|
Tokamak Physics Experiment
The Tokamak Physics Experiment (TPX) was a plasma physics experiment that was designed but not built. It was designed by an inter-organizational team in the USA led by Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory. The experiment was designed to test theories about how Tokamaks would behave in a high-performance, steady-state regime. Goals TPX was to be the successor to the Tokamak Fusion Test Reactor (TFTR). While TFTR was designed to achieve Q>1 (more fusion power produced by the plasma than injected into the plasma), TFTR only operated for short pulses, and did not provide data from and experience with plasmas behave like those of an economic Fusion power reactor. Specifically, TPX was designed to fill this need. TPX was designed to test theories which suggested ways of making a future fusion power reactor compact, economic, and reliable. Specifically, TPX was designed to be near steady state, with pulse lengths of 1,000 seconds (more than 15 minutes). It was designed to operate at hig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
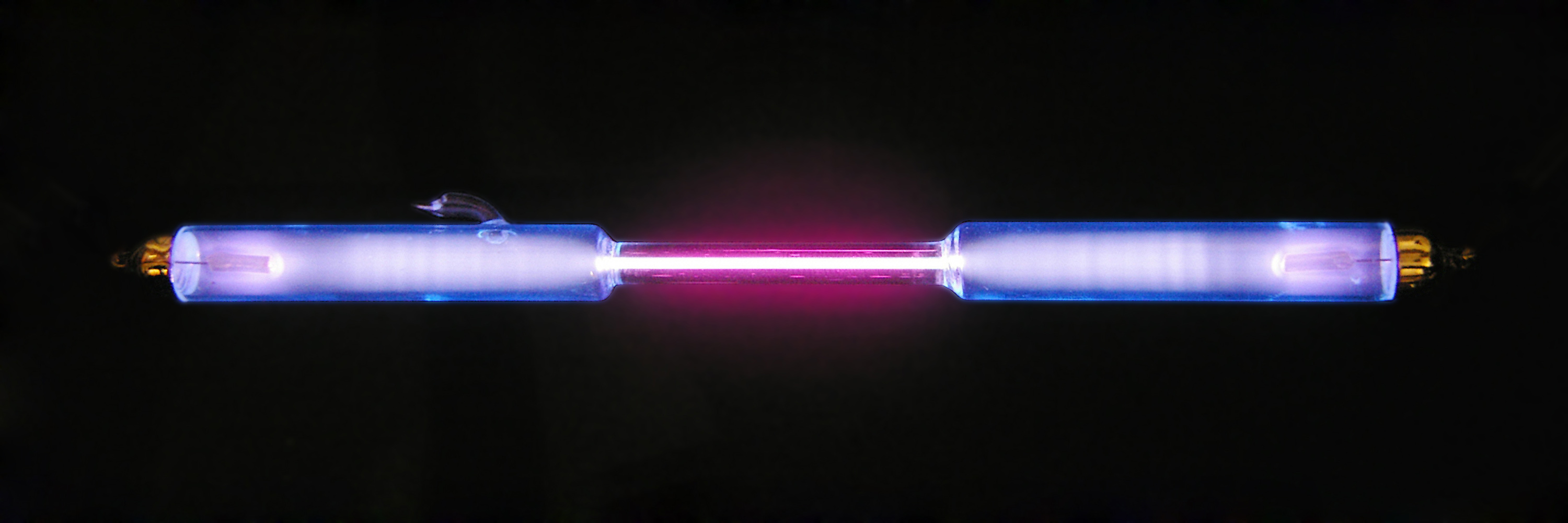
Plasma (physics)
Plasma () 1, where \nu_ is the electron gyrofrequency and \nu_ is the electron collision rate. It is often the case that the electrons are magnetized while the ions are not. Magnetized plasmas are ''anisotropic'', meaning that their properties in the direction parallel to the magnetic field are different from those perpendicular to it. While electric fields in plasmas are usually small due to the plasma high conductivity, the electric field associated with a plasma moving with velocity \mathbf in the magnetic field \mathbf is given by the usual Lorentz force, Lorentz formula \mathbf = -\mathbf\times\mathbf, and is not affected by Debye shielding. Mathematical descriptions To completely describe the state of a plasma, all of the particle locations and velocities that describe the electromagnetic field in the plasma region would need to be written down. However, it is generally not practical or necessary to keep track of all the particles in a plasma. Therefore, plasma physicist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compact Ignition Tokamak
The Compact Ignition Tokamak (CIT) was a plasma physics experiment that was designed but not built. It was designed by an inter-organizational team in the USA led by Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory. The experiment was designed to achieve a self-sustaining Thermonuclear fusion reaction (ignition) in a Tokamak with the minimum possible budget. History CIT was to be the successor experiment to the Tokamak Fusion Test Reactor (TFTR). Where TFTR was designed to achieve Q>1 (more fusion power produced by the plasma than injected into the plasma), CIT was designed to achieve ignition, here defined as Q>10 (fusion power produced is more than ten times the heating power). Design of CIT began in 1986, at which point it was expected that construction would begin in 1988 and complete in 1993. The estimated cost of construction was $285 Million in 1986 dollars. As development progressed, the tokamak design grew in size, magnetic field, and heating power. At some point in the early 1990 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niobium–tin
Niobium–tin is an intermetallic compound of niobium (Nb) and tin (Sn), used industrially as a type II superconductor. This intermetallic compound has a simple structure: A3B. It is more expensive than niobium–titanium (NbTi), but remains superconducting up to a magnetic flux density of , compared to a limit of roughly 15 T for NbTi. Nb3Sn was discovered to be a superconductor in 1954. The material's ability to support high currents and magnetic fields was discovered in 1961 and started the era of large-scale applications of superconductivity. The critical temperature is . Application temperatures are commonly around , the boiling point of liquid helium at atmospheric pressure. In April 2008 a record non-copper current density was claimed of 2,643 A mm−2 at 12 T and 4.2 K. History Nb3Sn was discovered to be a superconductor in 1954, one year after the discovery of V3Si, the first example of an A3B superconductor. In 1961 it was discovered that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
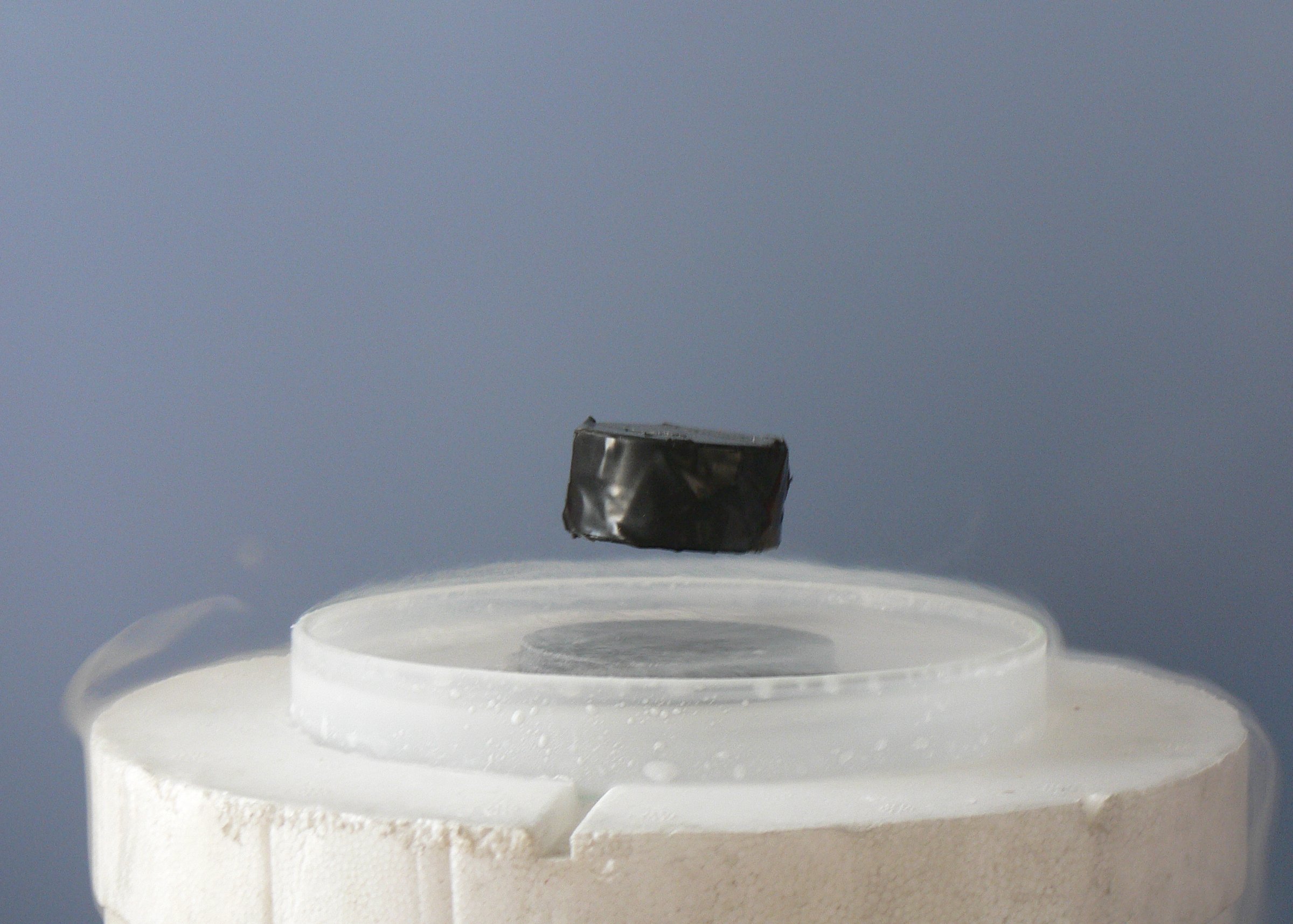
Superconductivity
Superconductivity is a set of physical properties observed in certain materials where electrical resistance vanishes and magnetic flux fields are expelled from the material. Any material exhibiting these properties is a superconductor. Unlike an ordinary metallic conductor, whose resistance decreases gradually as its temperature is lowered even down to near absolute zero, a superconductor has a characteristic critical temperature below which the resistance drops abruptly to zero. An electric current through a loop of superconducting wire can persist indefinitely with no power source. The superconductivity phenomenon was discovered in 1911 by Dutch physicist Heike Kamerlingh Onnes. Like ferromagnetism and atomic spectral lines, superconductivity is a phenomenon which can only be explained by quantum mechanics. It is characterized by the Meissner effect, the complete ejection of magnetic field lines from the interior of the superconductor during its transitions into the sup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deuterium
Deuterium (or hydrogen-2, symbol or deuterium, also known as heavy hydrogen) is one of two Stable isotope ratio, stable isotopes of hydrogen (the other being Hydrogen atom, protium, or hydrogen-1). The atomic nucleus, nucleus of a deuterium atom, called a deuteron, contains one proton and one neutron, whereas the far more common protium has no neutrons in the nucleus. Deuterium has a natural abundance in Earth's oceans of about one atom of deuterium among all atoms of hydrogen (see heavy water). Thus deuterium accounts for approximately 0.0156% by number (0.0312% by mass) of all the naturally occurring hydrogen in the oceans, while protium accounts for more than 99.98%. The abundance of deuterium changes slightly from one kind of natural water to another (see Vienna Standard Mean Ocean Water). (Tritium is yet another hydrogen isotope, with two neutrons, that is far more rare and is radioactive.) The name ''deuterium'' is derived from the Greek , meaning "second", to denot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Korea
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea (ROK), is a country in East Asia, constituting the southern part of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and sharing a Korean Demilitarized Zone, land border with North Korea. Its western border is formed by the Yellow Sea, while its eastern border is defined by the Sea of Japan. South Korea claims to be the sole legitimate government of the entire peninsula and List of islands of South Korea, adjacent islands. It has a Demographics of South Korea, population of 51.75 million, of which roughly half live in the Seoul Capital Area, the List of metropolitan areas by population, fourth most populous metropolitan area in the world. Other major cities include Incheon, Busan, and Daegu. The Korean Peninsula was inhabited as early as the Lower Paleolithic period. Its Gojoseon, first kingdom was noted in Chinese records in the early 7th century BCE. Following the unification of the Three Kingdoms of Korea into Unified Silla, Silla and Balhae in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
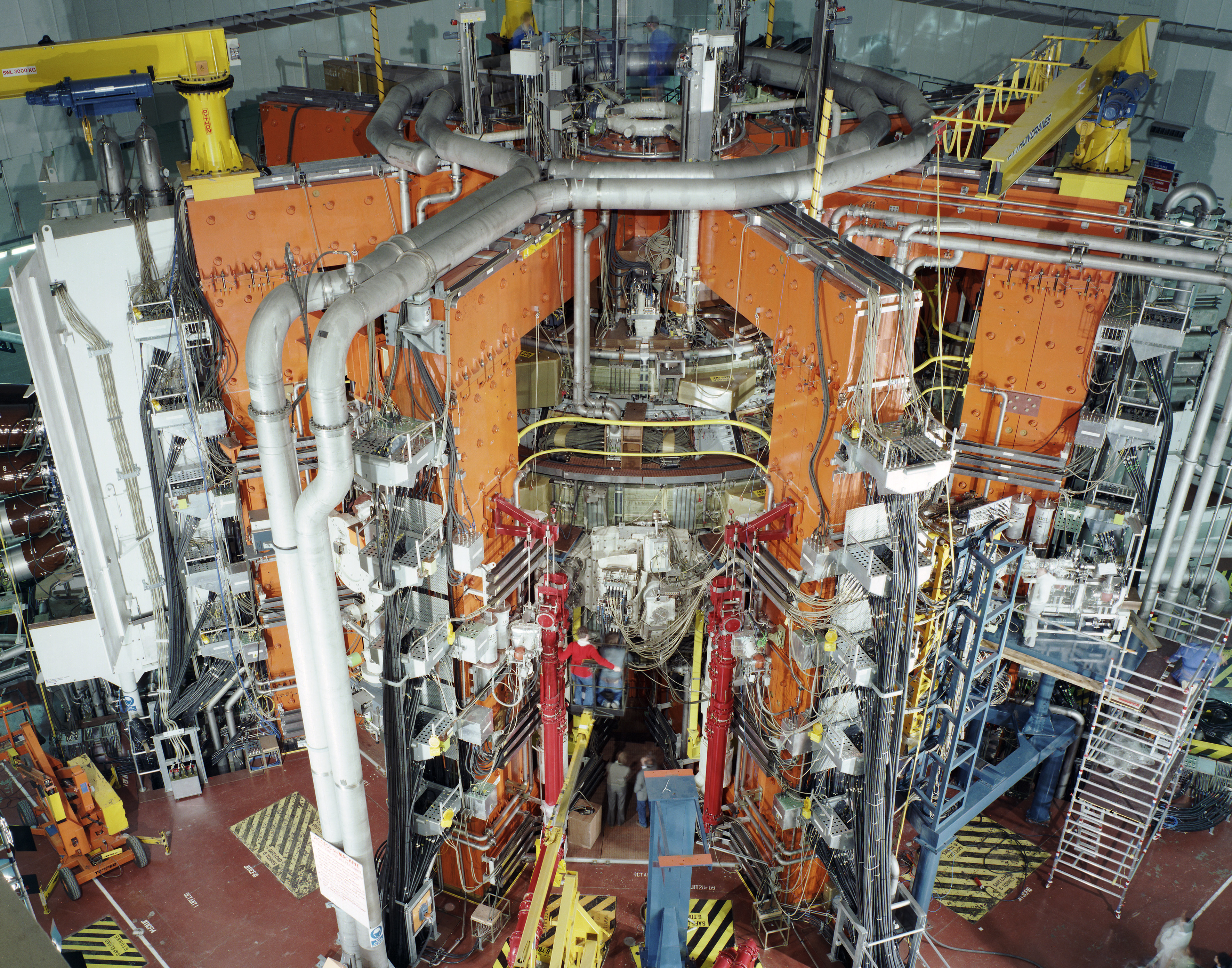
Tokamak
A tokamak (; russian: токамáк; otk, 𐱃𐰸𐰢𐰴, Toḳamaḳ) is a device which uses a powerful magnetic field to confine plasma in the shape of a torus. The tokamak is one of several types of magnetic confinement devices being developed to produce controlled thermonuclear fusion power. , it was the leading candidate for a practical fusion reactor. Tokamaks were initially conceptualized in the 1950s by Soviet physicists Igor Tamm and Andrei Sakharov, inspired by a letter by Oleg Lavrentiev. The first working tokamak was attributed to the work of Natan Yavlinsky on the T-1 in 1958. It had been demonstrated that a stable plasma equilibrium requires magnetic field lines that wind around the torus in a helix. Devices like the z-pinch and stellarator had attempted this, but demonstrated serious instabilities. It was the development of the concept now known as the safety factor (labelled ''q'' in mathematical notation) that guided tokamak development; by arranging the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Department Of Energy
The United States Department of Energy (DOE) is an executive department of the U.S. federal government that oversees U.S. national energy policy and manages the research and development of nuclear power and nuclear weapons in the United States. The DOE oversees the U.S. nuclear weapons program, nuclear reactor production for the United States Navy, energy-related research, and domestic energy production and energy conservation. The DOE was created in 1977 in the aftermath of the 1973 oil crisis. It sponsors more physical science research than any other U.S. federal agency, the majority of which is conducted through its system of National Laboratories. The DOE also directs research in genomics, with the Human Genome Project originating from a DOE initiative. The department is headed by the Secretary of Energy, who reports directly to the president of the United States and is a member of the Cabinet. The current Secretary of Energy is Jennifer Granholm, who has served ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta (plasma Physics)
The beta of a plasma, symbolized by ''β'', is the ratio of the plasma pressure (''p'' = ''n'' ''k''B ''T'') to the magnetic pressure (''p''mag = ''B''²/2 ''μ''0). The term is commonly used in studies of the Sun and Earth's magnetic field, and in the field of fusion power designs. In the fusion power field, plasma is often confined using strong magnets. Since the temperature of the fuel scales with pressure, reactors attempt to reach the highest pressures possible. The costs of large magnets roughly scales like ''β½''. Therefore, beta can be thought of as a ratio of money out to money in for a reactor, and beta can be thought of (very approximately) as an economic indicator of reactor efficiency. For tokamaks, betas of larger than 0.05 or 5% are desired for economically viable electrical production. The same term is also used when discussing the interactions of the solar wind with various magnetic fields. For example, beta in the corona of the Sun is about 0.01. Backgrou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory
Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL) is a United States Department of Energy national laboratory for plasma physics and nuclear fusion science. Its primary mission is research into and development of fusion as an energy source. It is known in particular for the development of the stellarator and tokamak designs, along with numerous fundamental advances in plasma physics and the exploration of many other plasma confinement concepts. PPPL grew out of the top-secret Cold War project to control thermonuclear reactions, called Project Matterhorn. The focus of this program changed from H-bombs to fusion power in 1951, when Lyman Spitzer developed the stellarator concept and was granted funding from the Atomic Energy Commission to study the concept. This led to a series of machines in the 1950s and 60s. In 1961, after declassification, Project Matterhorn was renamed the Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory. PPPL's stellarators proved unable to meet their performance goals. In 196 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bootstrap Current
In a toroidal fusion power device, a plasma is confined within a donut-shaped cylinder. If the gas pressure of the plasma varies across the radius of the cylinder, a self-generated current will spontaneously arise within the plasma, due to collisions between trapped particles Trapped may refer to: Films * ''Trapped'' (1931 film), a crime drama short starring Lina Basquette * ''Trapped'' (1937 film), an American western starring Charles Starrett * ''Trapped'' (1949 film), a semidocumentary film noir directed by Richar ... and passing particles. This current is called the bootstrap current, and is commonly found in tokamak fusion devices. The tokamak uses a combination of external magnets and a current driven in the plasma to create a stable confinement system. One goal of advanced tokamak designs is to maximize the bootstrap current, and thereby reduce or eliminate the need for an external current driver. This could dramatically reduce the cost and complexity of the device. From ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fusion Power
Fusion power is a proposed form of power generation that would generate electricity by using heat from nuclear fusion, nuclear fusion reactions. In a fusion process, two lighter atomic nucleus, atomic nuclei combine to form a heavier nucleus, while releasing energy. Devices designed to harness this energy are known as fusion reactors. Research into fusion reactors began in the 1940s, but as of 2022, only one design, an Inertial confinement fusion, inertial confinement laser-driven fusion machine at the US National Ignition Facility, has conclusively produced a positive fusion energy gain factor, i.e. more power output than input. Fusion processes require fuel and a confined environment with sufficient temperature, pressure, and confinement time to create a plasma (physics), plasma in which fusion can occur. The combination of these figures that results in a power-producing system is known as the Lawson criterion. In stars, the most common fuel is hydrogen, and gravity provides ext ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |