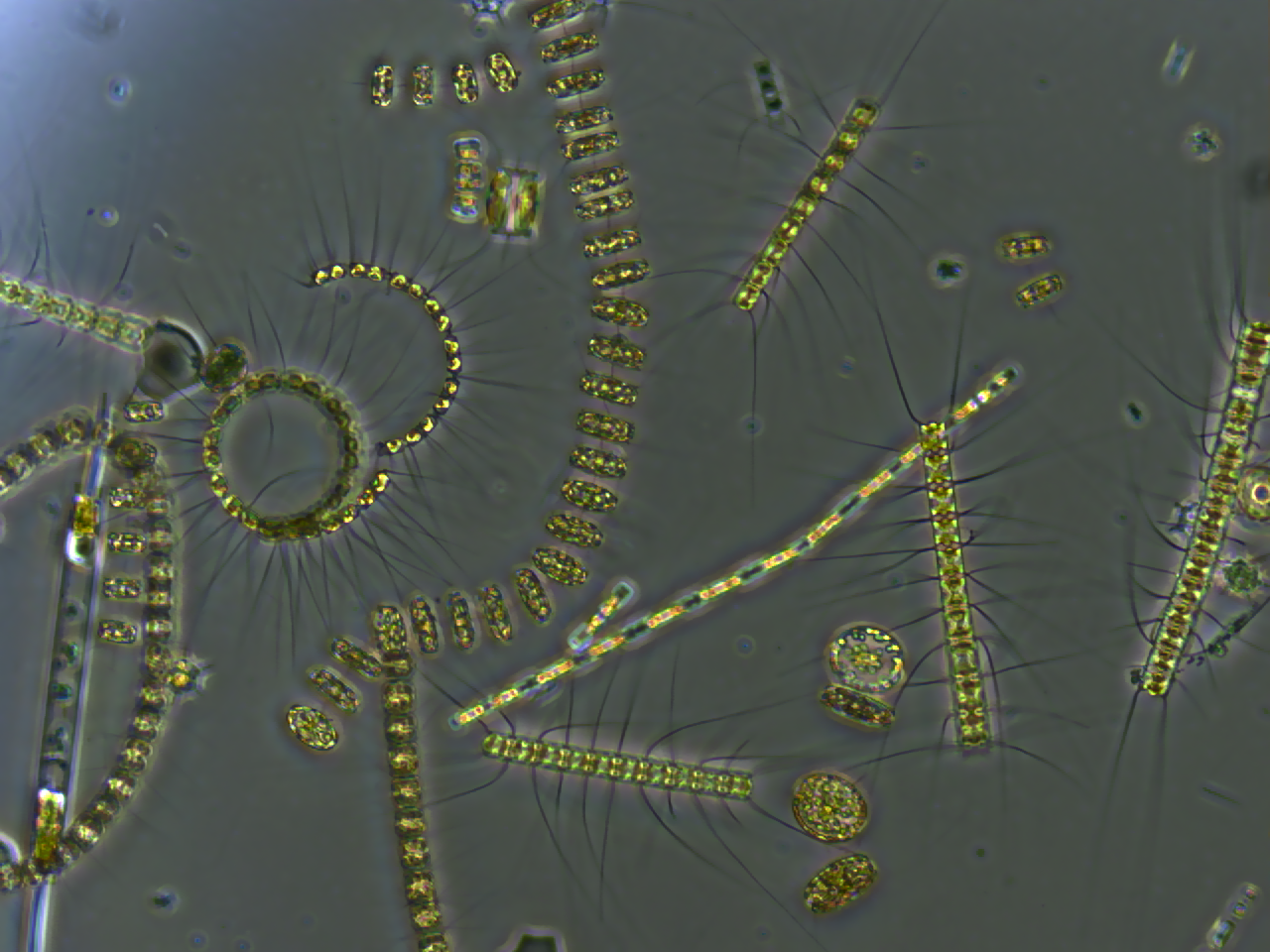
Phytoplankton
Phytoplankton () are the autotrophic (self-feeding) components of the plankton community and a key part of ocean and freshwater ecosystems. The name comes from the Greek words (), meaning 'plant', and (), meaning 'wanderer' or 'drifter'. Phytoplankton obtain their energy through photosynthesis, as do trees and other plants on land. This means phytoplankton must have light from the sun, so they live in the well-lit surface layers (euphotic zone) of oceans and lakes. In comparison with terrestrial plants, phytoplankton are distributed over a larger surface area, are exposed to less seasonal variation and have markedly faster turnover rates than trees (days versus decades). As a result, phytoplankton respond rapidly on a global scale to climate variations. Phytoplankton form the base of marine and freshwater food webs and are key players in the global carbon cycle. They account for about half of global photosynthetic activity and at least half of the oxygen production, despite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algae
Algae (; singular alga ) is an informal term for a large and diverse group of photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms. It is a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from unicellular microalgae, such as ''Chlorella,'' ''Prototheca'' and the diatoms, to multicellular forms, such as the giant kelp, a large brown alga which may grow up to in length. Most are aquatic and autotrophic (they generate food internally) and lack many of the distinct cell and tissue types, such as stomata, xylem and phloem that are found in land plants. The largest and most complex marine algae are called seaweeds, while the most complex freshwater forms are the ''Charophyta'', a division of green algae which includes, for example, ''Spirogyra'' and stoneworts. No definition of algae is generally accepted. One definition is that algae "have chlorophyll ''a'' as their primary photosynthetic pigment and lack a sterile covering of cells around thei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tonicella Lineata
''Tonicella lineata'', commonly known as the lined chiton, is a species of chiton from the North Pacific. Size and description ''Tonicella lineata'' is a very colorful chiton, having blue, purple or black straight or zig-zag lines on each of the eight valves. The background color of the valves is often brown or red, but can also be bright blue or yellow to orange. The girdle is hairless and brown to red or pink, often with regular yellow or white patches. This species grows to 5 cm in length. Similar species ''Tonicella lokii'' is extremely similar but has radiating bands on the girdle. ''Tonicella undocaerulea'' is very similar but lacks a dark border to the concentric blue lines on the anterior plate. ''Mopalia spectabilis'' looks superficially similar due to its bright blue wavy lines on the valves, but has a hairy girdle.Baldwin, A. (2007). Illustrated Keys to the chitons (Polyplacophora). Accessed from: It can also be confused with ''Tonicella insignis'' ( Reeve, 184 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reproductive Cycle
In biology, a biological life cycle (or just life cycle or lifecycle when the biological context is clear) is a series of changes in form that an organism undergoes, returning to the starting state. "The concept is closely related to those of the life history, development and ontogeny, but differs from them in stressing renewal." Transitions of form may involve growth, asexual reproduction, or sexual reproduction. In some organisms, different "generations" of the species succeed each other during the life cycle. For plants and many algae, there are two multicellular stages, and the life cycle is referred to as alternation of generations. The term life history is often used, particularly for organisms such as the red algae which have three multicellular stages (or more), rather than two.Dixon, P.S. 1973. ''Biology of the Rhodophyta.'' Oliver & Boyd. Life cycles that include sexual reproduction involve alternating haploid (''n'') and diploid (2''n'') stages, i.e., a change of ploid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gonad
A gonad, sex gland, or reproductive gland is a mixed gland that produces the gametes and sex hormones of an organism. Female reproductive cells are egg cells, and male reproductive cells are sperm. The male gonad, the testicle, produces sperm in the form of spermatozoa. The female gonad, the ovary, produces egg cells. Both of these gametes are haploid cells. Some hermaphroditic animals have a type of gonad called an ovotestis. Evolution It is hard to find a common origin for gonads, but gonads most likely evolved independently several times. Regulation The gonads are controlled by luteinizing hormone and follicle-stimulating hormone, produced and secreted by gonadotropes or gonadotrophins in the anterior pituitary gland. This secretion is regulated by gonadotropin-releasing hormone produced in the hypothalamus. Development Gonads start developing as a common primordium (an organ in the earliest stage of development), in the form of genital ridges, which are only l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypothesis
A hypothesis (plural hypotheses) is a proposed explanation for a phenomenon. For a hypothesis to be a scientific hypothesis, the scientific method requires that one can test it. Scientists generally base scientific hypotheses on previous observations that cannot satisfactorily be explained with the available scientific theories. Even though the words "hypothesis" and "theory" are often used interchangeably, a scientific hypothesis is not the same as a scientific theory. A working hypothesis is a provisionally accepted hypothesis proposed for further research in a process beginning with an educated guess or thought. A different meaning of the term ''hypothesis'' is used in formal logic, to denote the antecedent of a proposition; thus in the proposition "If ''P'', then ''Q''", ''P'' denotes the hypothesis (or antecedent); ''Q'' can be called a consequent. ''P'' is the assumption in a (possibly counterfactual) ''What If'' question. The adjective ''hypothetical'', meaning "hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spring Bloom
The spring bloom is a strong increase in phytoplankton abundance (i.e. stock) that typically occurs in the early spring and lasts until late spring or early summer. This seasonal event is characteristic of temperate North Atlantic, sub-polar, and coastal waters.Mann, K.H., Lazier, J.R.N. (2006). ''Dynamics of Marine Ecosystems: Biological-Physical Interactions in the Oceans''. Oxford: Blackwell Publishing Ltd. Miller, C.B. (2004). "Biological Oceanography" Oxford: Blackwell Publishing Ltd. Phytoplankton blooms occur when growth exceeds losses, however there is no universally accepted definition of the magnitude of change or the threshold of abundance that constitutes a bloom. The magnitude, spatial extent and duration of a bloom depends on a variety of abiotic and biotic factors. Abiotic factors include light availability, nutrients, temperature, and physical processes that influence light availability,Oviatt, C., Keller, A., and Reed, L. (2002). "Annual Primary Production in Narr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)