|
Thia-crown Ether
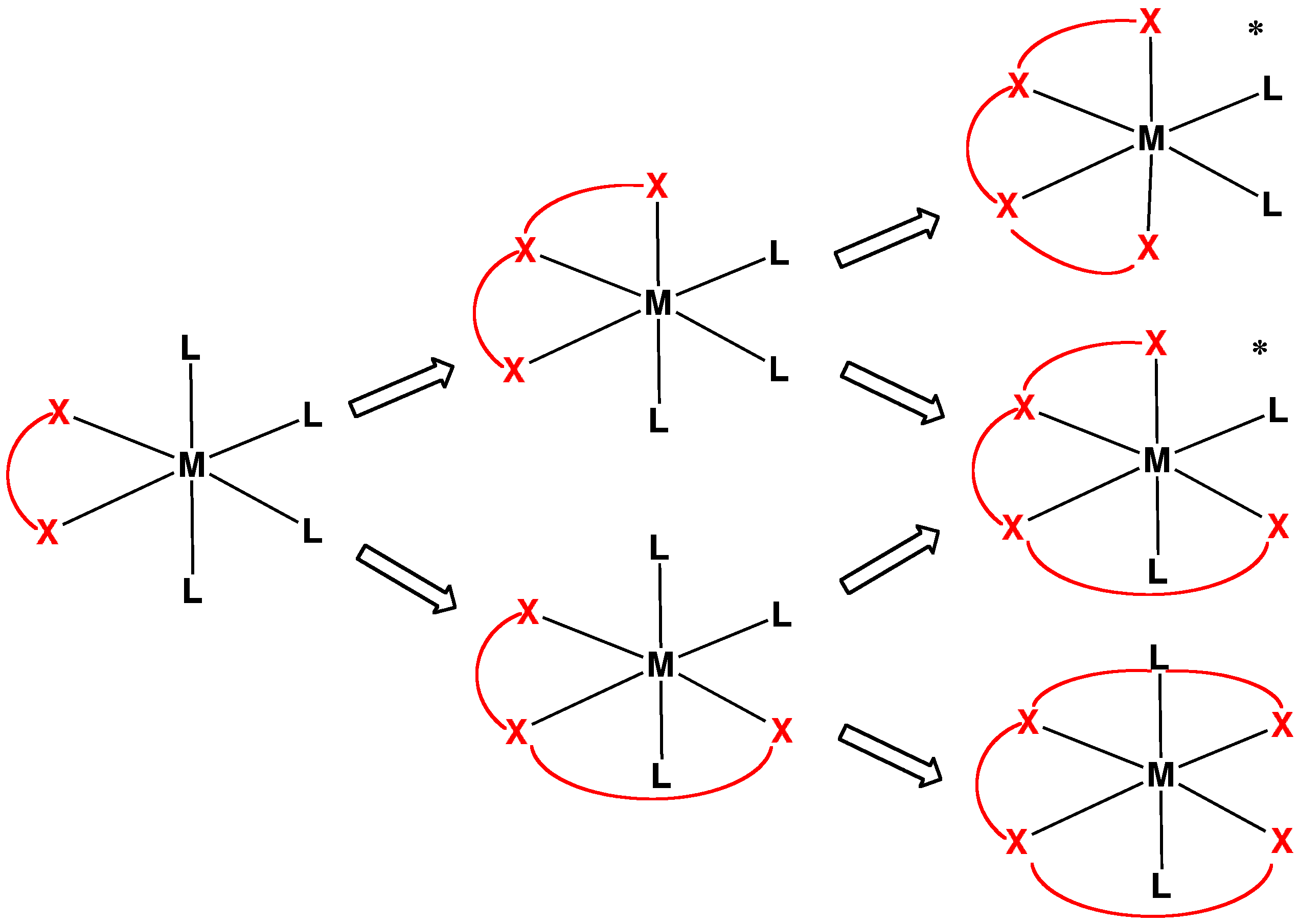
In organic chemistry, thia-crown ethers are organosulfur compounds which are the ''thia'' analogues of crown ethers (cyclic polyethers). That is, they have a sulfur atom (sulfide linkage, ) in place of each oxygen atom (ether linkage, ) around the ring. While the parent crown ethers have the formulae , the parent ''thia''-crown ethers have the formulae , where ''n'' = 3, 4, 5, 6. They have trivial names "''x''-ane-S''y''", where ''x'' and ''y'' are the number of atoms in the ring and the number of those atoms that are sulfur, respectively. Thia-crown ethers exhibit affinities for transition metals. 1,4,7-Trithiacyclononane (9-ane-S3) is a tridentate ligand and forms complexes with many metal ions, including those considered hard, such as copper(II) and iron(II). Tetradentate 14-ane-S4 and the hexadentate A hexadentate ligand in coordination chemistry A coordination complex consists of a central atom or ion, which is usually metallic and is called the ''coordination centre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1,4,7-Trithiacyclononane
1,4,7-Trithiacyclononane, also called 9-ane-S3, is the thia-crown ether with the formula (CH2CH2S)3. This cyclic thioether is most often encountered as a tridentate ligand in coordination chemistry, where it forms transition metal thioether complexes. 9-ane-S3 forms complexes with many metal ions, including those considered hard, such as copper(II) and iron(II). Most of its complexes have the formula (9-ane-S3)2sup>2+ and are octahedral. The point group of (9-ane-S3)2sup>2+ is S6. Synthesis This compound was first reported in 1977, and the current synthesis entails the assembly within the coordination sphere In coordination chemistry, the first coordination sphere refers to the array of molecules and ions (the ligands) directly attached to the central metal atom. The second coordination sphere consists of molecules and ions that attached in various ... of a metal ion followed by decomplexation: : References {{DEFAULTSORT:Trithiacyclononane, 1,4,7- Chelating agent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coordination Complex
A coordination complex consists of a central atom or ion, which is usually metallic and is called the ''coordination centre'', and a surrounding array of bound molecules or ions, that are in turn known as '' ligands'' or complexing agents. Many metal-containing compounds, especially those that include transition metals (elements like titanium that belong to the Periodic Table's d-block), are coordination complexes. Nomenclature and terminology Coordination complexes are so pervasive that their structures and reactions are described in many ways, sometimes confusingly. The atom within a ligand that is bonded to the central metal atom or ion is called the donor atom. In a typical complex, a metal ion is bonded to several donor atoms, which can be the same or different. A polydentate (multiple bonded) ligand is a molecule or ion that bonds to the central atom through several of the ligand's atoms; ligands with 2, 3, 4 or even 6 bonds to the central atom are common. These ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thioethers
In organic chemistry, an organic sulfide (British English sulphide) or thioether is an organosulfur functional group with the connectivity as shown on right. Like many other sulfur-containing compounds, volatile sulfides have foul odors. A sulfide is similar to an ether except that it contains a sulfur atom in place of the oxygen. The grouping of oxygen and sulfur in the periodic table suggests that the chemical properties of ethers and sulfides are somewhat similar, though the extent to which this is true in practice varies depending on the application. Nomenclature Sulfides are sometimes called thioethers, especially in the old literature. The two organic substituents are indicated by the prefixes. (CH3)2S is called dimethylsulfide. Some sulfides are named by modifying the common name for the corresponding ether. For example, C6H5SCH3 is methyl phenyl sulfide, but is more commonly called thioanisole, since its structure is related to that for anisole, C6H5OCH3. The modern sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfur Heterocycles
Sulfur (or sulphur in British English) is a chemical element with the symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with a chemical formula S8. Elemental sulfur is a bright yellow, crystalline solid at room temperature. Sulfur is the tenth most abundant element by mass in the universe and the fifth most on Earth. Though sometimes found in pure, native form, sulfur on Earth usually occurs as sulfide and sulfate minerals. Being abundant in native form, sulfur was known in ancient times, being mentioned for its uses in ancient India, ancient Greece, China, and ancient Egypt. Historically and in literature sulfur is also called brimstone, which means "burning stone". Today, almost all elemental sulfur is produced as a byproduct of removing sulfur-containing contaminants from natural gas and petroleum.. Downloahere The greatest commercial use of the element is the production ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ag(18-ane-S6) Dication
A&G, AG, Ag or ag may refer to Businesses and organizations * A&G Railroad (former reporting mark AG) * Action Group (Nigeria), a political party during the Nigerian First Republic * Aktiengesellschaft, a German type of corporation * Assemblies of God, the world's largest Pentecostal organization * Associated Group, a Pakistani company * Astronomische Gesellschaft, a German astronomical society * IATA code for Aruba Airlines Entertainment * '' American Gladiators'' (1989–1996 TV series) * ''American Gladiators'' (2008 TV series) Government and military * Adjutant general, the Army branch responsible for personnel * Administrator-General of South West Africa, the head of government in Namibia prior to independence in 1990 * Aerographer's mate, a rating or specialty in the US Navy that deals with weather and oceanography * American Holland-class submarine (''Amerikansky Golland''), a class of Imperial Russian submarines * Army green, the color of the US Army service un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hexadentate Ligand
A hexadentate ligand in coordination chemistry is a ligand that combines with a central metal atom with six bonds. One example of a hexadentate ligand that can form complexes with soft metal ions is TPEN. A commercially important hexadentate ligand is EDTA. The denticity In coordination chemistry, denticity () refers to the number of donor groups in a given ligand that bind to the central metal atom in a coordination complex. In many cases, only one atom in the ligand binds to the metal, so the denticity equals ... of hexadentate ligands is often denoted with the prefix κ6. Topology The way the donor atoms are joined together in the molecule is its topology. Some topologies are simple, such as the linear or ring shapes. The molecule can also be branched, either at a donor atom, or at a non-donor atom. Example shapes are the tripod, and amplector, with a bifurcation at each end. Rigid molecules can be used to force unusual coordination such as trigonal prism. F. Lions ident ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetradentate Ligand
In chemistry, tetradentate ligands are ligands that bind four donor atoms to a central atom to form a coordination complex. This number of donor atoms that bind is called denticity and is a method of classifying ligands. Tetradentate ligands are common in nature in the form of chlorophyll, which has a core ligand called chlorin, and heme, which has a core ligand called porphyrin. They are responsible for the colour observed in plants and humans. Phthalocyanine is an artificial macrocyclic tetradentate ligand that is used to make blue and green pigments. Shape Tetradentate ligands can be classified by the topology of the connections between donor atoms. Common forms are linear (also called sequential), ring or tripodal. A tetrapodal ligand that is also tetradentate has four legs with donor atoms and a bridgehead that is not a donor. Upon binding with a central atom, there are several arrangements possible (known as geometric isomers). Linear ligands A linear tetradentate lig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron
Iron () is a chemical element with Symbol (chemistry), symbol Fe (from la, Wikt:ferrum, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 element, group 8 of the periodic table. It is, Abundance of the chemical elements#Earth, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in front of oxygen (32.1% and 30.1%, respectively), forming much of Earth's outer core, outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common abundance of elements in Earth's crust, element in the Earth's crust. In its metallic state, iron is rare in the Earth's crust, limited mainly to deposition by meteorites. Iron ores, by contrast, are among the most abundant in the Earth's crust, although extracting usable metal from them requires kilns or Metallurgical furnace, furnaces capable of reaching or higher, about higher than that required to smelting, smelt copper. Humans started to master that process in Eurasia during the 2nd millennium BC, 2nd millennium BC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orange color. Copper is used as a conductor of heat and electricity, as a building material, and as a constituent of various metal alloys, such as sterling silver used in jewelry, cupronickel used to make marine hardware and coins, and constantan used in strain gauges and thermocouples for temperature measurement. Copper is one of the few metals that can occur in nature in a directly usable metallic form ( native metals). This led to very early human use in several regions, from circa 8000 BC. Thousands of years later, it was the first metal to be smelted from sulfide ores, circa 5000 BC; the first metal to be cast into a shape in a mold, c. 4000 BC; and the first metal to be purposely alloyed with another metal, tin, to create ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hard And Soft Metal
Hard may refer to: * Hardness, resistance of physical materials to deformation or fracture * Hard water, water with high mineral content Arts and entertainment * ''Hard'' (TV series), a French TV series * Hard (band), a Hungarian hard rock supergroup * Hard (music festival), in the U.S. * ''Hard'' (EP), Goodbye Mr Mackenzie, 1993 * ''Hard'' (Brainpower album), 2008 * ''Hard'' (Gang of Four album), 1983 * ''Hard'' (Jagged Edge album), 2003 * "Hard" (song), a 2009 song by Rihanna * "Hard", a song by Royce da 5'9" from the 2016 album ''Layers'' * "Hard", a song by Why Don't We from the 2018 album ''8 Letters'' * ''Hard'', a 2017 EP from the band The Neighbourhood *"Hard", a song by Sophie from the 2015 compilation album ''Product'' Places * Hard, Austria * Hard (Zürich), Switzerland Other uses * Hard (surname) * Nickname of Masaki Sumitani ( HardGay / HardoGay ) * Hard (nautical), a beach or slope convenient for hauling out vessels * Hard (video game player), Anthony Barkho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain carbon atoms.Clayden, J.; Greeves, N. and Warren, S. (2012) ''Organic Chemistry''. Oxford University Press. pp. 1–15. . Study of structure determines their structural formula. Study of properties includes physical and chemical properties, and evaluation of chemical reactivity to understand their behavior. The study of organic reactions includes the chemical synthesis of natural products, drugs, and polymers, and study of individual organic molecules in the laboratory and via theoretical ( in silico) study. The range of chemicals studied in organic chemistry includes hydrocarbons (compounds containing only carbon and hydrogen) as well as compounds based on carbon, but also containing other elements, especially oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, phosphorus (i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |