|
Thomas Of Cantimpré
Thomas of Cantimpré (Latin: Thomas Cantimpratensis or Thomas Cantipratensis) ( Sint-Pieters-Leeuw, 1201 – Louvain, 15 May 1272) was a Flemish Catholic medieval writer, preacher, theologian and a friar belonging to the Dominican Order. He is best known for his encyclopedic woek on nature ''De natura rerum'', for the moral text ''Bonum universale de Apibus'' and for his hagiographical writings. Biography Thomas of Cantimpré was born of noble parentage in 1201, at Sint-Pieters-Leeuw (a small town near Brussels), in the Duchy of Brabant. In 1206 his father (returning from Palestine, where he had fought alongside Richard I of England) sent Thomas to Liège, where he began to tackle the difficulties of the trivium and quadrivium, studying from age 5 to age 11; in Liège he also had the chance to meet Jacques de Vitry, who was preaching there. In 1217, at the age of 16, he entered the Canons Regular of St. Augustine at their the Abbey of Cantimpré, near Cambrai, where was later ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Of Cantimpré De Natura Rerum Ms 411 Fol 3r
Thomas may refer to: People * List of people with given name Thomas * Thomas (name) * Thomas (surname) * Saint Thomas (other) * Thomas Aquinas (1225–1274) Italian Dominican friar, philosopher, and Doctor of the Church * Thomas the Apostle * Thomas (bishop of the East Angles) (fl. 640s–650s), medieval Bishop of the East Angles * Thomas (Archdeacon of Barnstaple) (fl. 1203), Archdeacon of Barnstaple * Thomas, Count of Perche (1195–1217), Count of Perche * Thomas (bishop of Finland) (1248), first known Bishop of Finland * Thomas, Earl of Mar (1330–1377), 14th-century Earl, Aberdeen, Scotland Geography Places in the United States * Thomas, Illinois * Thomas, Indiana * Thomas, Oklahoma * Thomas, Oregon * Thomas, South Dakota * Thomas, Virginia * Thomas, Washington * Thomas, West Virginia * Thomas County (other) * Thomas Township (other) Elsewhere * Thomas Glacier (Greenland) Arts, entertainment, and media * ''Thomas'' (Burton novel) 1969 novel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
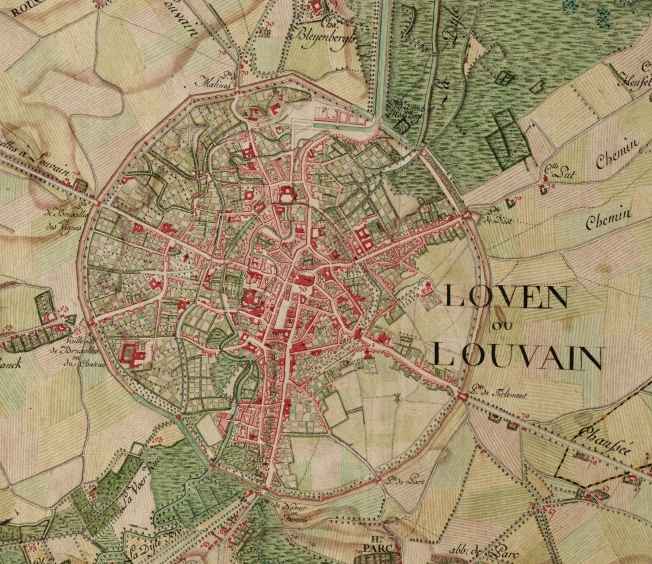
Leuven
Leuven (, ) or Louvain (, , ; german: link=no, Löwen ) is the capital and largest city of the province of Flemish Brabant in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is located about east of Brussels. The municipality itself comprises the historic city and the former neighbouring municipalities of Heverlee, Kessel-Lo, a part of Korbeek-Lo, Wilsele and Wijgmaal. It is the eighth largest city in Belgium, with more than 100,244 inhabitants. KU Leuven, Belgium's largest university, has its flagship campus in Leuven, which has been a university city since 1425. This makes it the oldest university city in the Low Countries. The city is home of the headquarters of Anheuser-Busch InBev, the world's largest beer brewer and sixth-largest fast-moving consumer goods company. History Middle Ages The earliest mention of Leuven (''Loven'') dates from 891, when a Viking army was defeated by the Frankish king Arnulf of Carinthia (see: Battle of Leuven). According to a legend, the city's red ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Of Christ
Blood of Christ, also known as the Most Precious Blood of Our Lord Jesus Christ, in Christian theology refers to (a) the physical blood actually shed by Jesus Christ primarily on the Cross, and the salvation which Christianity teaches was accomplished thereby; or (b) the sacramental blood (wine) present in the Eucharist or Lord's Supper, which some Christian denominations believe to be the same blood of Christ shed on the Cross. The Roman and Eastern Catholic Churches, Eastern Orthodox Church, the Oriental Orthodox churches, the Assyrian and Ancient Churches of the East, and Lutherans, together with High church Anglicans, know this as the real presence of Christ in the Eucharist. The Catholic Church uses the term "transubstantiation" to describe the change of the bread and wine into the body and blood of Christ. The Eastern Orthodox Churches used the same term to describe the change, as in the decrees of the 1672 Synod of Jerusalem, and the ''Catechism of St. Philaret (Drozdo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Accusation
Blood libel or ritual murder libel (also blood accusation) is an antisemitic canardTurvey, Brent E. ''Criminal Profiling: An Introduction to Behavioral Evidence Analysis'', Academic Press, 2008, p. 3. "Blood libel: An accusation of ritual murder made against one or more persons, typically of the Jewish faith".Chanes, Jerome A. ''Antisemitism: A Reference Handbook'', ABC-CLIO, 2004, pp. 34–45. "Among the most serious of these nti-Jewishmanifestations, which reverberate to the present day, were those of the libels: the leveling of charges against Jews, particularly the blood libel and the libel of desecrating the host."Goldish, Matt. ''Jewish Questions: Responsa on Sephardic Life in the Early Modern Period'', Princeton University Press, 2008, p. 8. "In the period from the twelfth to the twentieth centuries, Jews were regularly charged with blood libel or ritual murder that Jews kidnapped and murdered non-Jews as part of a Jewish religious ritual." which falsely accuses Jews of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formicarius
The ''Formicarius'', written 1436–1438 by Johannes Nider during the Council of Florence and first printed in 1475, is the second book ever printed to discuss witchcraft (the first book being Alphonso de Spina's ''Fortalitium Fidei''). Nider dealt specifically with witchcraft in the fifth section of the book. Unlike his successors, he did not emphasize the idea of the Witches' Sabbath and was skeptical of the claim that witches could fly by night. With over 25 manuscript copies from fifteenth and early sixteenth century editions from the 1470s to 1692, the ''Formicarius'' is an important work for the study of the origins of the witch trials in Early Modern Europe, as it sheds light on their earliest phase during the first half of the 15th century. Nider was one of the first to transform the idea of sorcery to its more modern perception of witchcraft. Prior to the fifteenth century, magic was thought to be performed by educated males who performed intricate rituals. In Nider's ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
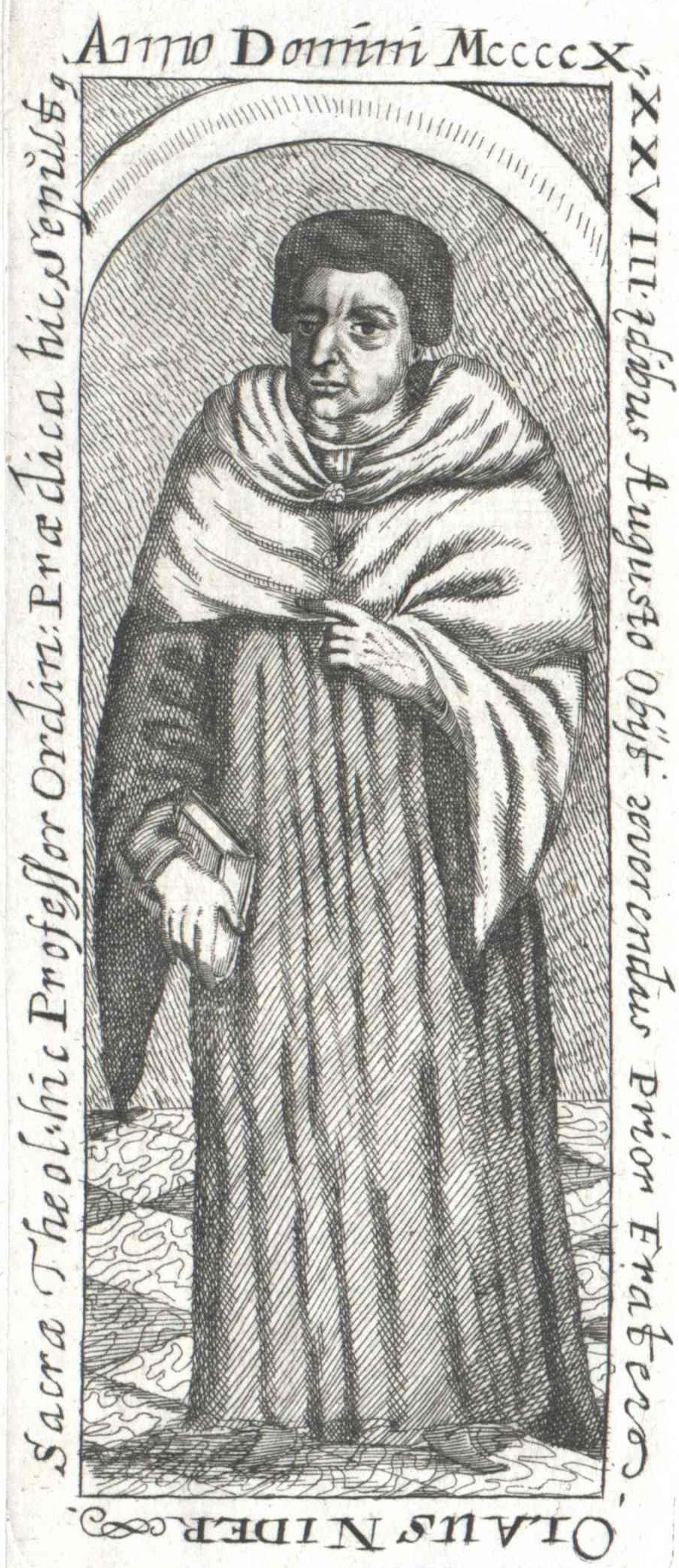
Johannes Nider
Johannes Nider (c. 1380 – 13 August 1438) was a German theologian. __NOTOC__ Life Nider was born in Swabia. He entered the Order of Preachers at Colmar and after profession was sent to Vienna for his philosophical studies, which he finished at Cologne, where he was ordained. He gained a wide reputation in Germany as a preacher and was active at the Council of Constance. After making a study of the convents of his order of strict observance in Italy he returned to the University of Vienna, where in 1425 he began teaching as Master of Theology. Elected prior of the Dominican convent at Nuremberg in 1427, he successively served as ''socius'' to his master general and vicar of the reformed convents of the German province. In this capacity he maintained his early reputation of reformer and in 1431 he was chosen prior of the convent of strict observance at Basle. He became identified with the Council of Basle as theologian and legate, making several embassies to the Hussites at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Douai
Douai (, , ,; pcd, Doï; nl, Dowaai; formerly spelled Douay or Doway in English) is a city in the Nord département in northern France. It is a sub-prefecture of the department. Located on the river Scarpe some from Lille and from Arras, Douai is home to one of the region's most impressive belfries. History Its site probably corresponds to that of a 4th-century Roman fortress known as Duacum. From the 10th century, the town was a romance fiefdom of the counts of Flanders. The town became a flourishing textile market centre during the Middle Ages, historically known as Douay or Doway in English. In 1384, the county of Flanders passed into the domains of the Dukes of Burgundy and thence in 1477 into Habsburg possessions. In 1667, Douai was taken by the troops of Louis XIV of France, and by the 1668 Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle, the town was ceded to France. During successive sieges from 1710 to 1712, Douai was almost completely destroyed by the British Army. By 1713, the town ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. Since the 17th century, Paris has been one of the world's major centres of finance, diplomacy, commerce, fashion, gastronomy, and science. For its leading role in the arts and sciences, as well as its very early system of street lighting, in the 19th century it became known as "the City of Light". Like London, prior to the Second World War, it was also sometimes called the capital of the world. The City of Paris is the centre of the Île-de-France region, or Paris Region, with an estimated population of 12,262,544 in 2019, or about 19% of the population of France, making the region France's primate city. The Paris Region had a GDP of €739 billion ($743 billion) in 2019, which is the highest in Europe. According to the Economist Intelli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deventer
Deventer (; Sallands: ) is a city and municipality in the Salland historical region of the province of Overijssel, Netherlands. In 2020, Deventer had a population of 100,913. The city is largely situated on the east bank of the river IJssel, but it also has a small part of its territory on the west bank. In 2005 the municipality of Bathmen (with a population of about 5,000 people) was merged with Deventer as part of a national effort to reduce bureaucracy in the country. Deventer is one of the oldest cities in the Netherlands. The place is already mentioned in 9th-century sources of the Diocese of Utrecht. In a charter from 877 AD mentions seven hooves in ''Daventre portu'' (the Deventer harbor). In 952 AD, Deventer is mentioned as a city in a gift certificate from King Otto I. After the place had acquired more and more rights and privileges over time, it received the municipal lands from Emperor Henry V in 1123. This is considered by historians to be the moment of Deventer o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exemplum
An exemplum (Latin for "example", pl. exempla, ''exempli gratia'' = "for example", abbr.: ''e.g.'') is a moral anecdote, brief or extended, real or fictitious, used to illustrate a point. The word is also used to express an action performed by another and used as an example or model. Exemplary literature This genre sprang from the above, in classical, medieval and Renaissance literature, consisting of lives of famous figures, and using these (by emphasizing good or bad character traits) to make a moral point. Collections of Exempla helped medieval preachers to adorn their sermons, to emphasize moral conclusions or illustrate a point of doctrine. The subject matter could be taken from fables, folktales, legends, real history, or natural history. Jacques de Vitry's book of exempla, c. 1200, Nicholas Bozon's ''Les contes moralisés'' (after 1320), and Odo of Cheriton's ''Parabolae'' (after 1225) were famous medieval collections aimed particularly at preachers. Geoffrey Chaucer's '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exemplum
An exemplum (Latin for "example", pl. exempla, ''exempli gratia'' = "for example", abbr.: ''e.g.'') is a moral anecdote, brief or extended, real or fictitious, used to illustrate a point. The word is also used to express an action performed by another and used as an example or model. Exemplary literature This genre sprang from the above, in classical, medieval and Renaissance literature, consisting of lives of famous figures, and using these (by emphasizing good or bad character traits) to make a moral point. Collections of Exempla helped medieval preachers to adorn their sermons, to emphasize moral conclusions or illustrate a point of doctrine. The subject matter could be taken from fables, folktales, legends, real history, or natural history. Jacques de Vitry's book of exempla, c. 1200, Nicholas Bozon's ''Les contes moralisés'' (after 1320), and Odo of Cheriton's ''Parabolae'' (after 1225) were famous medieval collections aimed particularly at preachers. Geoffrey Chaucer's '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jordan Of Saxony
Jordan of Saxony, (referred to in Latin as Jordanis, also known as de Alamania; c. 1190 – 1237), was one of the first leaders of the Dominican Order. His feast day is February 13. Life Jordan belonged to the noble German family of the Counts of Eberstein. He was born in the Castle of Borrenstrick, in the diocese of Paderborn. He began his studies in his native land, and was sent to complete them at the University of Paris."Blessed Jordan of Saxony, OP", The Dominicans, Province of the Most Holy Name of Jesus, February 13, 2012 While a student he met Dominic de Guzman, the founder of the Order of Preachers, and was inspired by the pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |