|
Tlaxcaltec
The Tlaxcalans, or Tlaxcaltecs, are a Nahua people who live in the Mexican state of Tlaxcala. Pre-Columbian history The Tlaxcaltecs were originally a conglomeration of three distinct ethnic groups who spoke Nahuatl, Otomi, and Pinome that comprised the four city-states of the Tlaxcala Confederation. Eventually, the Nahuatl speakers became the dominant ethnic group. Despite early attempts by the Mexica, the Tlaxcaltecs were never conquered by the Aztec Triple Alliance. Some of the wars between the Tlaxcalans and the Aztecs are called the xochiyaoyatl (flower wars), as their objective was not to conquer but rather to capture enemy warriors for sacrifice.Hassig, Ross (1988). ''Aztec Warfare: Imperial Expansion and Political Control''. Norman: University of Oklahoma Press. p. 130. . Spanish colonial history Eager to overthrow the Aztecs, which were their hated enemies, the Tlaxcaltecs allied with Hernán Cortés and his fellow Spanish conquistadors and were instrumental in the inv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Conquest Of The Aztec Empire
The Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire, also known as the Conquest of Mexico or the Spanish-Aztec War (1519–21), was one of the primary events in the Spanish colonization of the Americas. There are multiple 16th-century narratives of the events by Spanish conquistadors, their indigenous allies, and the defeated Aztecs. It was not solely a contest between a small contingent of Spaniards defeating the Aztec Empire but rather the creation of a coalition of Spanish invaders with tributaries to the Aztecs, and most especially the Aztecs' indigenous enemies and rivals. They combined forces to defeat the Mexica of Tenochtitlan over a two-year period. For the Spanish, the expedition to Mexico was part of a project of Spanish colonization of the New World after twenty-five years of permanent Spanish settlement and further exploration in the Caribbean. Significant events in the conquest of Mesoamerica Historical sources for the conquest of Mexico recount some of the same events in bot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xicotencatl The Younger
Xicotencatl II Axayacatl, also known as Xicotencatl the Younger (died 1521), was a prince and warleader, probably with the title of ''Tlacochcalcatl'', of the pre-Columbian state of Tlaxcallan at the time of the Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire. Biography He was the son of the ruler of Tizatlan, one of the four confederate altepeme of the Tlaxcallan state, of which Xicotencatl the Younger was considered to be the ''de facto'' ruler because of his father's weakened health. His Nahuatl name, pronounced , is sometimes also spelled Xīcohtēncatl and means "person from Xīcohtēnco," a place name that can be translated "at the edge of the bumblebees." He is known primarily as the leader of the force that was dispatched from Tlaxcallan to intercept the forces of Hernán Cortés and his Totonac allies as they entered Tlaxcallan territory when going inland from the Veracruz coast.Diaz, B., 1963, The Conquest of New Spain, London: Penguin Books, His actions are described in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nahuas
The Nahuas () are a group of the indigenous people of Mexico, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, and Nicaragua. They comprise the largest indigenous group in Mexico and second largest in El Salvador. The Mexica (Aztecs) were of Nahua ethnicity, and the Toltecs are often thought to have been as well, though in the pre-Columbian period Nahuas were subdivided into many groups that did not necessarily share a common identity. Their Nahuan languages, or Nahuatl, consist of many variants, several of which are mutually unintelligible. About 1.5 million Nahuas speak Nahuatl and another million speak only Spanish. Fewer than 1,000 native speakers of Nahuatl remain in El Salvador. It is suggested that the Nahua peoples originated near Aridoamerica, in regions of the present day Mexican states of Durango and Nayarit or the Bajío region. They split off from the other Uto-Aztecan speaking peoples and migrated into central Mexico around 500 CE. The Nahua then settled in and around the Basin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tlaxcala (Nahua State)
Tlaxcala ( 'place of maize tortillas') was a pre-Columbian city and state in central Mexico. During the Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire, Tlaxcala allied with the Spanish Empire against the Aztecs, supplying a large contingent for and sometimes most of the Spanish-led army that eventually destroyed the Aztec Empire. History The Tlaxcalans arrived in Central Mexico during the Late Postclassic. They first settled near Texcoco in the valley of Mexico, between the settlement of Cohuatlinchan and the shore of Lake Texcoco. After some years the Tlaxcallans were driven out of the valley of Mexico and moved to the east, splitting into three groups along the way. While one group continued north towards the modern state of Hidalgo and another remained in the vicinity of Texcoco, a third group arrived in the modern valley of Tlaxcala, where they established the city of Tepetícpac Texcallan under the leadership of Culhuatecuhtli Quanex. Over the subsequent years, the Tlaxcallan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nahuatl
Nahuatl (; ), Aztec, or Mexicano is a language or, by some definitions, a group of languages of the Uto-Aztecan language family. Varieties of Nahuatl are spoken by about Nahua peoples, most of whom live mainly in Central Mexico and have smaller populations in the United States. Nahuatl has been spoken in central Mexico since at least the seventh century CE. It was the language of the Aztec/ Mexica, who dominated what is now central Mexico during the Late Postclassic period of Mesoamerican history. During the centuries preceding the Spanish and Tlaxcalan conquest of the Aztec Empire, the Aztecs had expanded to incorporate a large part of central Mexico. Their influence caused the variety of Nahuatl spoken by the residents of Tenochtitlan to become a prestige language in Mesoamerica. After the conquest, when Spanish colonists and missionaries introduced the Latin alphabet, Nahuatl also became a literary language. Many chronicles, grammars, works of poetry, administrative docu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tlaxcala
Tlaxcala (; , ; from nah, Tlaxcallān ), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Tlaxcala ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Tlaxcala), is one of the 32 states which comprise the Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided into 60 municipalities and the capital city is Tlaxcala City. It is located in East-Central Mexico, in the altiplano region, with the eastern portion dominated by the Sierra Madre Oriental. It is bordered by the states of Puebla to the north, east and south, México to the west and Hidalgo to the northwest. It is the smallest state of the republic, accounting for only 0.2% of the country's territory. The state is named after its capital, Tlaxcala, which was also the name of the Pre-Columbian city and culture. The Tlaxcalans allied themselves with the Spanish to defeat the Aztecs, with concessions from the Spanish that allowed the territory to remain mostly intact throughout 300 years of colonial period. After Mexican Independence, Tlaxcala was declared a f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mexica
The Mexica (Nahuatl: , ;''Nahuatl Dictionary.'' (1990). Wired Humanities Project. University of Oregon. Retrieved August 29, 2012, frolink/ref> singular ) were a Nahuatl-speaking indigenous people of the Valley of Mexico who were the rulers of the Aztec Empire. The Mexica established Tenochtitlan, a settlement on an island in Lake Texcoco, in 1325. A dissident group in Tenochtitlan separated and founded the settlement of Tlatelolco with its own dynastic lineage. In 1521, they were conquered by an alliance of Spanish conquistadors and indigenous people including the Tlaxcaltecs led by Hernán Cortés. Names The ''Mexica'' are eponymous of the place name Mexico (''Mēxihco'' ), originally referring to the interconnected settlements in the valley that is now Mexico City. The group was also known as the Culhua-Mexica in recognition of its kinship alliance with the neighboring Culhua, descendants of the revered Toltecs, who occupied the Toltec capital of Tula from the 10th to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xicotencatl I
Xicotencatl I or Xicotencatl the Elder (c. 11 House (1425) – c. 4 Rabbit (1522)) was a long-lived ''tlatoani'' (king) of Tizatlan, a Nahua ''altepetl'' within the pre-Columbian confederacy of Tlaxcala, in what is now Mexico. Etymology His Nahuatl name, pronounced , is sometimes spelled Xicohtencatl. In 1519 he was baptized as Lorenzo Xicotencatl or Don Lorenzo de Vargas. Biography At the time of the Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire he was very old and of poor health. He was instrumental in aligning the Tlaxcala with Hernán Cortés' Spaniards.Diaz, B., 1963, The Conquest of New Spain, London: Penguin Books, Tlaxcalan historian Diego Muñoz Camargo wrote of him that he was more than 120 years old and that he could only see Cortés if he had someone lift his eyelids for him. He also writes that he had more than 500 wives and concubines and consequently a large number of children, including Xicotencatl II and the wife of Jorge de Alvarado - Doña Lucía. His great ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hernán Cortés
Hernán Cortés de Monroy y Pizarro Altamirano, 1st Marquess of the Valley of Oaxaca (; ; 1485 – December 2, 1547) was a Spanish ''conquistador'' who led an expedition that caused the fall of the Aztec Empire and brought large portions of what is now mainland Mexico under the rule of the King of Castile in the early 16th century. Cortés was part of the generation of Spanish explorers and conquistadors who began the first phase of the Spanish colonization of the Americas. Born in Medellín, Spain, to a family of lesser nobility, Cortés chose to pursue adventure and riches in the New World. He went to Hispaniola and later to Cuba, where he received an '' encomienda'' (the right to the labor of certain subjects). For a short time, he served as '' alcalde'' (magistrate) of the second Spanish town founded on the island. In 1519, he was elected captain of the third expedition to the mainland, which he partly funded. His enmity with the Governor of Cuba, Diego Velázquez de Cu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
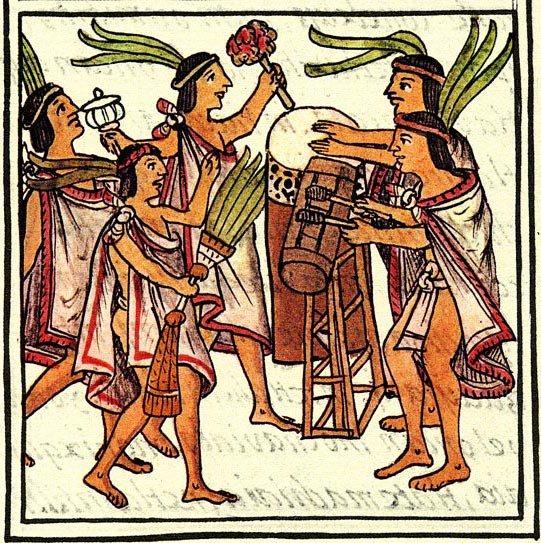
Aztec Religion
The Aztec religion is a monistic pantheism in which the Nahua concept of was construed as the supreme god , as well as a diverse pantheon of lesser gods and manifestations of nature. The popular religion tended to embrace the mythological and polytheistic aspects, and the Aztec Empire's state religion sponsored both the monism of the upper classes and the popular heterodoxies. The Aztec Empire officially recognized the most popular cults such that the deity was represented in the central temple precinct of the capital . The imperial cult was specifically that of the distinctive warlike patron god of the Mexica . Subjugated peoples were allowed to retain their own religious traditions in conquered provinces so long as they added the imperial god to their local pantheons, while the Empire would often incorporate practices from its new territories into the mainstream religion. In common with many other indigenous Mesoamerican civilizations, the Aztecs put great ritual emphasis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
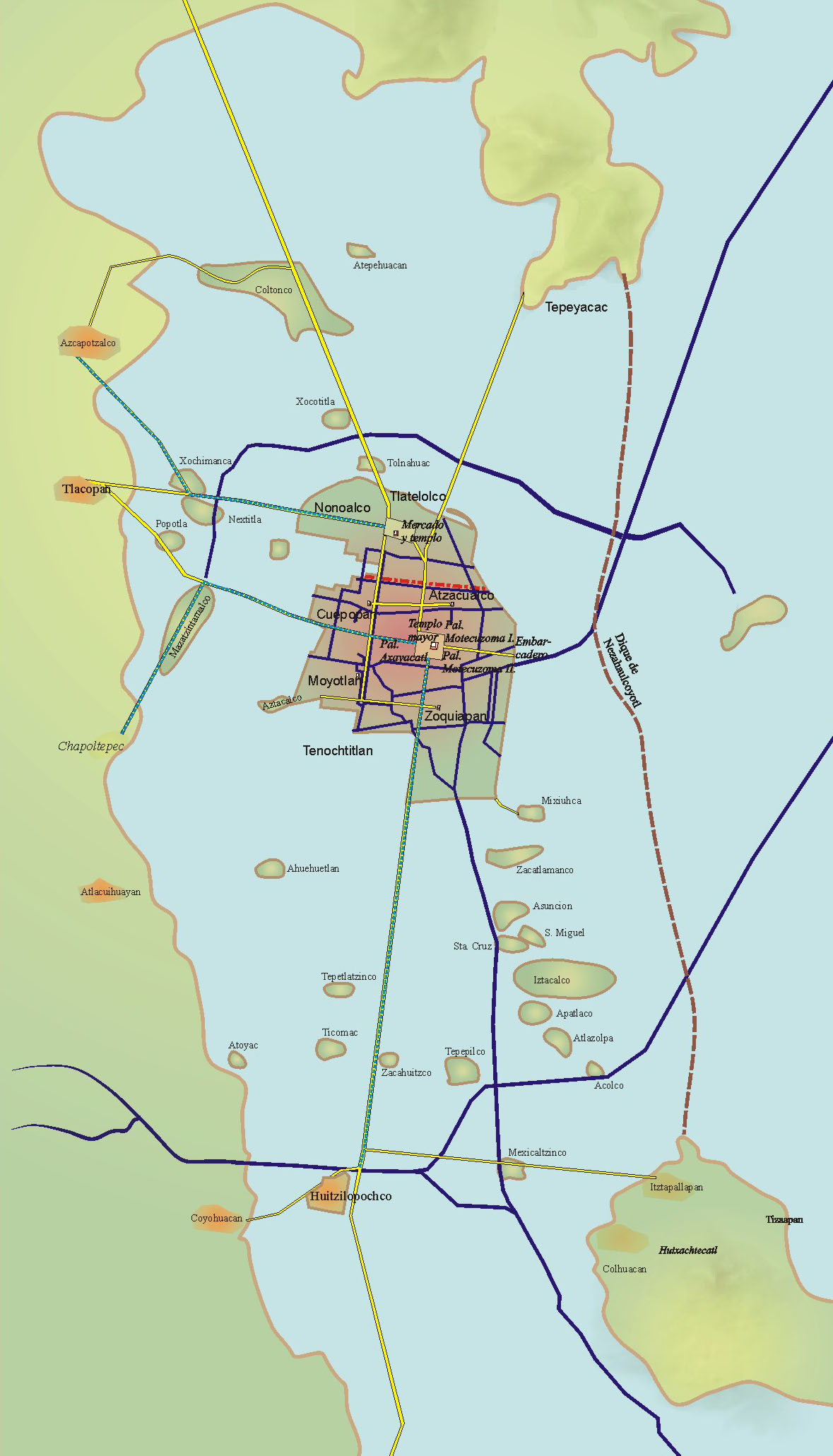
Tenochtitlan
, ; es, Tenochtitlan also known as Mexico-Tenochtitlan, ; es, México-Tenochtitlan was a large Mexican in what is now the historic center of Mexico City. The exact date of the founding of the city is unclear. The date 13 March 1325 was chosen in 1925 to celebrate the 600th anniversary of the city. The city was built on an island in what was then Lake Texcoco in the Valley of Mexico. The city was the capital of the expanding Aztec Empire in the 15th century until it was captured by the Spanish in 1521. At its peak, it was the largest city in the pre-Columbian Americas. It subsequently became a '' cabecera'' of the Viceroyalty of New Spain. Today, the ruins of are in the historic center of the Mexican capital. The World Heritage Site of contains what remains of the geography (water, boats, floating gardens) of the Mexica capital. was one of two Mexica (city-states or polities) on the island, the other being . The city is located in modern-day Mexico City. Etymolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Habsburg Spain
Habsburg Spain is a contemporary historiographical term referring to the huge extent of territories (including modern-day Spain, a piece of south-east France, eventually Portugal, and many other lands outside of the Iberian Peninsula) ruled between the 16th and 18th centuries (1516–1713) by kings from the Spanish branch of the House of Habsburg (also associated with its role in the history of Central and Eastern Europe). Habsburg Spain was a composite monarchy and a personal union. The Habsburg Hispanic Monarchs (chiefly Charles I and Philip II) reached the zenith of their influence and power ruling the Spanish Empire. They controlled territories over the five continents, including the Americas, the East Indies, the Low Countries, Belgium, Luxembourg, and territories now in Italy, France and Germany in Europe, the Portuguese Empire from 1580 to 1640, and various other territories such as small enclaves like Ceuta and Oran in North Africa. This period of Spanish history ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |