|
Thiocarbonyl Compounds
In organic chemistry, thioketones (; also known as thiones or thiocarbonyls) are organosulfur compounds related to conventional ketones in which the oxygen has been replaced by a sulfur. Instead of a structure of , thioketones have the structure , which is reflected by the prefix "thio-" in the name of the functional group. Unhindered alkylthioketones typically tend to form polymers or rings. Structure and bonding The C=S bond length of thiobenzophenone is 1.63 Å, which is comparable to 1.64 Å, the C=S bond length of thioformaldehyde, measured in the gas phase. Due to steric interactions, the phenyl groups are not coplanar and the dihedral angle SC-CC is 36°. Unhindered dialkylthiones polymerize or oligomerize but thio camphor is well characterized red solid. Consistent with the double bond rule, most alkyl thioketones are unstable with respect to dimerization.Organosulfur Chemistry I: Topics in Current Chemistry, 1999, Volume 204/1999, 127-181, The energy difference betwe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thioketone Structural Formulae V
In organic chemistry, thioketones (; also known as thiones or thiocarbonyls) are organosulfur compounds related to conventional ketones in which the oxygen has been replaced by a sulfur. Instead of a structure of , thioketones have the structure , which is reflected by the prefix "thio-" in the name of the functional group. Unhindered alkylthioketones typically tend to form polymers or rings. Structure and bonding The C=S bond length of thiobenzophenone is 1.63 Å, which is comparable to 1.64 Å, the C=S bond length of thioformaldehyde, measured in the gas phase. Due to steric interactions, the phenyl groups are not coplanar and the dihedral angle SC-CC is 36°. Unhindered dialkylthiones polymerize or oligomerize but thio camphor is well characterized red solid. Consistent with the double bond rule, most alkyl thioketones are unstable with respect to dimerization.Organosulfur Chemistry I: Topics in Current Chemistry, 1999, Volume 204/1999, 127-181, The energy difference betwe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bis(trimethylsilyl)sulfide
Bis(trimethylsilyl) sulfide is the chemical compound with the formula ((CH3)3Si)2S. Often abbreviated ( tms)2S, this colourless, vile-smelling liquid is a useful aprotic source of "S2−" in chemical synthesis. Synthesis The reagent is prepared by treating trimethylsilyl chloride with anhydrous sodium sulfide: :2 (CH3)3SiCl + Na2S → ((CH3)3Si)2S + 2 NaCl ((CH3)3Si)2S must be protected from air because it hydrolyzes readily: :((CH3)3Si)2S + H2O → ((CH3)3Si)2O + H2S Use in synthesis Bis(trimethylsilyl)sulfide is a reagent for the conversion of metal oxides and chlorides into the corresponding sulfides. This transformation exploits the affinity of silicon(IV) for oxygen and halides. An idealized reaction is: :((CH3)3Si)2S + MO → ((CH3)3Si)2O + MS In a similar way, it has been used in the conversion of aldehyde In organic chemistry, an aldehyde () is an organic compound containing a functional group with the structure . The functional group itself (w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thioacetone
Thioacetone is an organosulfur compound belonging to the -thione group called thioketones, with a chemical formula (CH3)2CS. It is an unstable orange or brown substance that can be isolated only at low temperatures. Above , thioacetone readily converts to a polymer and a trimer, trithioacetone. It has an extremely potent, unpleasant odor, and is considered one of the worst-smelling chemicals known. Thioacetone was first obtained in 1889 by Baumann and Fromm, as a minor impurity in their synthesis of trithioacetone.William H. Sharkey (1979): "Polymerization through the carbon-sulfur double bond". ''Polymerization'', series ''Advances in Polymer Science'', volume 17, pages 73-103. Preparation Thioacetone is usually obtained by cracking the cyclic trimer trithioacetone, CH3)2CSsub>3. The trimer is prepared by pyrolysis of allyl isopropyl sulfide or by treating acetone with hydrogen sulfide in the presence of a Lewis acid. The trimer cracks at to give the thione. : Polym ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thioketene
In organic chemistry, thioketenes are organosulfur compounds analogous to ketenes with the general formula , where R is alkyl or aryl. Thioketene (ethenthione) is also the name of the compound , which is the simplest thioketene. Thioketenes are reactive, tending to polymerize. Some thioketenes are produced as transient species upon pyrolysis of 1,2,3-thiadiazoles. Bis(trifluoromethyl)thioketene () is a rare example of a stable thioketene. Another stable thioketene is carbon subsulfide Carbon subsulfide is an organic, sulfur-containing chemical compound with the formula and structure . This deep red liquid is immiscible with water but soluble in organic solvents. It readily polymerizes at room temperature to form a hard bla ... (). It has been suggested that thioketene could be involved in cell damage processes.{{cite journal , last1 = Dekant , first1 = Wolfgang , last2 = Urban , first2 = Gudrun , last3 = Goersmann , first3 =Claus, last4 = Anders , first4 = M.W. , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thial
In organic chemistry, a thial or thioaldehyde is a functional group which is similar to an aldehyde, , in which a sulfur (S) atom replaces the oxygen (O) atom of the aldehyde (R represents an alkyl or aryl group). Thioaldehydes are even more reactive than thioketones. Unhindered thioaldehydes are generally too reactive to be isolated — for example, thioformaldehyde, , condenses to the cyclic trimer 1,3,5-trithiane. Thioacrolein, , formed by decomposition of allicin from garlic, undergoes a self Diels-Alder reaction giving isomeric vinyldithiins. While thioformaldehyde is highly reactive, it is found in interstellar space along with its mono- and di-deuterated isotopologues. With sufficient steric bulk, however, stable thioaldehydes can be isolated. In early work, the existence of thioaldehydes was inferred by trapping processes. For instance the reaction of with benzaldehyde was proposed to form thiobenzaldehyde, which forms a cycloadduct with the dithiophosphine ylides to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dithiirane
In organic chemistry, episulfides are a class of organic compounds that contain a saturated, heterocyclic ring consisting of two carbon atoms and one sulfur atom. It is the sulfur analogue of an epoxide or aziridine. They are also known as thiiranes, olefin sulfides, thioalkylene oxides, and thiacyclopropanes. Episulfides are less common and generally less stable than epoxides. The most common derivative is ethylene sulfide (). Structure According to electron diffraction, the and distances in ethylene sulfide are respectively 1.473 and 1.811 Å. The and angles are respectively 66.0 and 48.0°. Preparation History A number of chemists in the early 1900s, including Staudinger and Pfenninger (1916), as well as Delepine (1920) studied episulfides.Sander, M. Thiiranes. Chem. Rev. 1966, 66(3), 297-339. I 1934 Dachlauer and Jackel devised a general synthesis of episulfides from epoxides using alkali thiocyanates and thiourea. Contemporary methods Following the lead of Dac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1,3-dipole
In organic chemistry, a 1,3-dipolar compound or 1,3-dipole is a dipolar compound with delocalized electrons and a separation of charge over three atoms. They are reactants in 1,3-dipolar cycloadditions. The dipole has at least one resonance structure with positive and negative charges having a 1,3 relationship which can generally be denoted as , where a may be a carbon, oxygen or nitrogen, b may be nitrogen or oxygen, and c may be a carbon, oxygen or nitrogen. Known 1,3-dipoles are: * Azides () * Ozone () * Nitro compounds () * Diazo compounds () * Some oxides ** Azoxide compounds (RN(O)NR) ** Carbonyl oxides ( Criegee zwitterions)Li, Jie Jack''Criegee mechanism of ozonolysis''Book: Name Reactions. 2006, 173-174, ** Nitrile oxides () ** Nitrous oxide () ** Nitrones () * Some imines: ** Azomethine imine ** Nitrilimines (, analogous to nitrile oxide) ** Carbonyl imines * Some ylides ** Azomethine ylide Azomethine ylides are nitrogen-based 1,3-dipoles, consisting of an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
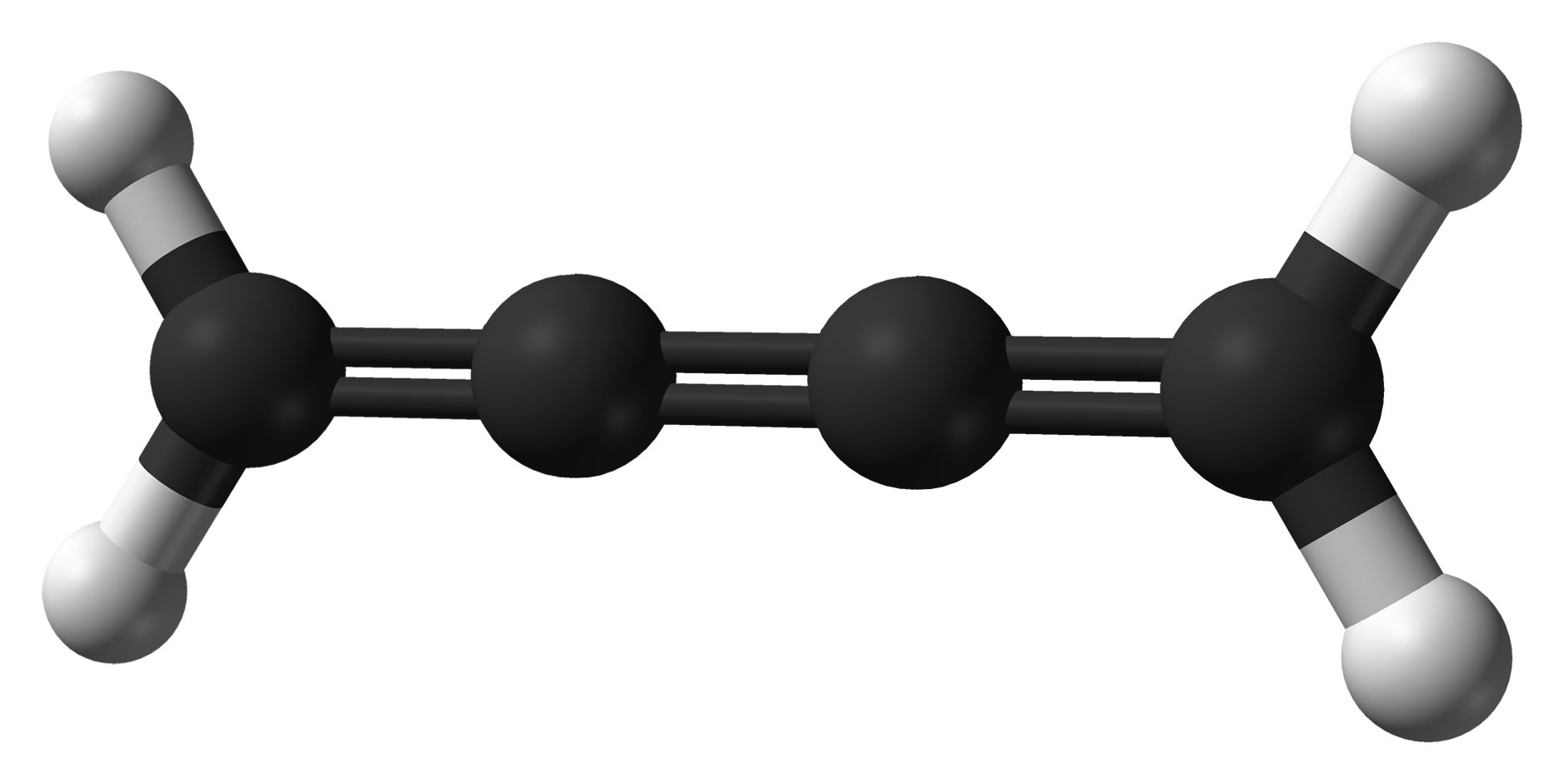
Cumulene
In organic chemistry, a cumulene is a compound having three or more ''cumulative'' (consecutive) double bonds. They are analogous to allenes, only having a more extensive chain. The simplest molecule in this class is butatriene (), which is also called simply ''cumulene''. Unlike most alkanes and alkenes, cumulenes tend to be rigid, comparable to polyynes. Cumulene carbenes for ''n'' from 3 to 6 have been observed in interstellar molecular clouds and in laboratory experiments by using microwave and infrared spectroscopy. (The more stable cumulenes are difficult to detect optically because they lack an electric dipole moment.) Cumulenes containing heteroatoms are called heterocumulenes; an example is carbon suboxide. Synthesis The first reported synthesis of a butatriene is that of tetraphenylbutatriene in 1921. The most common synthetic method for butatriene synthesis is based on reductive coupling of a geminal dihalo vinylidene. Tetraphenylbutatriene was reported synt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzophenone
Benzophenone is the organic compound with the formula (C6H5)2CO, generally abbreviated Ph2CO. It is a white solid that is soluble in organic solvents. Benzophenone is a widely used building block in organic chemistry, being the parent diarylketone. Uses Benzophenone can be used as a photo initiator in UV(Ultra-violet)-curing applications such as inks, imaging, and clear coatings in the printing industry. Benzophenone prevents ultraviolet ( UV) light from damaging scents and colors in products such as perfumes and soaps. Benzophenone can also be added to plastic packaging as a UV blocker to prevent photo-degradation of the packaging polymers or its contents. Its use allows manufacturers to package the product in clear glass or plastic (such as a PETE water bottle). Without it, opaque or dark packaging would be required. In biological applications, benzophenones have been used extensively as photophysical probes to identify and map peptide–protein interactions. Benzophenone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blue
Blue is one of the three primary colours in the RYB colour model (traditional colour theory), as well as in the RGB (additive) colour model. It lies between violet and cyan on the spectrum of visible light. The eye perceives blue when observing light with a dominant wavelength between approximately 450 and 495 nanometres. Most blues contain a slight mixture of other colours; azure contains some green, while ultramarine contains some violet. The clear daytime sky and the deep sea appear blue because of an optical effect known as Rayleigh scattering. An optical effect called Tyndall effect explains blue eyes. Distant objects appear more blue because of another optical effect called aerial perspective. Blue has been an important colour in art and decoration since ancient times. The semi-precious stone lapis lazuli was used in ancient Egypt for jewellery and ornament and later, in the Renaissance, to make the pigment ultramarine, the most expensive of all pigments. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.png)