|
Tikana Rural LLG
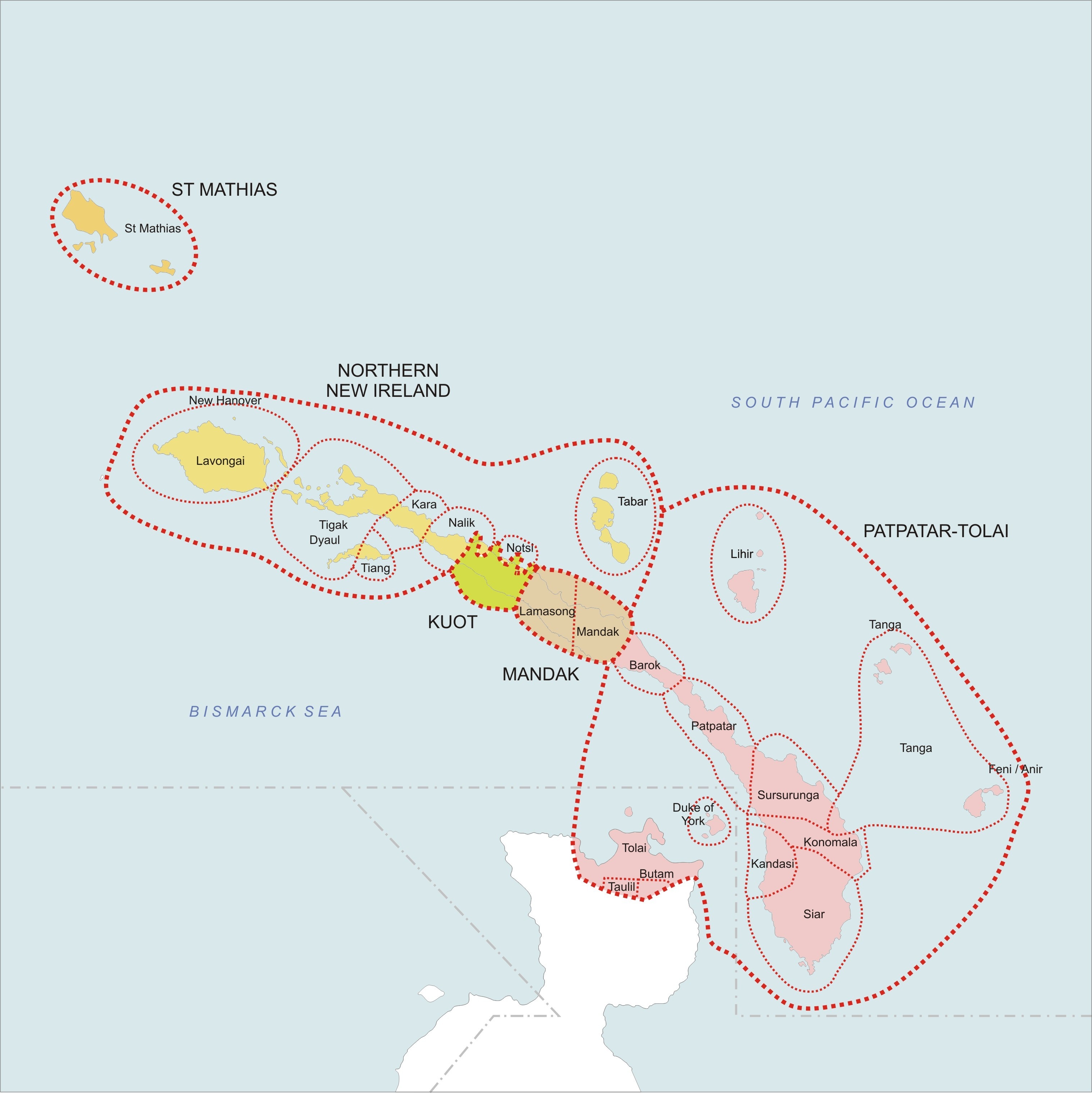
Tikana Rural LLG is a local government area in New Ireland Province, Papua New Guinea. The LLG administers the northern section of the island of New Ireland, as well as Djaul Island and some Tigak islands in the strait between New Ireland and New Hanover. The LLG is located in Kavieng District and the LLG headquarters is Kavieng, although Kavieng has its own urban LLG. ''Tikana'' is a portmanteau word derived from the names of the three language areas that make up the LLG: Tigak, Kara and Nalik. Population is 33,222 (PNG Census 2011). The Kuot language is spoken in the southern part of the LLG. The LLG president is Ken Bart. Wards *01. Enang *02. Nonovaul *03. Panapai *04. Kaselok *05. Bagatare *06. Lokono *07. Ngavalus *08. Paruai *09. Lemakot *10. Panamana *11. Madina *12. Kafkaf (Kuot language The Kuot language, or Panaras, is a language isolate, the only non- Austronesian language spoken on the island of New Ireland, Papua New Guinea. Lindström (2002: 30) es ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kavieng District
Kavieng District is the northernmost district of New Ireland Province in Papua New Guinea. The district contains the northern part of the island of New Ireland, as well as New Hannover, and the St. Matthias Group. The district headquarters is Kavieng and the district has four LLG areas, Kavieng Urban LLG, Lavongai Rural LLG, Tikana Rural LLG Tikana Rural LLG is a local government area in New Ireland Province, Papua New Guinea. The LLG administers the northern section of the island of New Ireland, as well as Djaul Island and some Tigak islands in the strait between New Ireland and ... and Murat Rural LLG. {{Districts_of_New_Ireland_Province Districts of Papua New Guinea New Ireland Province ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Djaul Island also known as the Djaul language and spoken on Dyaul Island
{{Disambiguation ...
Djaul may refer to: * Dyaul Island in the New Ireland chain of Papua New Guinea *Tiang language The Tiang language also known as Djaul is a language spoken in Papua New Guinea.Tiang Ethnologue, 2012, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nalik Language
The Nalik language is spoken by 5,000 or so people, based in 17 villages in Kavieng District, New Ireland, Papua New Guinea. It is an Austronesian language and member of the New Ireland group of languages with an SVO phrase structure. New Ireland languages are among the first Papua New Guinea languages recorded by Westerners. Laxudumau, spoken in the village of Lakudumau, is transitional to Kara, but is not intelligible to speakers of Nalik. Speakers Speakers of Nalik reside in a series of villages in northern central New Ireland. The Nalik speaking region is an approximately thirty-kilometer-long band of the island that spans approximately ten kilometers wide and is flanked on its north by the Kara speaking region and to its south by speakers of Kuot, the only non-Austronesian language on New Ireland. In the past, Lugagon, Fesoa, and Fessoa have been used to reference Nalik which are all names of villages in the region. Phonology Consonants A Nalik Phonology analys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kara Language (Papua New Guinea)
Kara (also Lemusmus or Lemakot) is an Austronesian language spoken by about 5,000 people in 1998 in the Kavieng District of New Ireland Province, Papua New Guinea. Laxudumau, spoken in the village of Lakudumau, is transitional to Nalik. Phonology Consonants Kara contains fourteen consonants. Single consonants are found within the head of a word, intervocalically between two vowels, finally and in sequences of less than two words medially. Voiceless consonants /p, t, q, ɸ, s/ create a cluster on the second consonant. Voiced consonants /b, d, g, β, ɣ/ appear initially and intervocally. They appear as the second consonant of a cluster. An example would be �alβal'tree sap'.Schlie, Perry, & Schlie, Ginny. (n.d.). A Kara Phonology. In ''Phonologies of Austronesian Languages, II'' (Data Papers in Papua New Guinea Languages, pp. 100). Ukarumpa via Lae: Summer Inst. of Ling. It is notable that different dialects change the use of consonants. ''West Kara'' replaces /s/ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tigak Language
Tigak (or Omo) is an Austronesian language spoken by about 6,000 people (in 1991) in the Kavieng District of New Ireland Province, Papua New Guinea. The Tigak language area includes the provincial capital, Kavieng. Phonology Phoneme inventory of the Tigak language: /r/ can also be realized as allophonically. Both /k, ɡ/ are back-released as ̠, ɡ̠ Two vowels /i u/ in word-initial form can also be released as consonantal allophones j External links * Paradisec The Pacific and Regional Archive for Digital Sources in Endangered Cultures (PARADISEC) is a cross-institutional project that supports work on endangered languages and cultures of the Pacific and the region around Australia. They digitise reel-to ... includea number of collections with Tigak language materials References Meso-Melanesian languages Languages of New Ireland Province {{MesoMelanesian-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portmanteau
A portmanteau word, or portmanteau (, ) is a blend of wordsGarner's Modern American Usage , p. 644. in which parts of multiple words are combined into a new word, as in ''smog'', coined by blending ''smoke'' and ''fog'', or ''motel'', from ''motor'' and ''hotel''. In , a portmanteau is a single morph that is analyzed as representing two (or more) underlying s. When portmanteaus shorten es ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kavieng Urban LLG
The Kavieng Urban LLG is a local government area A local government area (LGA) is an administrative division of a country that a local government is responsible for. The size of an LGA varies by country but it is generally a subdivision of a State (administrative division), state, province, divi ... in New Ireland Province, Papua New Guinea. The LLG is located in Kavieng District and the LLG headquarters is Kavieng. This LLG has six wards. The population is 16,725 (Census 2011) and the Lord Mayor is Hon. Stanley Mansini MPA. Wards *04. Bagail *05. Kulangit *06. Maiom *80. Kavieng Urban References * * * * {{NewIrelandProvince-geo-stub Local-level governments of New Ireland Province ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kavieng
Kavieng is the capital of the Papua New Guinean province of New Ireland and the largest town on the island of the same name. The town is located at Balgai Bay, on the northern tip of the island. As of 2009, it had a population of 17,248. Kavieng is the main port for New Ireland, and is both a trading and tourist destination. Several dive companies operate from the town, as the area is known for its diving, both for natural sites and wrecks dating from the Second World War. There are plane and shipwrecks in Kavieng Harbor itself, as well as several more nearby. The town is serviced by Kavieng Airport, with daily connections to Port Moresby. It lies at one end of the Boluminski Highway which runs of sealed road to Namatanai. Kavieng has all the usual services of a local administrative center: local government offices; shopping; hotels (such as the Kavieng Hotel, the Malagan Beach Resort hotel and the Kavieng Club (the former "colonial club" in the town)); a hospital providing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Hanover Island
New Hanover Island, (german: Neuhannover), also called Lavongai, is a large volcanic island in the New Ireland Province of Papua New Guinea. This region is part of the Bismarck Archipelago and lies at . Measuring some , it had a population of 5,000 in 1960, which increased to approximately 17,160 by 2000. In the interior the Tirpitz Range reaches a height of 2,800 feet. Culture Friedrich Ratzel in ''The History of Mankind''Ratzel, Friedrich. The History of Mankind. (London: MacMillan, 1896). URLwww.inquirewithin.biz/history/american_pacific/oceania/melanesian-ornament.htm accessed 21 October 2009. reported in 1896, when discussing Melanesian ornament, that there were luxurious feather ornament displays in New Hanover, showing much taste in the combination of forms and colours with vegetable fibres and beads on sticks. An example was a delicately formed face in feather-mosaic forming the head of a hairpin. See also *Johnson cult (so called) *List of volcanoes in Papua New Guinea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tigak
Tigak (or Omo) is an Austronesian language spoken by about 6,000 people (in 1991) in the Kavieng District of New Ireland Province, Papua New Guinea. The Tigak language area includes the provincial capital, Kavieng. Phonology Phoneme inventory of the Tigak language: /r/ can also be realized as allophonically. Both /k, ɡ/ are back-released as ̠, ɡ̠ Two vowels /i u/ in word-initial form can also be released as consonantal allophones j External links * Paradisec includea number of collections with Tigak language materials References Meso-Melanesian languages Languages of New Ireland Province {{MesoMelanesian-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Ireland (island)
New Ireland (Tok Pisin: ''Niu Ailan'') or Latangai, is a large island in Papua New Guinea, approximately in area with 120,000 people. It is named after the island of Ireland. It is the largest island of New Ireland Province, lying northeast of the island of New Britain. Both islands are part of the Bismarck Archipelago, named after Otto von Bismarck, and they are separated by Saint George's Channel. The administrative centre of the island and of New Ireland province is the town of Kavieng located at the northern end of the island. While the island was part of German New Guinea, it was named Neumecklenburg ("New Mecklenburg"). Geography The island is part of the Bismarck Archipelago and is often described as having the shape of a musket. New Ireland is surrounded by the Bismarck Sea in the southwest and by the Pacific Ocean in the northeast. For much of its in length, the island's width varies between less than to , yet the central mountainous spine is very steep an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Ireland Province
New Ireland Province, formerly New Mecklenburg (german: Neu-Mecklenburg), and Nova Hibernia, is the northeasternmost province of Papua New Guinea. Physical geography The largest island of the province is New Ireland. Also part of the province are numerous smaller islands, including Saint Matthias Group (Mussau, Emirau), New Hanover, Djaul, Tabar Group ( Tabar, Tatau, Simberi), Lihir, Tanga Group (Malendok, Boang), Feni Islands (Ambitle, Babase) and Anir. The land area of the province is around 9 560 km². The sea area within the Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) of New Ireland Province is around 230,000 km². Ecology In the early days of the French Revolution while searching for a lost scientific expedition the vessel La Recherche passed by New Ireland. On board was the prominent botanist Jacques-Julien Houtou de Labillardière who noted in his journal fine stands of teak (tectona grandis) trees growing at the southern end of the island. This marks the easter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |