|
Tocco Family
The House of Tocco ( ''Tocchi'', grc-gre, Τόκκος, Tókkos Τόκκοι, ''Tokkoi'') was an Italian noble family from Benevento that came to prominence in the late 14th and 15th centuries, when they ruled various territories in western Greece as Counts Palatine of Cephalonia and Zakynthos and Despots of Epirus. During their brief period of rule in Greece, they were one of the most ambitious and able Latin dynasties in the region, and they were one of the few to leave descendants lasting until modern times. The earliest known members of the family are recorded in the 12th century in Benevento, though Tocco family genealogies claimed that they originated much earlier, with forged connections to ancient Gothic kings Theodoric the Great and Totila, as well as to the ancient Epirote king Pyrrhus. Members of the family held various prominent offices during the rule of the Hohenstaufen and Angevin dynasties in the Kingdom of Sicily. As a result of the family's loyalty to the Ange ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guglielmo Tocco
Guglielmo Tocco (died in Naples, 22 September 1335)Cawley, was the governor of the Greece, Greek island of Corfu in the 1330s and the founder of the Tocco family, Tocco dynasty. Guglielmo was born the son of Pietro Tocco, a notary in Melfi, in the Capetian House of Anjou, Angevin Kingdom of Naples. In 1330/1 he was named governor of Corfu by Philip I of Taranto.Kazhdan (1990), p. 2090 He was married twice. By his first marriage to Giovanna Torelli he had one son, Pietro Tocco, seneschal of Robert of Taranto and Count of Martina Franca. By his second marriage, to Margaret Orsini, the daughter of John I Orsini, County palatine of Cephalonia and Zakynthos, Count palatine of Cephalonia, he had four children: * Leonardo I Tocco (died 1375/1377), who became Count palatine of Cephalonia and Zakynthos in 1357, beginning the Tocco line that ruled over the Ionian Islands and eventually Despotate of Epirus, Epirus * Nicoletto Tocco (died 1347/1354), who became a monk * Lisulo or Ludovico To ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monteaperti
Monteaperti (or ''Montaperti'') is a village in Tuscany, central Italy, administratively a frazione of the comune of Castelnuovo Berardenga, province of Siena. At the time of the 2001 census its population was 465. . Monteaperti is about 12 km from and 8 km from Castelnuovo Berardenga. The place is known for being the scene of the |
Totila
Totila, original name Baduila (died 1 July 552), was the penultimate King of the Ostrogoths, reigning from 541 to 552 AD. A skilled military and political leader, Totila reversed the tide of the Gothic War, recovering by 543 almost all the territories in Italy that the Eastern Roman Empire had captured from his Kingdom in 540. A relative of Theudis, sword-bearer of Theodoric the Great and king of the Visigoths, Totila was elected king by Ostrogothic nobles in the autumn of 541 after King Witigis had been carried off prisoner to Constantinople. Totila proved himself both as a military and political leader, winning the support of the lower classes by liberating slaves and distributing land to the peasants. After a successful defence at Verona, Totila pursued and defeated a numerically superior army at the Battle of Faventia in 542 AD. Totila followed these victories by defeating the Romans outside Florence and capturing Naples. By 543, fighting on land and sea, he had reconq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
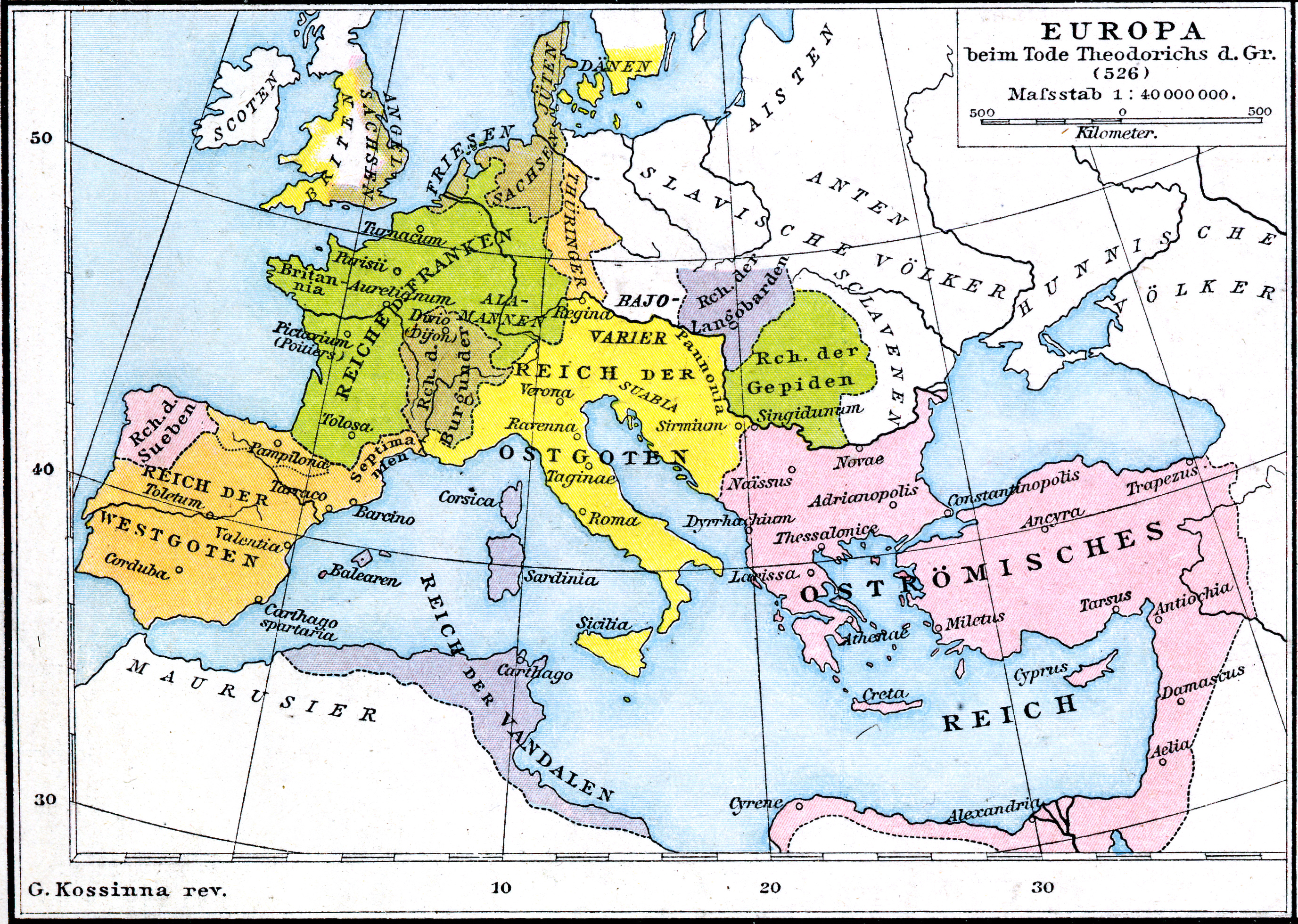
Theodoric The Great
Theodoric (or Theoderic) the Great (454 – 30 August 526), also called Theodoric the Amal ( got, , *Þiudareiks; Greek: , romanized: ; Latin: ), was king of the Ostrogoths (471–526), and ruler of the independent Ostrogothic Kingdom of Italy between 493 and 526, regent of the Visigoths (511–526), and a patrician of the Eastern Roman Empire. As ruler of the combined Gothic realms, Theodoric controlled an empire stretching from the Atlantic Ocean to the Adriatic Sea. Though Theodoric himself only used the title 'king' (''rex''), some scholars characterize him as a Western Roman Emperor in all but name, since he ruled large parts of the former Western Roman Empire, had received the former Western imperial regalia from Constantinople in 497, and was referred to by the title ''augustus'' by some of his subjects. As a young child of an Ostrogothic nobleman, Theodoric was taken as a hostage to Constantinople, where he spent his formative years and received an East Roman education (' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latins (Middle Ages)
The name Latin was in the Middle Ages a common demonym among the followers of the Latin Church of Western Christianity. It derived from the Ecclesiastical Latin that was developed by the Latin Church fathers in the ''Western Church''. Although Latin language was the official language of the Roman Empire, going back to the Italic tribe who in antiquity developed in Ancient Rome, the name was used irrespective of ethnicity, including by Germanic, Italic, Celtic and Slavic peoples. Thus the people associated with the states created during the Crusades were generally referred to as Latins or Franks, the latter being one prominent group represented. In the Byzantine Empire, and the broader Greek Orthodox world, it was generally a negative characterisation, especially after the East-West schism in 1054. It did not share this negative connotation in the West, where many self-identified with the term, such as Petrarch, when he states ''"Sumus enim non greci, non barbari, sed itali et l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benevento
Benevento (, , ; la, Beneventum) is a city and ''comune'' of Campania, Italy, capital of the province of Benevento, northeast of Naples. It is situated on a hill above sea level at the confluence of the Calore Irpino (or Beneventano) and the Sabato. In 2020, Benevento has 58,418 inhabitants. It is also the seat of a Catholic archbishop. Benevento occupies the site of the ancient Beneventum, originally Maleventum or even earlier Maloenton. The meaning of the name of the town is evidenced by its former Latin name, translating as good or fair wind. In the imperial period it was supposed to have been founded by Diomedes after the Trojan War. Due to its artistic and cultural significance, the Santa Sofia Church in Benevento was declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2011, as part of a group of seven historic buildings inscribed as Longobards in Italy, Places of Power (568–774 A.D.). A patron saint of Benevento is Saint Bartholomew, the Apostle, whose relics are kept ther ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plural
The plural (sometimes abbreviated pl., pl, or ), in many languages, is one of the values of the grammatical category of number. The plural of a noun typically denotes a quantity greater than the default quantity represented by that noun. This default quantity is most commonly one (a form that represents this default quantity of one is said to be of ''singular'' number). Therefore, plurals most typically denote two or more of something, although they may also denote fractional, zero or negative amounts. An example of a plural is the English word ''cats'', which corresponds to the singular ''cat''. Words of other types, such as verbs, adjectives and pronouns, also frequently have distinct plural forms, which are used in agreement with the number of their associated nouns. Some languages also have a dual (denoting exactly two of something) or other systems of number categories. However, in English and many other languages, singular and plural are the only grammatical numbers, exce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carlo III Di Tocco Cantelmo Stuart
Don Carlo III di Tocco Cantelmo Stuart (4 April 1827 – 24 March 1884), or Carlo di Tocco for short, was a 19th-century Italian noble, serving as the Prince of Montemiletto and the titular Prince of Achaea from the death of his father Francesco di Tocco Cantelmo Stuart in 1877 to his own death in 1884. Carlo III di Tocco Cantelmo Stuart was the last living member of the Tocco family, which had once ruled the Despotate of Epirus. Carlo was prominent among the nobility of Italy, having held high honors in the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies until its fall in 1861 and thereafter becoming a leader figure among those who sought to restore it. Biography Carlo III di Tocco Cantelmo Stuart was born in Naples on 4 April 1827, as the eldest son of Francesco di Tocco Cantelmo Stuart, Prince of Montemiletto and titular Prince of Achaea, and Maria Maddalena di Tocco Cantelmo Stuart. Francesco and Maria Maddalena were cousins. Upon his Francesco's death on 16 April 1877, Carlo inherited father's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carlo Capece Galeota
Don Carlo Capece Galeota (17 February 1824 – 14 August 1908) was an Italian nobleman, holding the titles of Duke of Regina and Duke of Sant'Angelo a Fasanella from the death of his father Francesco Capece Galeota in 1838 to his own death in 1908. From 1889 onwards, Carlo was also recognized as the heir to the extinct Tocco family (extinct in 1884), as he was a matrilineal descendant of the family, assuming their titles of Prince of Montemiletto and titular Prince of Achaea, among others. Biography Carlo Capece Galeota was born in Naples on 17 February 1824. He was the son of Francesco Capece Galeota, Duke of Regina and Duke of Sant'Angelo a Fasanella, and Maria Maddalena di Tocco Cantelmo Stuart. Upon his father Francesco's death on 5 May 1838, Carlo inherited his titles. Though they held two ducal titles, the Capece Galeota family primarily identified themselves only with the title of 'Duke of Regina' (''Duca della Regina'' in Italian). On 24 March 1884, Carlo III di Tocco C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Montefalcione
Montefalcione (Irpino: ) is a town and ''comune'' of the province of Avellino in the Campania region of southern Italy. The town lies on a hill which at its summit is above sea level. In 1861 it was the location of a revolt against the newly formed government of Italy. People *Nicola Mancino Nicola Mancino (born 15 October 1931) is an Italian politician. He was President of the Senate of the Republic from 1996 to 2001. He was also president of Campania's regional parliament from 1965 to 1971, governor of Campania from 1971 to 1972 ... References External links Official websiteMontefalcione tourist information Cities and towns in Campania {{Campania-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manocalzati
Manocalzati (Irpino: ) is a town and ''comune'' in the province of Avellino, Campania, Southern Italy. The area produces chestnuts, nuts and grapes. History Traces from the Iron Age indicate this town existed in the 8th century BC. Manocalzati was later a fiefdom of the San Barbato family. Main sights The town retains its original medieval In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the Post-classical, post-classical period of World history (field), global history. It began with t ... appearance, with narrow streets and palaces with decorated portals from the 18th and 19th centuries. There are two churches from the 18th century: Saint Michael (belltower built in the 16th century) and Saint Anna. Within Manocalzati is San Barbato, a small hamlet overlooking the Serinese valley. Its medieval architecture is composed of houses surrounding a medieval castle. References Exte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fontanarosa
Fontanarosa is a town and ''comune'' in the province of Avellino, Campania, southern Italy Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical .... References Cities and towns in Campania {{Campania-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |