|
Timing Marks
A timing mark is an indicator used for setting the timing of the ignition system of an engine, typically found on the crankshaft pulley (as pictured) or the flywheel, being the largest radius rotating at crankshaft speed and therefore the place where marks at one degree intervals will be farthest apart. On older engines it is common to set the ignition timing using a timing light, which flashes in time with the ignition system (and hence engine rotation), so when shone on the timing marks makes them appear stationary due to the stroboscopic effect. The ignition timing can then be adjusted to fire at the correct point in the engine's rotation, typically a few degrees before top dead centre and advancing with increasing engine speed. The timing can be adjusted by loosening and slightly rotating the distributor in its seat. Modern engines usually use a crank sensor directly connected to the engine management system. The term can also be used to describe the tick marks along the len ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timing Marks
A timing mark is an indicator used for setting the timing of the ignition system of an engine, typically found on the crankshaft pulley (as pictured) or the flywheel, being the largest radius rotating at crankshaft speed and therefore the place where marks at one degree intervals will be farthest apart. On older engines it is common to set the ignition timing using a timing light, which flashes in time with the ignition system (and hence engine rotation), so when shone on the timing marks makes them appear stationary due to the stroboscopic effect. The ignition timing can then be adjusted to fire at the correct point in the engine's rotation, typically a few degrees before top dead centre and advancing with increasing engine speed. The timing can be adjusted by loosening and slightly rotating the distributor in its seat. Modern engines usually use a crank sensor directly connected to the engine management system. The term can also be used to describe the tick marks along the len ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
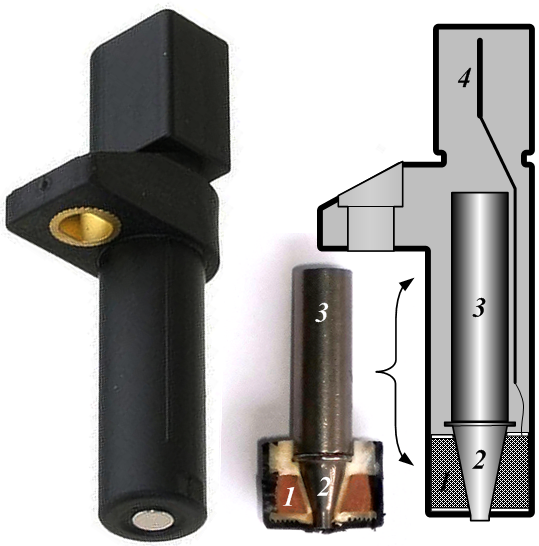
Crank Sensor
A crank sensor (CKP) is an electronic device used in an internal combustion engine, both petrol and diesel, to monitor the position or rotational speed of the crankshaft. This information is used by engine management systems to control the fuel injection or the ignition system timing and other engine parameters. Before electronic crank sensors were available, the distributor would have to be manually adjusted to a timing mark on petrol engines. The crank sensor can be used in combination with a similar camshaft position sensor (CMP) to monitor the relationship between the pistons and valves in the engine, which is particularly important in engines with variable valve timing. This method is also used to "synchronise" a four stroke engine upon starting, allowing the management system to know when to inject the fuel. It is also commonly used as the primary source for the measurement of engine speed in revolutions per minute. Common mounting locations include the main crank pulley ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ignition Systems
Ignition may refer to: Science and technology * Firelighting, the human act of creating a fire for warmth, cooking and other uses * Combustion, an exothermic chemical reaction between a fuel and an oxidant * Fusion ignition, the point at which a nuclear fusion reaction becomes self-sustaining * Ignition SCADA, software by Inductive Automation Arts and entertainment * ''Ignition'' (video game), a top-down racing game for PC published in 1997 * ''Ignition'' (2001 film), directed by Yves Simoneau * Ignition Entertainment, a computer video games company founded in 2002 * '' Ignition! An Informal History of Liquid Rocket Propellants'', (1972) by John Drury Clark Music Albums and EPs * ''Ignition'' (B1A4 album), 2012 * ''Ignition'' (Darude album), 2001 * ''Ignition'' (John Waite album), 1982 * ''Ignition'' (Mark Boals album), 1998 * ''Ignition'' (Nicky Romero album), 2014 * ''Ignition'' (The Offspring album), 1992 * ''Ignition'' (The Music Machine album) * ''Ignition!'', album ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aztec Code
The Aztec Code is a matrix code invented by Andrew Longacre, Jr. and Robert Hussey in 1995.* The code was published by AIM, Inc. in 1997. Although the Aztec Code was patented, that patent was officially made public domain. Click "images" then "correction" to see dedication to the public domain. The Aztec Code is also published as ISO/IEC 24778:2008 standard. Named after the resemblance of the central finder pattern to an Aztec pyramid, Aztec Code has the potential to use less space than other matrix barcodes because it does not require a surrounding blank "quiet zone". Structure The symbol is built on a square grid with a bulls-eye pattern at its centre for locating the code. Data is encoded in concentric square rings around the bulls-eye pattern. The central bulls-eye is 9×9 or 13×13 pixels, and one row of pixels around that encodes basic coding parameters, producing a "core" of 11×11 or 15×15 squares. Data is added in "layers", each one containing two rings of pixe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Matrix
A Data Matrix is a two-dimensional code consisting of black and white "cells" or dots arranged in either a square or rectangular pattern, also known as a matrix. The information to be encoded can be text or numeric data. Usual data size is from a few bytes up to 1556 bytes. The length of the encoded data depends on the number of cells in the matrix. Error correction codes are often used to increase reliability: even if one or more cells are damaged so it is unreadable, the message can still be read. A Data Matrix symbol can store up to 2,335 alphanumeric characters. Data Matrix symbols are rectangular, usually square in shape and composed of square "cells" which represent bits. Depending on the coding used, a "light" cell represents a 0 and a "dark" cell is a 1, or vice versa. Every Data Matrix is composed of two solid adjacent borders in an "L" shape (called the "finder pattern") and two other borders consisting of alternating dark and light "cells" or modules (called the "ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PostBar
PostBar, also known as CPC 4-State, is the black-ink barcode system used by Canada Post in its automated mail sorting and delivery operations. It is similar to other 4 State barcode systems used by Australia Post and the United Kingdom's Royal Mail (from which it derives), but uses an obscured structure and encoding system unique to Canada Post. This particular bar code system is used on "flats" (which are larger-than-letter-size pieces of mail, such as magazines) and parcels. This symbology, derived from the RM4SCC system used by the British Royal Mail, uses a series of bars, each of which can individually have one of four possible states, to encode information used in automated sortation and delivery onto each piece of mail. Each bar can either be short and centred (known as a ''tracker''), medium and elevated (an ''ascender''), medium and lowered (a ''descender''), or full height. This symbology also uses an element known as a '' Data Content Identifier'' (or DCI), which spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barcode
A barcode or bar code is a method of representing data in a visual, machine-readable form. Initially, barcodes represented data by varying the widths, spacings and sizes of parallel lines. These barcodes, now commonly referred to as linear or one-dimensional (1D), can be scanned by special optical scanners, called barcode readers, of which there are several types. Later, two-dimensional (2D) variants were developed, using rectangles, dots, hexagons and other patterns, called ''matrix codes'' or ''2D barcodes'', although they do not use bars as such. 2D barcodes can be read using purpose-built 2D optical scanners, which exist in a few different forms. 2D barcodes can also be read by a digital camera connected to a microcomputer running software that takes a photographic image of the barcode and analyzes the image to deconstruct and decode the 2D barcode. A mobile device with an inbuilt camera, such as smartphone, can function as the latter type of 2D barcode reader using special ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
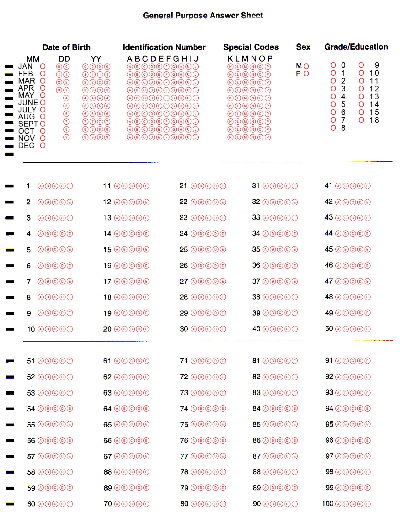
Optical Mark Recognition
Optical mark recognition (also called optical mark reading and OMR) is the process of reading information that people mark on surveys, tests and other paper documents. OMR is used to read questionnaires, multiple choice examination papers in the form of shaded areas. OMR background Many OMR devices have a scanner that shines a light onto a form. The device then looks at the contrasting reflectivity of the light at certain positions on the form. It will detect the black marks because they reflect less light than the blank areas on the form. Some OMR devices use forms that are printed on transoptic paper. The device can then measure the amount of light that passes through the paper. It will pick up any black marks on either side of the paper because they reduce the amount of light passing through. In contrast to the dedicated OMR device, desktop OMR software allows a user to create their own forms in a word processor or computer and print them on a laser laser printer. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Engine Management System
An engine control unit (ECU), also commonly called an engine control module (ECM), is a type of electronic control unit that controls a series of actuators on an internal combustion engine to ensure optimal engine performance. It does this by reading values from a multitude of sensors within the engine bay, interpreting the data using multidimensional performance maps (called lookup tables), and adjusting the engine actuators. Before ECUs, air–fuel mixture, ignition timing, and idle speed were mechanically set and dynamically controlled by mechanical and pneumatic means. If the ECU has control over the fuel lines, then it is referred to as an electronic engine management system (EEMS). The fuel injection system has the major role of controlling the engine's fuel supply. The whole mechanism of the EEMS is controlled by a stack of sensors and actuators. Workings Control of air–fuel ratio Most modern engines use some type of fuel injection to deliver fuel to the cylinders. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distributor
A distributor is an enclosed rotating switch used in spark-ignition internal combustion engines that have mechanically timed ignition. The distributor's main function is to route high voltage current from the ignition coil to the spark plugs in the correct firing order, and for the correct amount of time. Except in magneto systems and many modern computer controlled engines that use crank angle/position sensors, the distributor also houses a mechanical or inductive breaker switch to open and close the ignition coil's primary circuit. The first reliable battery operated ignition was the Delco ignition system developed by Dayton Engineering Laboratories Co. (Delco) and introduced in the 1910 Cadillac Model 30. This ignition was developed by Charles Kettering and was considered a wonder in its day. Atwater Kent invented his Unisparker ignition system about this time in competition with the Delco system. By the end of the 20th century mechanical ignitions were disappearing from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
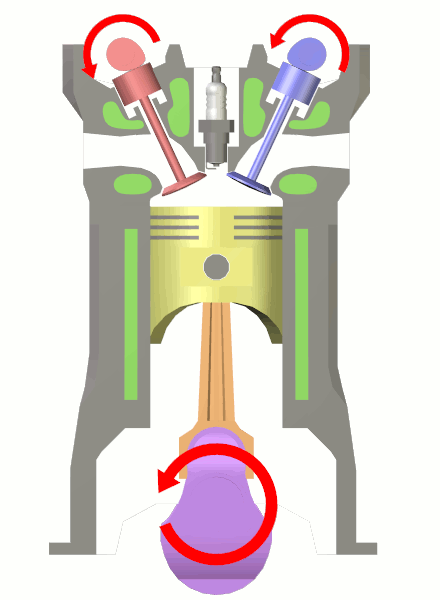
Ignition System
An ignition system generates a spark or heats an electrode to a high temperature to ignite a fuel-air mixture in spark ignition internal combustion engines, oil-fired and gas-fired boilers, rocket engines, etc. The widest application for spark ignition internal combustion engines is in petrol (gasoline) road vehicles such as cars and motorcycles. Compression ignition Diesel engines ignite the fuel-air mixture by the heat of compression and do not need a spark. They usually have glowplugs that preheat the combustion chamber to allow starting in cold weather. Other engines may use a flame, or a heated tube, for ignition. While this was common for very early engines it is now rare. The first electric spark ignition was probably Alessandro Volta's toy electric pistol from the 1780s. Siegfried Marcus patented his "Electrical igniting device for gas engines" on 7 October 1884. History Magneto systems The simplest form of spark ignition is that using a magneto. The engine spins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Top Dead Centre
In a reciprocating engine, the dead centre is the position of a piston in which it is either farthest from, or nearest to, the crankshaft. The former is known as Top Dead Centre (TDC) while the latter is known as Bottom Dead Centre (BDC). More generally, the dead centre is any position of a crank where the applied force is straight along its axis, meaning no turning force can be applied. Many sorts of machines are crank driven, including unicycles, bicycles, tricycles, various types of machine presses, gasoline engines, diesel engines, steam locomotives, and other steam engines. Crank-driven machines rely on the energy stored in a flywheel to overcome the dead centre, or are designed, in the case of multi-cylinder engines, so that dead centres can never exist on all cranks at the same time. A steam locomotive is an example of the latter, the connecting rods being arranged such that the dead centre for each cylinder occurs out of phase with the other one (or more) cylin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |