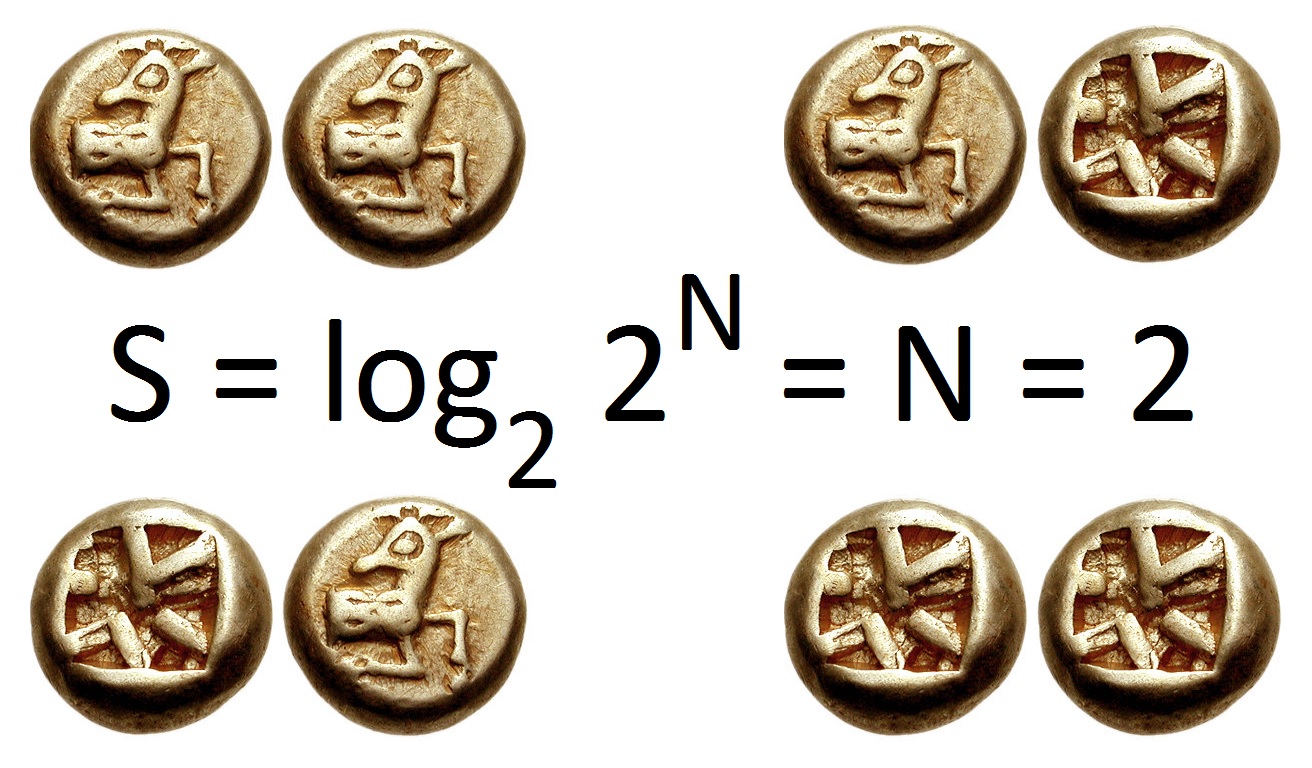|
Thresholding (image Processing)
In digital image processing, thresholding is the simplest method of segmenting images. From a grayscale image, thresholding can be used to create binary images. Definition The simplest thresholding methods replace each pixel in an image with a black pixel if the image intensity I_ is less than a fixed value called the threshold T, or a white pixel if the pixel intensity is greater than that threshold. In the example image on the right, this results in the dark tree becoming completely black, and the bright snow becoming completely white. Automatic thresholding While in some cases, the threshold T can be selected manually by the user, there are many cases where the user wants the threshold to be automatically set by an algorithm. In those cases, the threshold should be the "best" threshold in the sense that the partition of the pixels above and below the threshold should match as closely as possible the actual partition between the two classes of objects represented by those ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pavlovsk Railing Of Bridge Yellow Palace Winter
Pavlovsk may refer to: Russia *Pavlovsk, Saint Petersburg, a town in a suburban Pushkinskiy District of Saint Petersburg, Russia *Pavlovsk Urban Settlement, an administrative division and a municipal formation which the town of Pavlovsk in Pavlovsky District of Voronezh Oblast, Russia is incorporated as *Pavlovsk, Russia, several inhabited localities in Russia Ukraine *Pavlovsk, former name of the city of Mariupol, Ukraine See also * Novopavlovsk * Pavel * Pavlov (other) * Pavlovka (other) * Pavlovo * Pavlovsky (other) Pavlovsky (masculine), Pavlovskaya (feminine), or Pavlovskoye (neuter) may refer to: * Pavlovsky (surname) Places * Pavlovsky District, several districts in Russia * Pavlovskoye Urban Settlement, several municipal urban settlements in Russia * P ... * Petropavlovsk (other) {{Disambiguation, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Example Of Adaptive Thresholding
Example may refer to: * ''exempli gratia'' (e.g.), usually read out in English as "for example" * .example, reserved as a domain name that may not be installed as a top-level domain of the Internet ** example.com, example.net, example.org, and example.edu: second-level domain names reserved for use in documentation as examples * HMS ''Example'' (P165), an Archer-class patrol and training vessel of the Royal Navy Arts * ''The Example'', a 1634 play by James Shirley * ''The Example'' (comics), a 2009 graphic novel by Tom Taylor and Colin Wilson * Example (musician), the British dance musician Elliot John Gleave (born 1982) * ''Example'' (album), a 1995 album by American rock band For Squirrels See also * Exemplar (other), a prototype or model which others can use to understand a topic better * Exemplum, medieval collections of short stories to be told in sermons * Eixample The Eixample (, ) is a district of Barcelona between the old city (Ciutat Vella) a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CMYK Color Model
The CMYK color model (also known as process color, or four color) is a subtractive color model, based on the CMY color model, used in color printing, and is also used to describe the printing process itself. The abbreviation ''CMYK'' refers to the four ink plates used: cyan, magenta, yellow, and key (most often black). The CMYK model works by partially or entirely masking colors on a lighter, usually white, background. The ink reduces the light that would otherwise be reflected. Such a model is called ''subtractive'', as inks ''subtract'' some colors from white light; in the CMY model, white light minus red leaves cyan, white light minus green leaves magenta, and white light minus blue leaves yellow. In additive color models, such as RGB, white is the ''additive'' combination of all primary colored lights, and black is the absence of light. In the CMYK model, it is the opposite: white is the natural color of the paper or other background, and black results from a full ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circular Thresholding
Circular thresholding is an algorithm for Thresholding (image processing), automatic image threshold selection in image processing. Most threshold selection algorithms assume that the values (e.g. intensities) lie on a linear scale. However, some quantities such as hue and Orientation (geometry), orientation are a circular quantity, and therefore require circular thresholding algorithms. The example shows that the standard linear version of Otsu's method when applied to the hue channel of an image of blood cells fails to correctly segment the large white blood cells (leukocytes). In contrast the white blood cells are correctly segmented by the circular version of Otsu's method. Methods There are a relatively small number of circular image threshold selection algorithms. The following examples are all based on Otsu's method for linear histograms: * #Tseng1995, (Tseng, Li and Tung 1995) smooth the circular histogram, and apply Otsu's method. The histogram is cyclically rotated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HSL And HSV
HSL and HSV are the two most common cylindrical coordinate system, cylindrical-coordinate representations of points in an RGB color model. The two representations rearrange the geometry of RGB in an attempt to be more intuitive and color vision, perceptually relevant than the cartesian coordinate system, cartesian (cube) representation. Developed in the 1970s for computer graphics applications, HSL and HSV are used today in color tool, color pickers, in image editing software, and less commonly in image analysis and computer vision. HSL stands for ''hue'', ''saturation'', and ''lightness'', and is often also called HLS. HSV stands for ''hue'', ''saturation'', and ''value'', and is also often called HSB (''B'' for ''brightness''). A third model, common in computer vision applications, is HSI, for ''hue'', ''saturation'', and ''intensity''. However, while typically consistent, these definitions are not standardized, and any of these abbreviations might be used for any of these thre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binary And
In computer programming, a bitwise operation operates on a bit string, a bit array or a binary numeral (considered as a bit string) at the level of its individual bits. It is a fast and simple action, basic to the higher-level arithmetic operations and directly supported by the processor. Most bitwise operations are presented as two-operand instructions where the result replaces one of the input operands. On simple low-cost processors, typically, bitwise operations are substantially faster than division, several times faster than multiplication, and sometimes significantly faster than addition. While modern processors usually perform addition and multiplication just as fast as bitwise operations due to their longer instruction pipelines and other architectural design choices, bitwise operations do commonly use less power because of the reduced use of resources. Bitwise operators In the explanations below, any indication of a bit's position is counted from the right (least signif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RGB Color Model
The RGB color model is an additive color, additive color model in which the red, green, and blue primary colors of light are added together in various ways to reproduce a broad array of colors. The name of the model comes from the initials of the three additive primary colors, red, green, and blue. The main purpose of the RGB color model is for the sensing, representation, and display of images in electronic systems, such as televisions and computers, though it has also been used in conventional photography and Light-emitting diode#RGB systems, colored lighting. Before the electronic age, the RGB color model already had a solid theory behind it, based in Trichromacy, human perception of colors. RGB is a ''device-dependent'' color model: different devices detect or reproduce a given RGB value differently, since the color elements (such as phosphors or dyes) and their response to the individual red, green, and blue levels vary from manufacturer to manufacturer, or even in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ImageJ
ImageJ is a Java (programming language), Java-based image processing program developed at the National Institutes of Health and the Laboratory for Optical and Computational Instrumentation (LOCI, University of Wisconsin). Its first version, ImageJ 1.x, is developed in the public domain, while ImageJ2 and the related projects SciJava, ImgLib2, and SCIFIO are licensed with a permissive BSD licenses, BSD-2 license. ImageJ was designed with an open architecture that provides extensibility via Java plug-in (computing), plugins and recordable macros. Custom acquisition, analysis and processing plugins can be developed using ImageJ's built-in editor and a Java compiler. User-written plugins make it possible to solve many image processing and analysis problems, from three-dimensional live-cell imaging to radiology, radiological image processing, multiple imaging system data comparisons to automated hematology systems. ImageJ's plugin architecture and built-in development environment has mad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entropy (information Theory)
In information theory, the entropy of a random variable quantifies the average level of uncertainty or information associated with the variable's potential states or possible outcomes. This measures the expected amount of information needed to describe the state of the variable, considering the distribution of probabilities across all potential states. Given a discrete random variable X, which may be any member x within the set \mathcal and is distributed according to p\colon \mathcal\to[0, 1], the entropy is \Eta(X) := -\sum_ p(x) \log p(x), where \Sigma denotes the sum over the variable's possible values. The choice of base for \log, the logarithm, varies for different applications. Base 2 gives the unit of bits (or "shannon (unit), shannons"), while base Euler's number, ''e'' gives "natural units" nat (unit), nat, and base 10 gives units of "dits", "bans", or "Hartley (unit), hartleys". An equivalent definition of entropy is the expected value of the self-information of a v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pavlovsk Railing Of Bridge Yellow Palace Winter Bw Threshold
Pavlovsk may refer to: Russia *Pavlovsk, Saint Petersburg, a town in a suburban Pushkinskiy District of Saint Petersburg, Russia *Pavlovsk Urban Settlement, an administrative division and a municipal formation which the town of Pavlovsk in Pavlovsky District of Voronezh Oblast, Russia is incorporated as *Pavlovsk, Russia, several inhabited localities in Russia Ukraine *Pavlovsk, former name of the city of Mariupol, Ukraine See also * Novopavlovsk * Pavel * Pavlov (other) * Pavlovka (other) * Pavlovo * Pavlovsky (other) Pavlovsky (masculine), Pavlovskaya (feminine), or Pavlovskoye (neuter) may refer to: * Pavlovsky (surname) Places * Pavlovsky District, several districts in Russia * Pavlovskoye Urban Settlement, several municipal urban settlements in Russia * P ... * Petropavlovsk (other) {{Disambiguation, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histogram
A histogram is a visual representation of the frequency distribution, distribution of quantitative data. To construct a histogram, the first step is to Data binning, "bin" (or "bucket") the range of values— divide the entire range of values into a series of intervals—and then count how many values fall into each interval. The bins are usually specified as consecutive, non-overlapping interval (mathematics), intervals of a variable. The bins (intervals) are adjacent and are typically (but not required to be) of equal size. Histograms give a rough sense of the density of the underlying distribution of the data, and often for density estimation: estimating the probability density function of the underlying variable. The total area of a histogram used for probability density is always normalized to 1. If the length of the intervals on the ''x''-axis are all 1, then a histogram is identical to a relative frequency plot. Histograms are sometimes confused with bar charts. In a his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otsu's Method
In computer vision and image processing, Otsu's method, named after , is used to perform automatic image thresholding (image processing), thresholding. In the simplest form, the algorithm returns a single intensity threshold that separate pixels into two classes foreground and background. This threshold is determined by minimizing intra-class intensity variance, or equivalently, by maximizing inter-class variance. Otsu's method is a one-dimensional discrete analogue of Linear discriminant analysis#Fisher's linear discriminant, Fisher's discriminant analysis, is related to Jenks optimization method, and is equivalent to a globally optimal K-means clustering, ''k''-means performed on the intensity histogram. The extension to multi-level thresholding was described in the original paper, and computationally efficient implementations have since been proposed. Otsu's method The algorithm exhaustively searches for the threshold that minimizes the intra-class variance, defined as a weigh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |