|
Titanium Dioxide
Titanium dioxide, also known as titanium(IV) oxide or titania , is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula . When used as a pigment, it is called titanium white, Pigment White 6 (PW6), or CI 77891. It is a white solid that is insoluble to water, although mineral forms can appear black. As a pigment, it has a wide range of applications, including paint, sunscreen, and food coloring. When used as a food coloring, it has E number E171. World production in 2014 exceeded 9 million tonnes. It has been estimated that titanium dioxide is used in two-thirds of all pigments, and pigments based on the oxide have been valued at a price of $13.2 billion. Structure In all three of its main dioxides, titanium exhibits octahedral geometry, being bonded to six oxide anions. The oxides in turn are bonded to three Ti centers. The overall crystal structure of rutile is tetragonal in symmetry whereas anatase and brookite are orthorhombic. The oxygen substructures are all slight dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
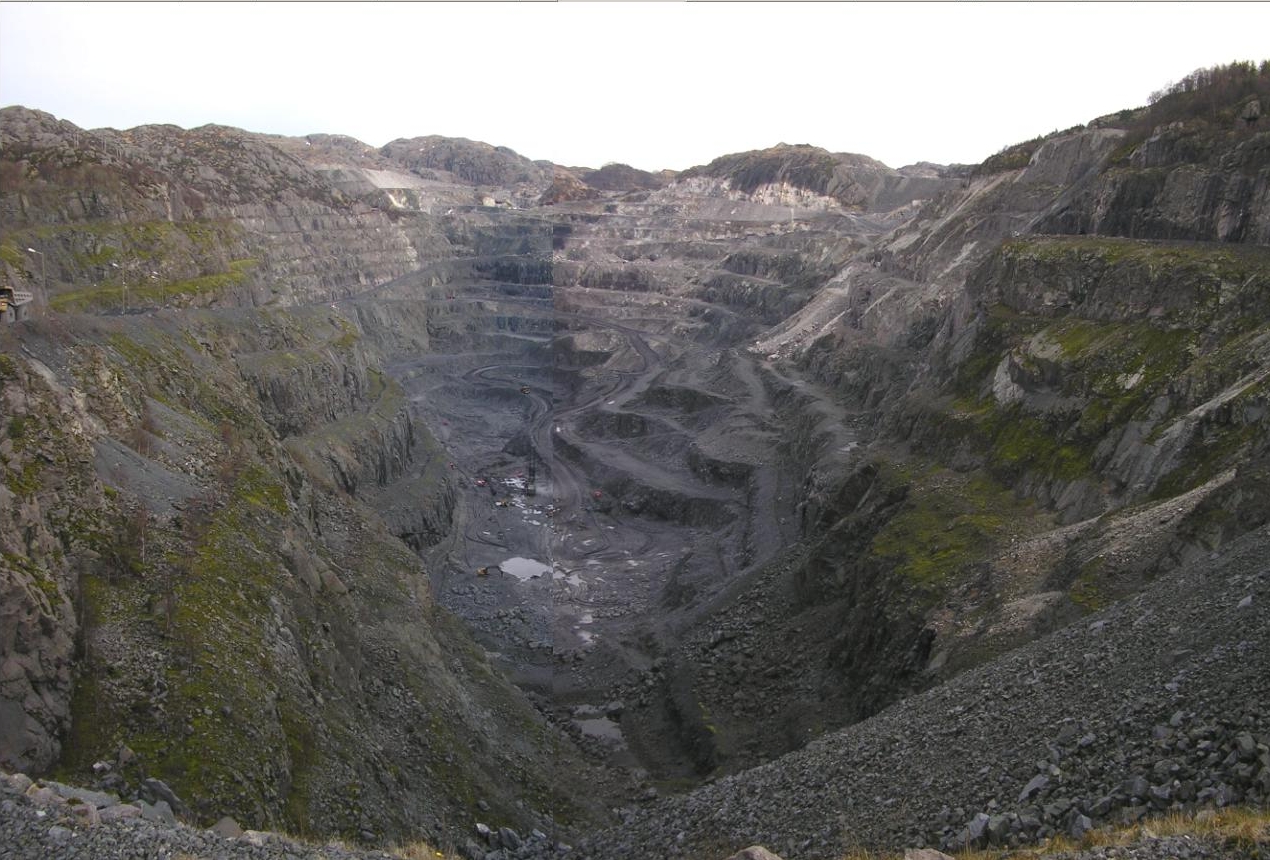
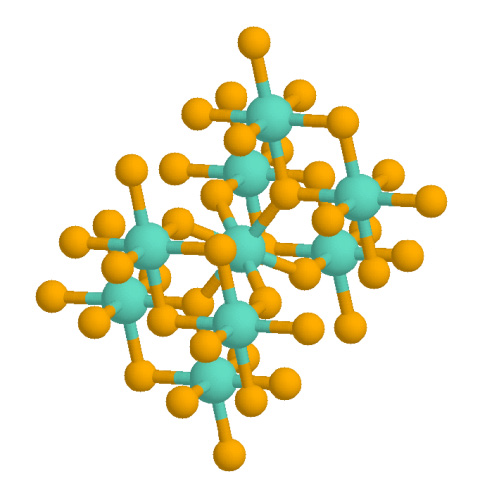
Rutile
Rutile is an oxide mineral composed of titanium dioxide (TiO2), the most common natural form of TiO2. Rarer polymorphs of TiO2 are known, including anatase, akaogiite, and brookite. Rutile has one of the highest refractive indices at visible wavelengths of any known crystal and also exhibits a particularly large birefringence and high dispersion. Owing to these properties, it is useful for the manufacture of certain optical elements, especially polarization optics, for longer visible and infrared wavelengths up to about 4.5 micrometres. Natural rutile may contain up to 10% iron and significant amounts of niobium and tantalum. Rutile derives its name from the Latin ('red'), in reference to the deep red color observed in some specimens when viewed by transmitted light. Rutile was first described in 1803 by Abraham Gottlob Werner. Occurrence Rutile is a common accessory mineral in high-temperature and high-pressure metamorphic rocks and in igneous rocks. Thermodynamically, ru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
E Number
E numbers ("E" stands for "Europe") are codes for substances used as food additives, including those found naturally in many foods such as vitamin C, for use within the European Union (EU) and European Free Trade Association (EFTA). Commonly found on food labels, their safety assessment and approval are the responsibility of the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). The fact that an additive has an E number implies that its use was at one time permitted in products for sale in the European Single Market; some of these additives are no longer allowed today. Having a single unified list for food additives was first agreed upon in 1962 with food colouring. In 1964, the directives for preservatives were added, in 1970 antioxidants were added, in 1974 emulsifiers, stabilisers, thickeners and gelling agents were added as well. Numbering schemes The numbering scheme follows that of the International Numbering System for Food Additives, International Numbering System (INS) as determ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monoclinic Crystal System
In crystallography, the monoclinic crystal system is one of the seven crystal systems. A crystal system is described by three vectors. In the monoclinic system, the crystal is described by vectors of unequal lengths, as in the orthorhombic system. They form a parallelogram prism. Hence two pairs of vectors are perpendicular (meet at right angles), while the third pair makes an angle other than 90°. Bravais lattices Two monoclinic Bravais lattices exist: the primitive monoclinic and the base-centered monoclinic. For the base-centered monoclinic lattice, the primitive cell has the shape of an oblique rhombic prism;See , row mC, column Primitive, where the cell parameters are given as a1 = a2, α = β it can be constructed because the two-dimensional centered rectangular base layer can also be described with primitive rhombic axes. Note that the length a of the primitive cell below equals \frac \sqrt of the conventional cell above. Crystal classes The table below organi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rutile
Rutile is an oxide mineral composed of titanium dioxide (TiO2), the most common natural form of TiO2. Rarer polymorphs of TiO2 are known, including anatase, akaogiite, and brookite. Rutile has one of the highest refractive indices at visible wavelengths of any known crystal and also exhibits a particularly large birefringence and high dispersion. Owing to these properties, it is useful for the manufacture of certain optical elements, especially polarization optics, for longer visible and infrared wavelengths up to about 4.5 micrometres. Natural rutile may contain up to 10% iron and significant amounts of niobium and tantalum. Rutile derives its name from the Latin ('red'), in reference to the deep red color observed in some specimens when viewed by transmitted light. Rutile was first described in 1803 by Abraham Gottlob Werner. Occurrence Rutile is a common accessory mineral in high-temperature and high-pressure metamorphic rocks and in igneous rocks. Thermodynamically, ru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxford University Press
Oxford University Press (OUP) is the university press of the University of Oxford. It is the largest university press in the world, and its printing history dates back to the 1480s. Having been officially granted the legal right to print books by decree in 1586, it is the second oldest university press after Cambridge University Press. It is a department of the University of Oxford and is governed by a group of 15 academics known as the Delegates of the Press, who are appointed by the vice-chancellor of the University of Oxford. The Delegates of the Press are led by the Secretary to the Delegates, who serves as OUP's chief executive and as its major representative on other university bodies. Oxford University Press has had a similar governance structure since the 17th century. The press is located on Walton Street, Oxford, opposite Somerville College, in the inner suburb of Jericho. For the last 500 years, OUP has primarily focused on the publication of pedagogical texts a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asterism (gemology)
An asterism () is a star-shaped concentration of reflected or refracted light from a gemstone. Asterisms can appear when a suitable stone is cut ''en cabochon'' i.e. shaped and polished (not faceted). A gemstone that exhibits this effect is referred to as a star stone or asteria. The best known is star sapphire, but many other minerals can also be asteria, usually due to impurities in the crystal structure. Archetype The archetypal asteria is the star sapphire, generally corundum with near uniform impurities which is bluish-grey and milky or opalescent, which when lit has a star of six rays. In the red instance stellate reflection is rarer; the star-ruby occasionally found with the star-sapphire in Sri Lanka is among the most valued of "fancy stones". Other examples are star-topaz and certain prized chatoyant (, ) chrysoberyl stones, particularly of the cymophane (yellow) variety. Description Asterism is generated by reflections of light from twin- lamellae or from extrem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
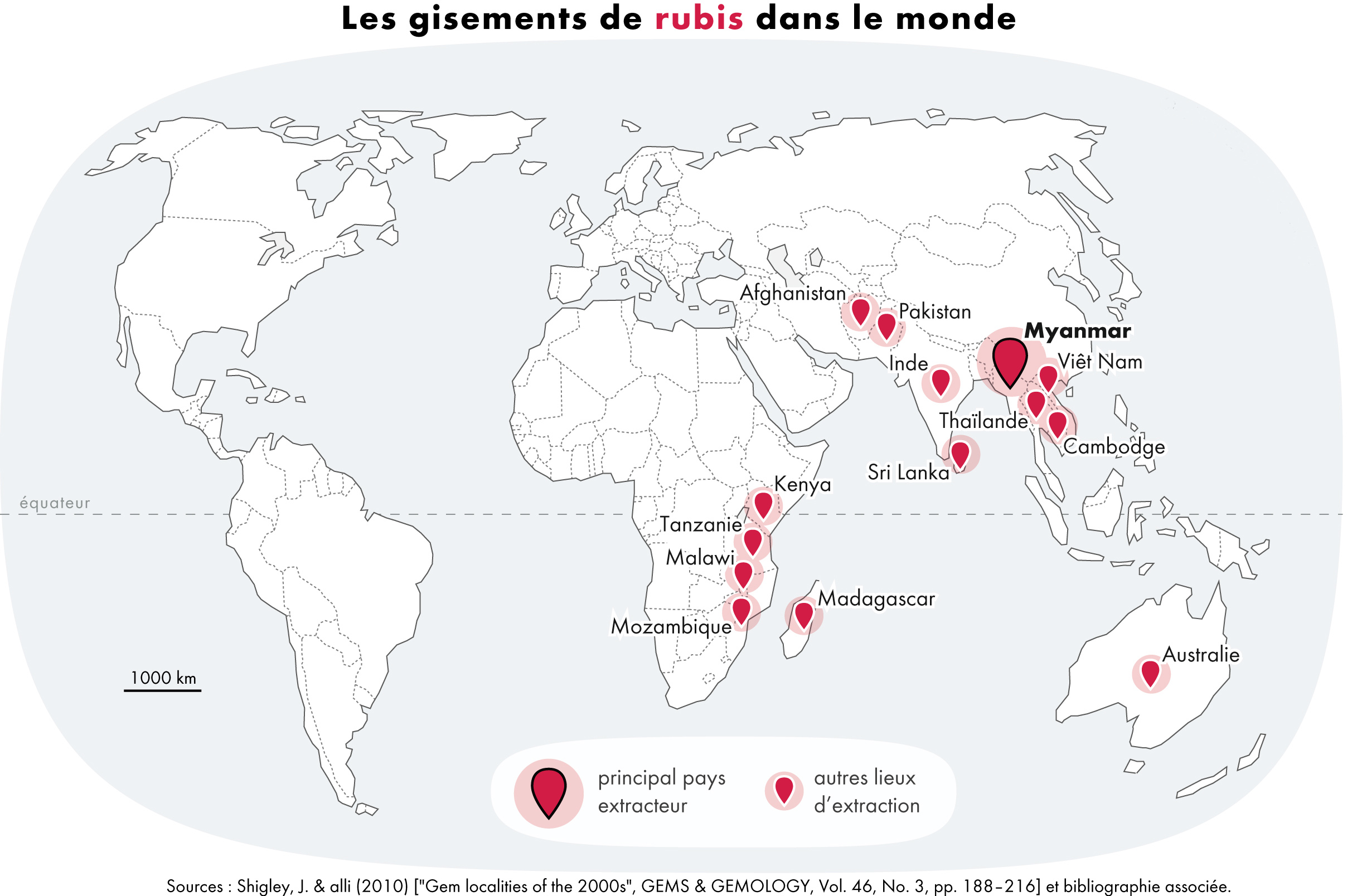
Ruby
A ruby is a pinkish red to blood-red colored gemstone, a variety of the mineral corundum (aluminium oxide). Ruby is one of the most popular traditional jewelry gems and is very durable. Other varieties of gem-quality corundum are called sapphires. Ruby is one of the traditional cardinal gems, alongside amethyst, sapphire, emerald, and diamond. The word ''ruby'' comes from ''ruber'', Latin for red. The color of a ruby is due to the element chromium. Some gemstones that are popularly or historically called rubies, such as the Black Prince's Ruby in the British Imperial State Crown, are actually spinels. These were once known as "Balas rubies". The quality of a ruby is determined by its color, cut, and clarity, which, along with carat (mass), carat weight, affect its value. The brightest and most valuable shade of red, called blood-red or pigeon blood, commands a large premium over other rubies of similar quality. After color follows clarity: similar to diamonds, a clear stone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Star Sapphire (jewel)
Sapphire is a precious gemstone, a variety of the mineral corundum, consisting of aluminium oxide () with trace amounts of elements such as iron, titanium, chromium, vanadium, or magnesium. The name sapphire is derived via the Latin "sapphirus" from the Greek "sappheiros", which referred to lapis lazuli. It is typically blue, but natural "fancy" sapphires also occur in yellow, purple, orange, and green colors; "parti sapphires" show two or more colors. Red corundum stones also occur, but are called rubies rather than sapphires. Pink-colored corundum may be classified either as ruby or sapphire depending on locale. Commonly, natural sapphires are cut and polished into gemstones and worn in jewelry. They also may be created synthetically in laboratories for industrial or decorative purposes in large crystal boules. Because of the remarkable hardness of sapphires 9 on the Mohs scale (the third hardest mineral, after diamond at 10 and moissanite at 9.5) sapphires are also used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leucoxene
Leucoxene is a fine granular alteration product of titanium minerals. It varies in color from yellow to brown. It consists mainly of rutile or anatase. It is observed in some igneous rocks and iron ore deposits as the result of the alteration of ilmenite, perovskite Perovskite (pronunciation: ) is a calcium titanium oxide mineral composed of calcium titanate (chemical formula ). Its name is also applied to the class of compounds which have the same type of crystal structure In crystallography, crystal ..., or titanite. References * Hurlbut, Cornelius S.; Klein, Cornelis, 1985, Manual of Mineralogy, 20th ed., Mindat.org Oxide minerals {{oxide-mineral-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
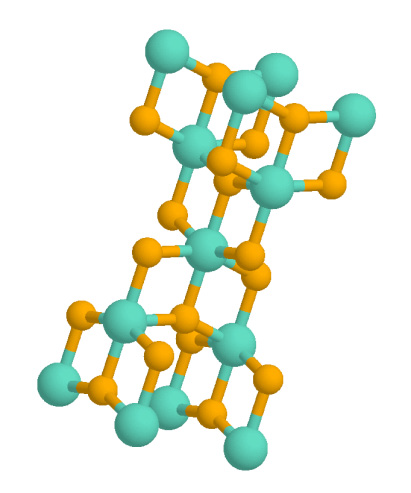
Anatase
Anatase is a metastable mineral form of titanium dioxide (TiO2) with a tetragonal crystal structure. Although colorless or white when pure, anatase in nature is usually a black solid due to impurities. Three other polymorphs (or mineral forms) of titanium dioxide are known to occur naturally: brookite, akaogiite, and rutile, with rutile being the most common and most stable of the bunch. Anatase is formed at relatively low temperatures and found in minor concentrations in igneous and metamorphic rocks. Thin films of TiO2-coated glass show antifogging and self-cleaning properties under ultraviolet radiation. Anatase is always found as small, isolated, and sharply developed crystals, and like rutile, it crystallizes in a tetragonal system. Anatase is metastable at all temperatures and pressures, with rutile being the equilibrium polymorph. Nevertheless, anatase is often the first titanium dioxide phase to form in many processes due to its lower surface energy, with a trans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ilmenite
Ilmenite is a titanium-iron oxide mineral with the idealized formula . It is a weakly magnetic black or steel-gray solid. Ilmenite is the most important ore of titanium and the main source of titanium dioxide, which is used in paints, printing inks, fabrics, plastics, paper, sunscreen, food and cosmetics. Structure and properties Ilmenite is a heavy (specific gravity 4.7), moderately hard (Mohs hardness 5.6 to 6), opaque black mineral with a submetallic luster. It is almost always massive, with thick tabular crystals being quite rare. It shows no discernible cleavage, breaking instead with a conchoidal to uneven fracture. Ilmenite crystallizes in the trigonal system with space group ''R''. The ilmenite crystal structure consists of an ordered derivative of the corundum structure; in corundum all cations are identical but in ilmenite Fe2+ and Ti4+ ions occupy alternating layers perpendicular to the trigonal c axis. Pure ilmenite is paramagnetic (showing only very weak attra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatase Crystal Structure
Anatase is a metastable mineral form of titanium dioxide (TiO2) with a tetragonal crystal structure. Although colorless or white when pure, anatase in nature is usually a black solid due to impurities. Three other polymorphs (or mineral forms) of titanium dioxide are known to occur naturally: brookite, akaogiite, and rutile, with rutile being the most common and most stable of the bunch. Anatase is formed at relatively low temperatures and found in minor concentrations in igneous and metamorphic rocks. Thin films of TiO2-coated glass show antifogging and self-cleaning properties under ultraviolet radiation. Anatase is always found as small, isolated, and sharply developed crystals, and like rutile, it crystallizes in a tetragonal system. Anatase is metastable at all temperatures and pressures, with rutile being the equilibrium polymorph. Nevertheless, anatase is often the first titanium dioxide phase to form in many processes due to its lower surface energy, with a transform ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)