|
Timeline Of The Discovery And Classification Of Minerals
Georgius Agricola is considered the 'father of mineralogy'. Nicolas Steno founded the stratigraphy (the study of stratum, rock layers (strata) and layering (stratification)), the geology characterizes the rocks in each layer and the mineralogy characterizes the minerals in each rock. The chemical elements were discovered in identified minerals and with the help of the identified elements the mineral crystal structure could be described. One milestone was the discovery of the geometrical law of crystallization by René Just Haüy, a further development of the work by Nicolas Steno and Jean-Baptiste L. Romé de l'Isle (the characterisation of a Crystallinity, crystalline mineral needs knowledge on crystallography). Important contributions came from some Saxon "Bergraths"/ Freiberg University of Mining and Technology, Freiberg Mining Academy: Johann Friedrich Henckel, Johann F. Henckel, Abraham Gottlob Werner and his students (August Breithaupt, Robert Jameson, José Bonifácio de Andrad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georgius Agricola
Georgius Agricola (; born Georg Pawer or Georg Bauer; 24 March 1494 – 21 November 1555) was a German Humanist scholar, mineralogist and metallurgist. Born in the small town of Glauchau, in the Electorate of Saxony of the Holy Roman Empire, he was broadly educated, but took a particular interest in the mining and refining of metals. For his groundbreaking work ''De Natura Fossilium'' published in 1546, he is generally referred to as the Father of Mineralogy.Rafferty, John P. (2012). ''Geological Sciences; Geology: Landforms, Minerals, and Rocks''. New York: Britannica Educational Publishing, p. 10. He is well known for his pioneering work '' De re metallica libri XII'', that was published in 1556, one year after his death. This 12-volume work is a comprehensive and systematic study, classification and methodical guide on all available factual and practical aspects, that are of concern for mining, the mining sciences and metallurgy, investigated and researched in its nat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Jameson
Robert Jameson Robert Jameson FRS FRSE (11 July 1774 – 19 April 1854) was a Scottish naturalist and mineralogist. As Regius Professor of Natural History at the University of Edinburgh for fifty years, developing his predecessor John Walker's concepts based on mineralogy into geological theories of Neptunism which held sway into the 1830s. Jameson is notable for his advanced scholarship, and his museum collection. The minerals and fossils collection of the Museum of Edinburgh University became one of the largest in Europe during Jameson's long tenure at the university. Early life Jameson was born in Leith on 11 July 1774, the son of Catherine Paton (1750–94) and Thomas Jameson (c.1750–1802), a soap manufacturer on Rotten Row (now Water Street). They lived on Sherrif Brae. His early education was spent at Leith Grammar School, after which he became the apprentice of the Leith surgeon John Cheyne (father of John Cheyne), with the aim of going to sea. He also atte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atomic Orbital
In atomic theory and quantum mechanics, an atomic orbital is a function describing the location and wave-like behavior of an electron in an atom. This function can be used to calculate the probability of finding any electron of an atom in any specific region around the atom's nucleus. The term ''atomic orbital'' may also refer to the physical region or space where the electron can be calculated to be present, as predicted by the particular mathematical form of the orbital. Each orbital in an atom is characterized by a set of values of the three quantum numbers , , and , which respectively correspond to the electron's energy, angular momentum, and an angular momentum vector component (magnetic quantum number). Alternative to the magnetic quantum number, the orbitals are often labeled by the associated harmonic polynomials (e.g., ''xy'', ). Each such orbital can be occupied by a maximum of two electrons, each with its own projection of spin m_s. The simple names s orbital, p orb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atomic Theory
Atomic theory is the scientific theory that matter is composed of particles called atoms. Atomic theory traces its origins to an ancient philosophical tradition known as atomism. According to this idea, if one were to take a lump of matter and cut it into ever smaller pieces, one would eventually reach a point where the pieces could not be further cut into anything smaller. Ancient Greek philosophers called these hypothetical ultimate particles of matter ''atomos'', a word which meant "uncut". In the early 1800s, the scientist John Dalton noticed that chemical substances seemed to combine and break down into other substances by weight in proportions that suggested that each chemical element is ultimately made up of tiny indivisible particles of consistent weight. Shortly after 1850, certain physicists developed the kinetic theory of gases and of heat, which mathematically modelled the behavior of gases by assuming that they were made of particles. In the early 20th century, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Dalton
John Dalton (; 5 or 6 September 1766 – 27 July 1844) was an English chemist, physicist and meteorologist. He is best known for introducing the atomic theory into chemistry, and for his research into colour blindness, which he had. Colour blindness is known as ''Daltonism'' in several languages, being named after him. Early life John Dalton was born into a Quaker family in Eaglesfield, near Cockermouth, in Cumberland, England. His father was a weaver. He received his early education from his father and from Quaker John Fletcher, who ran a private school in the nearby village of Pardshaw Hall. Dalton's family was too poor to support him for long and he began to earn his living, from the age of ten, in the service of wealthy local Quaker Elihu Robinson. Early career When he was 15, Dalton joined his older brother Jonathan in running a Quaker school in Kendal, Westmorland, about from his home. Around the age of 23, Dalton may have considered studying law or medicin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Felix Karl Ludwig Machatschki
Karl Ludwig Felix Machatschki (22 September 1895 – 17 February 1970) was an Austrian mineralogist. He was born in Arnfels (near Leibnitz) in Styria, Austria. He studied at the University of Graz, obtaining his habilitation in 1925; in 1927 he joined the group of Victor Goldschmidt in Oslo for one year. In 1930 he was appointed as a professor at the University of Tübingen. He changed university twice, first in 1941 to the University of Munich and finally in 1944 to the University of Vienna.Machatschki, Felix Karl Ludwig Austria-Forum In 1928 he published ''Zur Frage der Struktur und Konstitution der Feldspäte'', a paper in which he develops the concept of the atomic structure of |
William Lawrence Bragg
Sir William Lawrence Bragg, (31 March 1890 – 1 July 1971) was an Australian-born British physicist and X-ray crystallographer, discoverer (1912) of Bragg's law of X-ray diffraction, which is basic for the determination of crystal structure. He was joint recipient (with his father, William Henry Bragg) of the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1915, "For their services in the analysis of crystal structure by means of X-rays"; an important step in the development of X-ray crystallography. Bragg was knighted in 1941. As of 2021, he is the youngest ever Nobel laureate in physics, having received the award at the age of 25 years. Bragg was the director of the Cavendish Laboratory, Cambridge, when the discovery of the structure of DNA was reported by James D. Watson and Francis Crick in February 1953. Biography Early years Bragg was born in Adelaide, South Australia to Sir William Henry Bragg (1862–1942), Elder Professor of Mathematics and Physics at the University of Adelaide, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
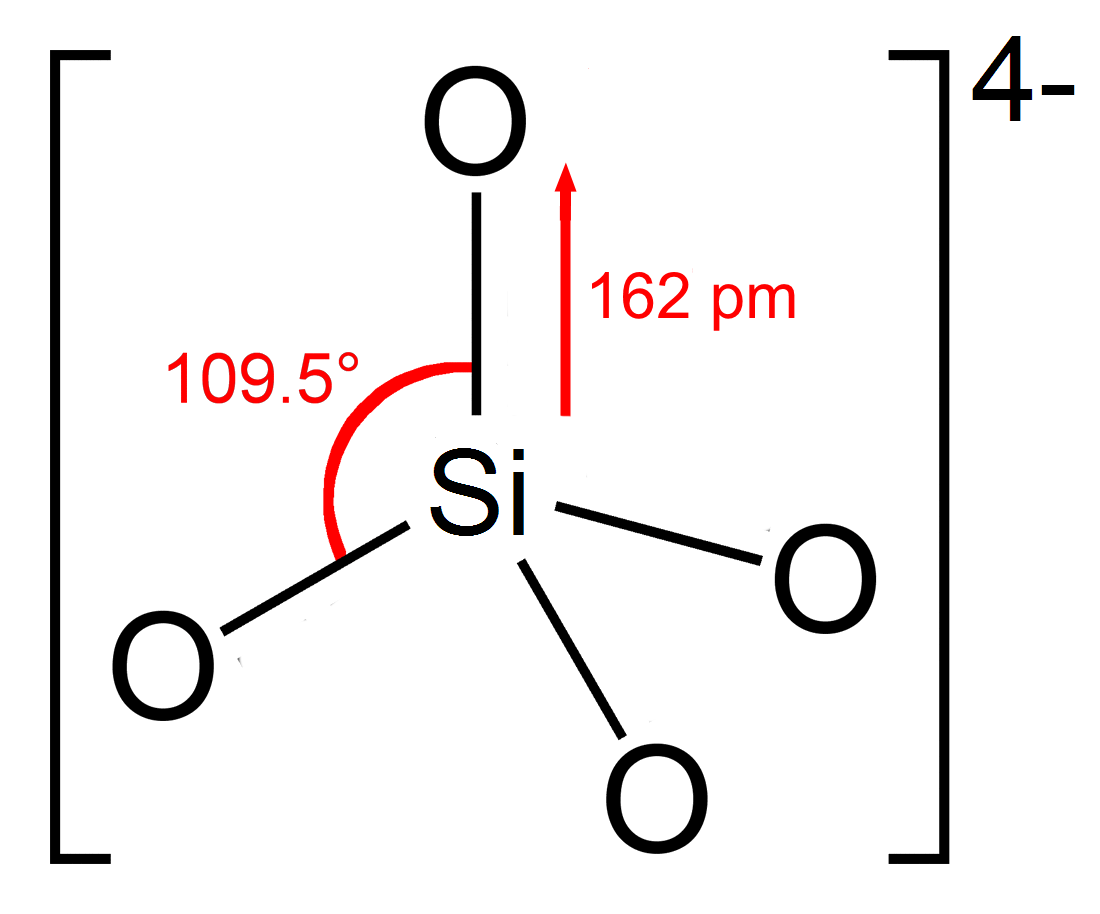
Silicate
In chemistry, a silicate is any member of a family of polyatomic anions consisting of silicon and oxygen, usually with the general formula , where . The family includes orthosilicate (), metasilicate (), and pyrosilicate (, ). The name is also used for any salt of such anions, such as sodium metasilicate; or any ester containing the corresponding chemical group, such as tetramethyl orthosilicate. The name "silicate" is sometimes extended to any anions containing silicon, even if they do not fit the general formula or contain other atoms besides oxygen; such as hexafluorosilicate .Most commonly, silicates are encountered as silicate minerals. For diverse manufacturing, technological, and artistic needs, silicates are versatile materials, both natural (such as granite, gravel, and garnet) and artificial (such as Portland cement, ceramics, glass, and waterglass). Structural principles In all silicates, silicon atom occupies the center of an idealized tetrahedron whose corner ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friedrich August Kekulé Von Stradonitz
Friedrich may refer to: Names * Friedrich (surname), people with the surname ''Friedrich'' * Friedrich (given name), people with the given name ''Friedrich'' Other * Friedrich (board game), a board game about Frederick the Great and the Seven Years' War * ''Friedrich'' (novel), a novel about anti-semitism written by Hans Peter Richter * Friedrich Air Conditioning, a company manufacturing air conditioning and purifying products *, a German cargo ship in service 1941-45 See also * Friedrichs (other) * Frederick (other) * Nikolaus Friedreich {{disambig ja:フリードリヒ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Bond
A chemical bond is a lasting attraction between atoms or ions that enables the formation of molecules and crystals. The bond may result from the electrostatic force between oppositely charged ions as in ionic bonds, or through the sharing of electrons as in covalent bonds. The strength of chemical bonds varies considerably; there are "strong bonds" or "primary bonds" such as covalent, ionic and metallic bonds, and "weak bonds" or "secondary bonds" such as dipole–dipole interactions, the London dispersion force and hydrogen bonding. Strong chemical bonding arises from the sharing or transfer of electrons between the participating atoms. Since opposite electric charges attract, the negatively charged electrons surrounding the nucleus and the positively charged protons within a nucleus attract each other. An electron positioned between two nuclei will be attracted to both of them, and the nuclei will be attracted toward electrons in this position. This attraction constitu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dmitri Ivanovich Mendeleev
Dmitri Ivanovich Mendeleev (sometimes transliterated as Mendeleyev or Mendeleef) ( ; russian: links=no, Дмитрий Иванович Менделеев, tr. , ; 8 February Old_Style_and_New_Style_dates">O.S._27_January.html" ;"title="Old_Style_and_New_Style_dates.html" ;"title="nowiki/> O.S._27_January">Old_Style_and_New_Style_dates.html"_;"title="nowiki/>Old_Style_and_New_Style_dates">O.S._27_January18342_February_[O.S._20_January.html" ;"title="Old Style and New Style dates">O.S. 27 January">Old_Style_and_New_Style_dates.html" ;"title="nowiki/>Old Style and New Style dates">O.S. 27 January18342 February [O.S. 20 January">Old Style and New Style dates">O.S. 27 January">Old_Style_and_New_Style_dates.html" ;"title="nowiki/>Old Style and New Style dates">O.S. 27 January18342 February [O.S. 20 January1907) was a Russian chemist and inventor. He is best known for formulating the Periodic Law and creating a version of the periodic table, periodic table of elements. He used th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Periodic Table
The periodic table, also known as the periodic table of the (chemical) elements, is a rows and columns arrangement of the chemical elements. It is widely used in chemistry, physics, and other sciences, and is generally seen as an icon of chemistry. It is a graphic formulation of the periodic law, which states that the properties of the chemical elements exhibit an approximate periodic dependence on their atomic numbers. The table is divided into four roughly rectangular areas called blocks. The rows of the table are called periods, and the columns are called groups. Elements from the same group of the periodic table show similar chemical characteristics. Trends run through the periodic table, with nonmetallic character (keeping their own electrons) increasing from left to right across a period, and from down to up across a group, and metallic character (surrendering electrons to other atoms) increasing in the opposite direction. The underlying reason for these trends is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |