|
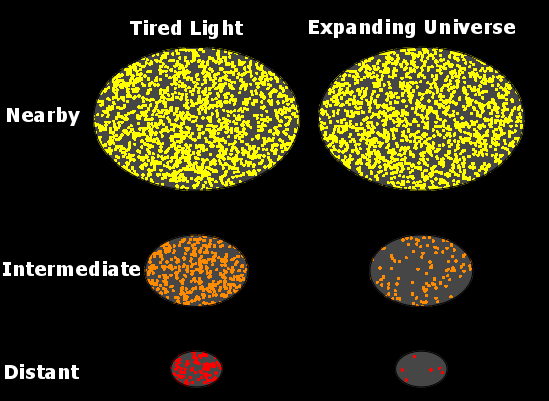
Tolman Surface Brightness Test
The Tolman surface brightness test is one out of six cosmological tests that were conceived in the 1930s to check the viability of and compare new cosmological models. Tolman's test compares the surface brightness of galaxy, galaxies as a function of their redshift (measured as ''z''). Such a comparison was first proposed in 1930 by Richard C. Tolman as a test of whether the universe is expanding universe, expanding or static universe, static. It is a unique test of cosmology, as it is independent of dark energy, dark matter and Hubble constant parameters, testing purely for whether Cosmological Redshift is caused by an expanding universe or not. For such a fundamental test of cosmology, it has seen very little attention (this page is a comprehensive summary of all work done). In a simple (static and flat) universe, the light received from an object drops proportional to the square of its distance and the apparent area of the object also drops proportional to the square of the dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tired Light
Tired light is a class of hypothetical redshift mechanisms that was proposed as an alternative explanation for the redshift-distance relationship. These models have been proposed as alternatives to the models that require metric expansion of space of which the Big Bang and the Steady State cosmologies are the most famous examples. The concept was first proposed in 1929 by Fritz Zwicky, who suggested that if photons lost energy over time through collisions with other particles in a regular way, the more distant objects would appear redder than more nearby ones. Zwicky himself acknowledged that any sort of scattering of light would blur the images of distant objects more than what is seen. Additionally, the surface brightness of galaxies evolving with time, time dilation of cosmological sources, and a thermal spectrum of the cosmic microwave background have been observed—these effects should not be present if the cosmological redshift was due to any tired light scattering mec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmological Test
Cosmology () is a branch of physics and metaphysics dealing with the nature of the universe. The term ''cosmology'' was first used in English in 1656 in Thomas Blount's ''Glossographia'', and in 1731 taken up in Latin by German philosopher Christian Wolff, in ''Cosmologia Generalis''. Religious or mythological cosmology is a body of beliefs based on mythological, religious, and esoteric literature and traditions of creation myths and eschatology. In the science of astronomy it is concerned with the study of the chronology of the universe. Physical cosmology is the study of the observable universe's origin, its large-scale structures and dynamics, and the ultimate fate of the universe, including the laws of science that govern these areas. It is investigated by scientists, such as astronomers and physicists, as well as philosophers, such as metaphysicians, philosophers of physics, and philosophers of space and time. Because of this shared scope with philosophy, theories in p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmological Model
Physical cosmology is a branch of cosmology concerned with the study of cosmological models. A cosmological model, or simply cosmology, provides a description of the largest-scale structures and dynamics of the universe and allows study of fundamental questions about its origin, structure, evolution, and ultimate fate.For an overview, see Cosmology as a science originated with the Copernican principle, which implies that celestial bodies obey identical physical laws to those on Earth, and Newtonian mechanics, which first allowed those physical laws to be understood. Physical cosmology, as it is now understood, began with the development in 1915 of Albert Einstein's general theory of relativity, followed by major observational discoveries in the 1920s: first, Edwin Hubble discovered that the universe contains a huge number of external galaxies beyond the Milky Way; then, work by Vesto Slipher and others showed that the universe is expanding. These advances made it possible ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface Brightness
In astronomy, surface brightness (SB) quantifies the apparent brightness or flux density per unit angular area of a spatially extended object such as a galaxy or nebula, or of the night sky background. An object's surface brightness depends on its surface luminosity density, i.e., its luminosity emitted per unit surface area. In visible and infrared astronomy, surface brightness is often quoted on a magnitude scale, in magnitudes per square arcsecond (MPSAS) in a particular filter band or photometric system. Measurement of the surface brightnesses of celestial objects is called surface photometry. General description The total magnitude is a measure of the brightness of an extended object such as a nebula, cluster, galaxy or comet. It can be obtained by summing up the luminosity over the area of the object. Alternatively, a photometer can be used by applying apertures or slits of different sizes of diameter. The background light is then subtracted from the measurement to obtain t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galaxy
A galaxy is a system of stars, stellar remnants, interstellar gas, dust, dark matter, bound together by gravity. The word is derived from the Greek ' (), literally 'milky', a reference to the Milky Way galaxy that contains the Solar System. Galaxies, averaging an estimated 100 million stars, range in size from dwarfs with less than a hundred million stars, to the largest galaxies known – supergiants with one hundred trillion stars, each orbiting its galaxy's center of mass. Most of the mass in a typical galaxy is in the form of dark matter, with only a few percent of that mass visible in the form of stars and nebulae. Supermassive black holes are a common feature at the centres of galaxies. Galaxies are categorized according to their visual morphology as elliptical, spiral, or irregular. Many are thought to have supermassive black holes at their centers. The Milky Way's central black hole, known as Sagittarius A*, has a mass four million times greater than the Sun. As o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Redshift
In physics, a redshift is an increase in the wavelength, and corresponding decrease in the frequency and photon energy, of electromagnetic radiation (such as light). The opposite change, a decrease in wavelength and simultaneous increase in frequency and energy, is known as a negative redshift, or blueshift. The terms derive from the colours red and blue which form the extremes of the visible light spectrum. In astronomy and cosmology, the three main causes of electromagnetic redshift are # The radiation travels between objects which are moving apart (" relativistic" redshift, an example of the relativistic Doppler effect) #The radiation travels towards an object in a weaker gravitational potential, i.e. towards an object in less strongly curved (flatter) spacetime (gravitational redshift) #The radiation travels through expanding space (cosmological redshift). The observation that all sufficiently distant light sources show redshift corresponding to their distance from Earth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard C
Richard is a male given name. It originates, via Old French, from Old Frankish and is a compound of the words descending from Proto-Germanic ''*rīk-'' 'ruler, leader, king' and ''*hardu-'' 'strong, brave, hardy', and it therefore means 'strong in rule'. Nicknames include "Richie", "Dick", "Dickon", " Dickie", "Rich", "Rick", "Rico", "Ricky", and more. Richard is a common English, German and French male name. It's also used in many more languages, particularly Germanic, such as Norwegian, Danish, Swedish, Icelandic, and Dutch, as well as other languages including Irish, Scottish, Welsh and Finnish. Richard is cognate with variants of the name in other European languages, such as the Swedish "Rickard", the Catalan "Ricard" and the Italian "Riccardo", among others (see comprehensive variant list below). People named Richard Multiple people with the same name * Richard Andersen (other) * Richard Anderson (other) * Richard Cartwright (other) * Ri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Expanding Universe
The expansion of the universe is the increase in distance between any two given gravitationally unbound parts of the observable universe with time. It is an intrinsic expansion whereby the scale of space itself changes. The universe does not expand "into" anything and does not require space to exist "outside" it. This expansion involves neither space nor objects in space "moving" in a traditional sense, but rather it is the metric (which governs the size and geometry of spacetime itself) that changes in scale. As the spatial part of the universe's spacetime metric increases in scale, objects become more distant from one another at ever-increasing speeds. To any observer in the universe, it appears that all of space is expanding, and that all but the nearest galaxies (which are bound by gravity) recede at speeds that are proportional to their distance from the observer. While objects within space cannot travel faster than light, this limitation does not apply to the effects of ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Static Universe
In cosmology, a static universe (also referred to as stationary, infinite, static infinite or static eternal) is a cosmological model in which the universe is both spatially and temporally infinite, and space is neither expanding nor contracting. Such a universe does not have so-called spatial curvature; that is to say that it is 'flat' or Euclidean. A static infinite universe was first proposed by English astronomer Thomas Digges (1546–1595). In contrast to this model, Albert Einstein proposed a temporally infinite but spatially finite model as his preferred cosmology during 1917, in his paper ''Cosmological Considerations in the General Theory of Relativity''. After the discovery of the redshift-distance relationship (deduced by the inverse correlation of galactic brightness to redshift) by American astronomers Vesto Slipher and Edwin Hubble, the astrophysicist Georges Lemaître interpreted the redshift as evidence of universal expansion and thus a Big Bang, whereas Swi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hubble Space Telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope (often referred to as HST or Hubble) is a space telescope that was launched into low Earth orbit in 1990 and remains in operation. It was not the first space telescope, but it is one of the largest and most versatile, renowned both as a vital research tool and as a public relations boon for astronomy. The Hubble telescope is named after astronomer Edwin Hubble and is one of NASA's Great Observatories. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) selects Hubble's targets and processes the resulting data, while the Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) controls the spacecraft. Hubble features a mirror, and its five main instruments observe in the ultraviolet, visible, and near-infrared regions of the electromagnetic spectrum. Hubble's orbit outside the distortion of Earth's atmosphere allows it to capture extremely high-resolution images with substantially lower background light than ground-based telescopes. It has recorded some of the most detaile ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allan Sandage
Allan Rex Sandage (June 18, 1926 – November 13, 2010) was an American astronomer. He was Staff Member Emeritus with the Carnegie Observatories in Pasadena, California. He determined the first reasonably accurate values for the Hubble constant and the age of the universe. Career Sandage was one of the most influential astronomers of the 20th century. He was born in Iowa City, Iowa, United States. He graduated from the University of Illinois in 1948. In 1953 he received a PhD from the California Institute of Technology; the German-born Wilson Observatory-based astronomer Walter Baade was his advisor. During this time Sandage was a graduate student assistant to cosmologist Edwin Hubble. He continued Hubble's research program after Hubble died in 1953. In 1952 Baade surprised his fellow astronomers by announcing (at the 1952 Conference of the International Astronomical Union, in Rome) his determination of two separate populations of Cepheid variable stars in the Andromeda Ga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Source Counts
The source counts distribution of radio-sources from a radio-astronomical survey is the cumulative distribution of the number of sources (''N'') brighter than a given flux density (''S''). As it is usually plotted on a log-log scale its distribution is known as the log ''N'' – log ''S'' plot. It is one of several cosmological tests that were conceived in the 1930s to check the viability of and compare new cosmological models. Early work to catalogue radio sources aimed to determine the source count distribution as a discriminating test of different cosmological models. For example, a uniform distribution of radio sources at low redshift, such as might be found in a 'steady-state Euclidean universe,' would produce a slope of −1.5 in the cumulative distribution of log(''N'') versus log(''S''). Data from the early Cambridge 2C survey (published 1955) apparently implied a (log(''N''), log(''S'')) slope of nearly −3.0. This appeared to invalidate the steady state t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |