|
Theodorus (consul 505)
Theodorus ( 505–523) was an Italian politician during the reign of Theodoric the Great. He held the consulship with Sabinianus as his colleague in 505. Theodorus was son of Caecina Decius Maximus Basilius (consul in 480), and brother of Albinus (consul in 493), Avienus (consul in 501), and Inportunus (consul in 509). While helping his brother Inportunus organize the games to celebrate Inportunus' consulate, the two of them were accused by the Greens of attacking them and killing one of their members. A surviving letter of Theodoric commands both of them to provide answers to these allegations before the tribunal of the ''inlustrius'' Caelianus and Agapitus. John Moorhead identifies Theodorus as the recipient of a surviving letter from bishop Fulgentius of Ruspe, written in 520. While Fulgentius admits they do not know each other, he is writing Theodorus on account of a number of mutual friends, providing him a good deal of spiritual advice, and ends by asking Theodorus to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
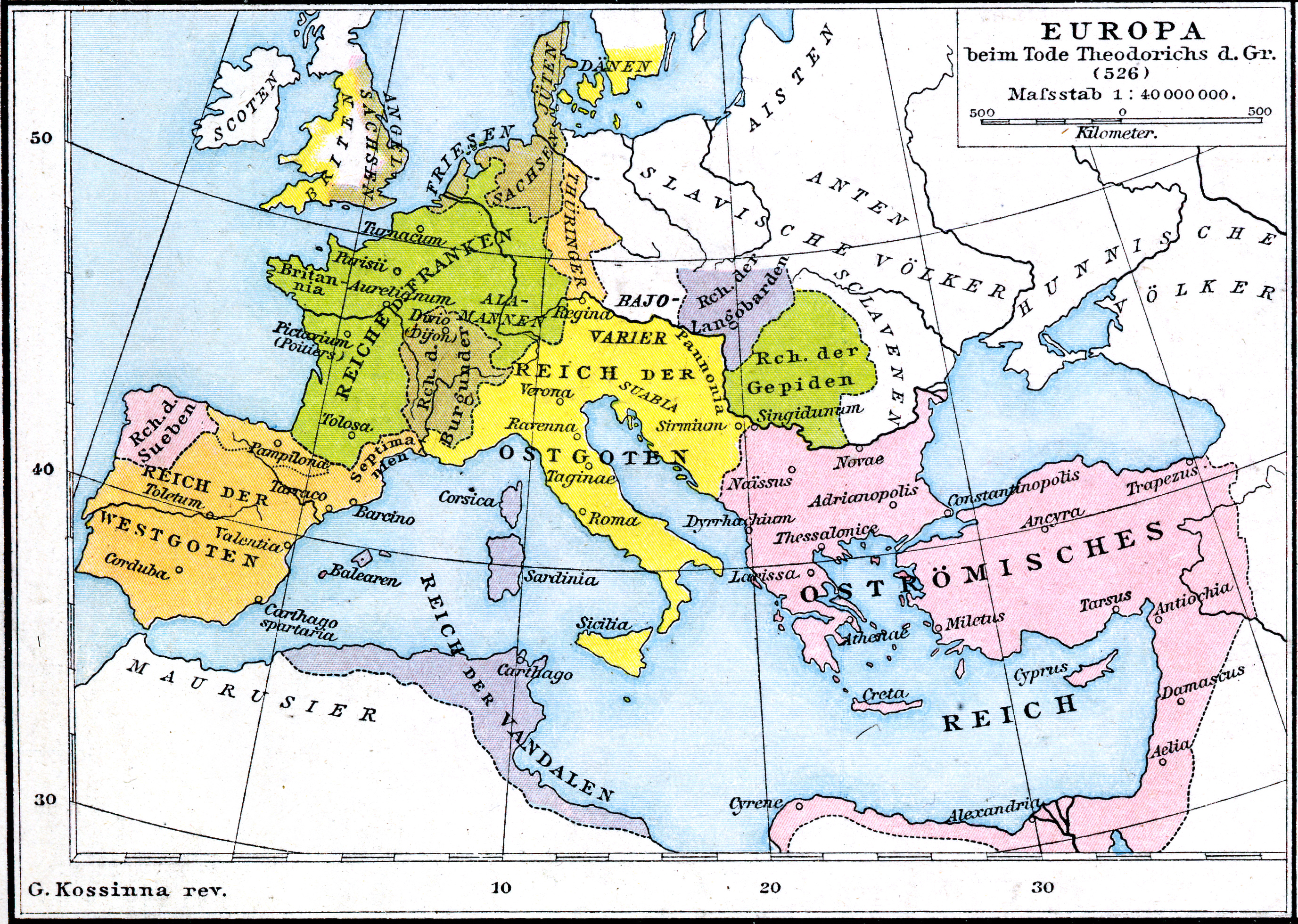
Theodoric The Great
Theodoric (or Theoderic) the Great (454 – 30 August 526), also called Theodoric the Amal ( got, , *Þiudareiks; Greek: , romanized: ; Latin: ), was king of the Ostrogoths (471–526), and ruler of the independent Ostrogothic Kingdom of Italy between 493 and 526, regent of the Visigoths (511–526), and a patrician of the Eastern Roman Empire. As ruler of the combined Gothic realms, Theodoric controlled an empire stretching from the Atlantic Ocean to the Adriatic Sea. Though Theodoric himself only used the title 'king' (''rex''), some scholars characterize him as a Western Roman Emperor in all but name, since he ruled large parts of the former Western Roman Empire, had received the former Western imperial regalia from Constantinople in 497, and was referred to by the title ''augustus'' by some of his subjects. As a young child of an Ostrogothic nobleman, Theodoric was taken as a hostage to Constantinople, where he spent his formative years and received an East Roman education (' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arianism
Arianism ( grc-x-koine, Ἀρειανισμός, ) is a Christological doctrine first attributed to Arius (), a Christian presbyter from Alexandria, Egypt. Arian theology holds that Jesus Christ is the Son of God, who was begotten by God the Father with the difference that the Son of God did not always exist but was begotten within time by God the Father, therefore Jesus was not coeternal with God the Father. Arius's trinitarian theology, later given an extreme form by Aetius and his disciple Eunomius and called anomoean ("dissimilar"), asserts a total dissimilarity between the Son and the Father. Arianism holds that the Son is distinct from the Father and therefore subordinate to him. The term ''Arian'' is derived from the name Arius; it was not what the followers of Arius's teachings called themselves, but rather a term used by outsiders. The nature of Arius's teachings and his supporters were opposed to the theological doctrines held by Homoousian Christians, regard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decii
The gens Decia was a plebeian family of high antiquity, which became illustrious in Roman history by the example of its members sacrificing themselves for the preservation of their country. The first of the family known to history was Marcus Decius, chosen as a representative of the plebeians during the secession of 495 BC.''Dictionary of Greek and Roman Biography and Mythology'', vol. I, pp. 946, 947 (" Decia Gens"). Origin ''Decius'' is the Latin form of the Oscan praenomen ''Dekis'', or its ''gentile'' equivalent, ''Dekiis''. The praenomen itself is the Oscan equivalent of the Latin name Decimus, and thus the nomen ''Decius'' is cognate with the Latin '' Decimius''. From this it may be supposed that the Decii were of Oscan extraction, perhaps arising from the Sabine portion of Rome's original inhabitants. In any event, they were already at Rome in the earliest years of the Republic, as one of them was chosen to represent the plebeians during the first secession in 495 BC. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
6th-century Roman Consuls
The 6th century is the period from 501 through 600 in line with the Julian calendar. In the West, the century marks the end of Classical Antiquity and the beginning of the Middle Ages. The collapse of the Western Roman Empire late in the previous century left Europe fractured into many small Germanic kingdoms competing fiercely for land and wealth. From the upheaval the Franks rose to prominence and carved out a sizeable domain covering much of modern France and Germany. Meanwhile, the surviving Eastern Roman Empire began to expand under Emperor Justinian, who recaptured North Africa from the Vandals and attempted fully to recover Italy as well, in the hope of reinstating Roman control over the lands once ruled by the Western Roman Empire. In its second Golden Age, the Sassanid Empire reached the peak of its power under Khosrau I in the 6th century.Roberts, J: "History of the World.". Penguin, 1994. The classical Gupta Empire of Northern India, largely overrun by the Huna, ended in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
6th-century Italo-Roman People
The 6th century is the period from 501 through 600 in line with the Julian calendar. In the West, the century marks the end of Classical Antiquity and the beginning of the Middle Ages. The collapse of the Western Roman Empire late in the previous century left Europe fractured into many small Germanic kingdoms competing fiercely for land and wealth. From the upheaval the Franks rose to prominence and carved out a sizeable domain covering much of modern France and Germany. Meanwhile, the surviving Eastern Roman Empire began to expand under Emperor Justinian, who recaptured North Africa from the Vandals and attempted fully to recover Italy as well, in the hope of reinstating Roman control over the lands once ruled by the Western Roman Empire. In its second Golden Age, the Sassanid Empire reached the peak of its power under Khosrau I in the 6th century.Roberts, J: "History of the World.". Penguin, 1994. The classical Gupta Empire of Northern India, largely overrun by the Huna (people), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flavius Areobindus Dagalaifus Areobindus
Flavius Areobindus Dagalaifus Areobindus ( grc-gre, Ἀρεόβινδος; 479–512) was an Eastern Roman general and politician. The scion of a distinguished line, he led troops in the Anastasian War, and served as consul in 506. During an urban riot in 512, Areobindus evaded a mob which wanted to force a change of government by proclaiming him emperor. He died soon after.Kazhdan (1991), p. 162 Origins and family Areobindus was born into an extremely distinguished family, which combined Roman and barbarian heritage: his father was Dagalaifus ( – after 461), consul in 461, who in turn was the son of Areobindus, consul in 434, both of Gothic origin. His mother was Godisthea (born ), daughter of Ardabur, general and consul in 447, and granddaughter of Aspar, the powerful Alan general and consul in 434.Martindale (1980), p. 143 Shortly after 478, Areobindus married Anicia Juliana (after 461 – 527/528), daughter of the Western Roman emperor Olybrius and his wife Placidia. Tog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ennodius Messala
Ennodius Messala was an Italian senator in Ostrogothic Italy. He was appointed consul for 506 with Areobindus Dagalaifus Areobindus as his colleague. His father was Anicius Probus Faustus, the leading supporter of Pope Symmachus in the Laurentian schism, and his brother was Rufius Magnus Faustus Avienus, one of the consuls for 502.Jeffrey Richards, ''The Popes and the Papacy in the Early Middle Ages'' (London:Routledge and Kegan Paul, 1979), p. 79 According to Magnus Felix Ennodius Magnus Felix Ennodius (473 or 47417 July 521 AD) was Bishop of Pavia in 514, and a Latin rhetorician and poet. He was one of four Gallo-Roman aristocrats of the fifth to sixth-century whose letters survive in quantity: the others are Sidonius Ap ..., Messala had a literary bent (''Ep''. 8.3, 9.12), and in 512 was engaged to a wealthy girl. (''Ep''. 9.26.35) References 6th-century Italo-Roman people 6th-century Roman consuls Imperial Roman consuls {{AncientRome-politician-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Roman Consuls
This is a list of consuls known to have held office, from the beginning of the Roman Republic to the latest use of the title in Imperial times, together with those magistrates of the Republic who were appointed in place of consuls, or who superseded consular authority for a limited period. Background Republican consuls From the establishment of the Republic to the time of Augustus, the consuls were the chief magistrates of the Roman state, and normally there were two of them, so that the executive power of the state was not vested in a single individual, as it had been under the kings. As other ancient societies dated historical events according to the reigns of their kings, it became customary at Rome to date events by the names of the consuls in office when the events occurred, rather than (for instance) by counting the number of years since the foundation of the city, although that method could also be used. If a consul died during his year of office, another was elected to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rufius Petronius Nicomachus Cethegus
Rufius Petronius Nicomachus Cethegus was a politician of Ostrogothic Italy and the Eastern Roman Empire. He was appointed consul for 504 AD, and held the post without a colleague. His father was Petronius Probinus, the consul for 489 and prominent supporter of Antipope Laurentius. John Moorhead has proposed identifying Cethegus with a Petronius of Rome, who with a Renatus of Ravenna, debated Severus of Antioch on the nature of Christ while Severus resided in Constantinople (508–511). If correct, this identification would put Cethegus in a circle of aristocratic intellectuals around Boethius. In December 546, when the King of the Ostrogoths, Totila, overcame the Byzantine defences and entered the city of Rome, Cethegus, who by his seniority had become president of the Senate ('caput senatus'), Decius (who had been consul in 529), and Anicius Faustus Albinus Basilius (who had been consul in 541) fled Rome with general Bessas. According to the '' Liber Pontificalis'', Cethegus a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agapitus (consul 517)
Flavius Agapitus (''floruit'' 502–523) was a Roman politician during the reign of Theodoric the Great. He held the consulship with Flavius Anastasius Paulus Probus Sabinianus Pompeius Anastasius as his colleague in 517. He started his public career late in life, having lived in seclusion in Liguria, where Ennodius made his acquaintance. Ennodius helped Agapitus obtain a high position at the court of Theodoric the Great in 502, and subsequently was appointed urban prefect of Rome. His Prefecture is mentioned in a legal document from the time of Theodoric. During his tenure as urban prefect, or shortly afterwards, he was made Patrician and settled many cases affecting the Senate. Ennodius comments that he had achieved a favorable reputation in the Senate, which possibly led to his appointment as consul. In 523, Agapitus was part of the entourage of Pope John I, who had been ordered by king Theodoric to proceed to Constantinople and obtain a moderation of Emperor Justin's decree o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Senate
The Roman Senate ( la, Senātus Rōmānus) was a governing and advisory assembly in ancient Rome. It was one of the most enduring institutions in Roman history, being established in the first days of the city of Rome (traditionally founded in 753 BC). It survived the overthrow of the Roman monarchy in 509 BC; the fall of the Roman Republic in the 1st century BC; the division of the Roman Empire in AD 395; and the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476; Justinian's attempted reconquest of the west in the 6th century, and lasted well into the Eastern Roman Empire's history. During the days of the Roman Kingdom, most of the time the Senate was little more than an advisory council to the king, but it also elected new Roman kings. The last king of Rome, Lucius Tarquinius Superbus, was overthrown following a coup d'état led by Lucius Junius Brutus, who founded the Roman Republic. During the early Republic, the Senate was politically weak, while the various executive magistr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Justin I
Justin I ( la, Iustinus; grc-gre, Ἰουστῖνος, ''Ioustînos''; 450 – 1 August 527) was the Eastern Roman emperor from 518 to 527. Born to a peasant family, he rose through the ranks of the army to become commander of the imperial guard, and when Emperor Anastasius died he out-maneouvered his rivals and was elected as his successor, in spite of being almost 70 years old. His reign is significant for the founding of the Byzantine Empire under the Justinian dynasty, Justinian dynasty that included his eminent nephew Justinian I and three succeeding emperors. His Queen consort, consort was Empress Euphemia (empress), Euphemia. He was noted for his strongly orthodox Christian views. This facilitated the ending of the Acacian schism between the churches of Rome and Constantinople, resulting in good relations between Justin and the papacy. Throughout his reign he stressed the religious nature of his office and passed edicts against various Christian groups seen at the tim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |