|
The Tale Of The Yaksha General
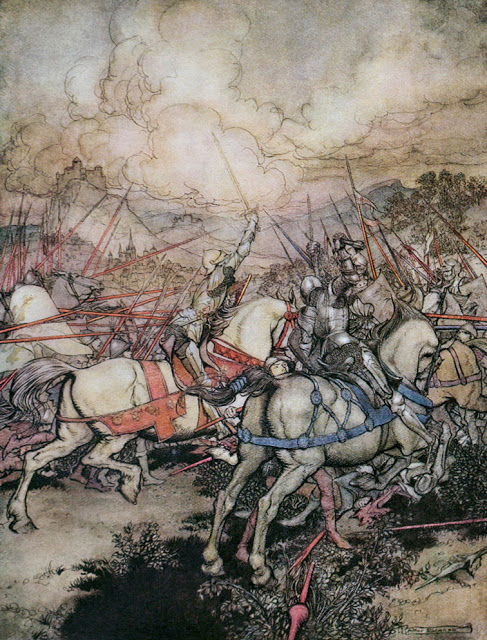
''The Tale of the Yaksha General'' (, ''Dạ Xoa bộ soái lục'') is a Vietnamese legend told in ''Truyền kỳ mạn lục'' by Nguyễn Dữ in the 16th century. It mythifies and fictionalizes the lives of Văn Dĩ Thành and Lê Ngộ, the leaders of a Vietnamese resistance during the Fourth Era of Northern Domination. Origin During the Ming domination of Vietnam, Văn Dĩ Thành (born 1380) gathered a resistance movement in Tổng Gối to fight the Ming occupiers, with Lê Ngộ as his deputy general. Because his army worn black clothes, they were called the Black-Clothed Army. He was famous for the "Six Precious Commandments" and the "Four Hopes for the Land" that he wrote and made his army follow. After some initial victories, Văn Dĩ Thành was cornered and killed by the Ming on March 12, 1416. Nowadays, he is deified by villages in the region as their guardian god, and Văn Sơn Tomb is said to be his grave. In ''Truyền kỳ mạn lục'' ''The Tale of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nguyễn Dữ
Nguyễn Dữ ( chữ Hán: 阮餘), also called Nguyễn Dữ (阮與), was a 16th-century poet of Vietnam known for the Truyền kỳ mạn lục (傳奇漫錄, ''Collection of Strange Tales'').Patricia M. Pelley ''Postcolonial Vietnam: new histories of the national past'' 2002 Page 134 "In the sixteenth century, Nguyễn Dữ and other scholars compiled Anthology of the Supernatural." Nguyễn Dữ was born in Đỗ Tùng village, Gia Phúc district, Hải Dương province, Việt Nam. He was a student of Nguyễn Bỉnh Khiêm (1491-1585), a well-known Vietnamese educator, philosopher, and poet. Truyền kỳ mạn lục was his only publication. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Nguyen, Du Vietnamese male writers Vietnamese Confucianists People of Revival Lê dynasty Year of birth unknown Year of death unknown Lê dynasty writers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chuanqi (short Story)
''Chuanqi'' is a form of fictional short story in Classical Chinese first formed in the Tang dynasty. The term often refers specifically to fictions written in the Tang dynasty, in which case the fictions are also called ''Tang chuanqi'' or ''chuanqi wen''. ''Chuanqi'' originated from the ''Zhiguai xiaoshuo'' of the Six Dynasties, was first formed in Early Tang dynasty, became popular in Middle Tang and dwindled in the Song dynasty. ''Chuanqi'' has four main themes: love, gods and demons, ''xiayi'' (heroes and knights-errant) and history. Well known works of ''chuanqi'' include '' The World Inside a Pillow'' and '' Renshi zhuan'' (The Story of Lady Ren) by Shen Jiji, ''Yingying's Biography'' by Yuan Zhen, ''The Tale of Huo Xiaoyu'' by Jiang Fang, '' The Tale of Li Wa'' by Bai Xingjian, ''The Governor of Nanke'' by Li Gongzuo, ''Chang hen ge zhuan'' by Chen Hong, ''Hongxian zhuan'' by Yuan Jiao and ''The Tale of the Curly-Bearded Guest'' by Du Guangting. Unlike general ''Biji xiaosh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historical Fantasy
Historical fantasy is a category of fantasy and genre of historical fiction that incorporates fantastic elements (such as magic) into a more "realistic" narrative. There is much crossover with other subgenres of fantasy; those classed as Arthurian, Celtic, or Dark Ages could just as easily be placed in historical fantasy. Stories fitting this classification generally take place prior to the 20th century. Films of this genre may have plots set in biblical times or classical antiquity. They often have plots based very loosely on mythology or legends of Greek-Roman history, or the surrounding cultures of the same era. Overview Historical fantasy usually takes one of four common approaches: # Magic, mythical creatures such as dragons or other supernatural elements, such as magic rings co-exist invisibly with the mundane world, with the majority of people being unaware of it. In this, it has a close similarity to contemporary fantasy. This commonly overlaps with the secret hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Truyền Kỳ Mạn Lục
The ''Truyền kỳ mạn lục'' (傳奇漫錄, "Casual Records of Transmitted Strange Tales") is a 16th-century Vietnamese historical text, in part a collection of legends, by Nguyễn Dữ (阮餘) composed in Chữ Hán. The collection was translated into French by UNESCO The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ... in 1962. Components ''Truyền kì mạn lục'' contains 20 stories ( vi, truyện), tales ( vi, lục) and records ( vi, ký) in 4 volumes, each contains 5 works: Volume 1 * '' The Record at Xiang King's Temple'' * '' The Story of the Virtuous Wife in Khoái Châu'' * '' The Story of the Cotton Tree'' * '' The Tale of the Tea Boy Reincarnated'' * '' The Record of the Strange Encounter in the Western Camp'' Volume 2 * '' The Tale of the Lawsuit in Dra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
16th Century
The 16th century begins with the Julian year 1501 ( MDI) and ends with either the Julian or the Gregorian year 1600 ( MDC) (depending on the reckoning used; the Gregorian calendar introduced a lapse of 10 days in October 1582). The 16th century is regarded by historians as the century which saw the rise of Western civilization and the Islamic gunpowder empires. The Renaissance in Italy and Europe saw the emergence of important artists, authors and scientists, and led to the foundation of important subjects which include accounting and political science. Copernicus proposed the heliocentric universe, which was met with strong resistance, and Tycho Brahe refuted the theory of celestial spheres through observational measurement of the 1572 appearance of a Milky Way supernova. These events directly challenged the long-held notion of an immutable universe supported by Ptolemy and Aristotle, and led to major revolutions in astronomy and science. Galileo Galilei became a champion o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Văn Dĩ Thành
Văn Dĩ Thành (chữ Hán: 文以誠; 1380–1416) was the leader of a resistance movement during the Fourth Era of Northern Domination in Vietnam in the 15th century. Family The surname Văn Dĩ Thành's ancestors was originally Hoa and they were carpenters from Bảo Hà (Vĩnh Bảo, Haiphong). His father moved to Tổng Gối in Tân Hội commune, Đan Phượng district, Hanoi and gave birth to him there. His father Văn Dĩ Thành was ordered by Hồ Quý Ly to join the construction of Citadel of the Hồ Dynasty. Anti-Ming activities In 1407, Hồ dynasty was defeated and Vietnam was annexed by the Ming dynasty. Văn Dĩ Thành built a resistance army with Lê Ngộ to fight the northern occupiers. His army was based in Tổng Gối and worn black clothes, so they were called the "Black-clothed army". The movement was also called the "Black-clothed Uprising". Văn Dĩ Thành was honored as the "Black-clothed Yaksha general". He put his base in Đống Đám mound, in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fourth Era Of Northern Domination
The Fourth Era of Northern Domination was a period of Vietnamese history, from 1407 to 1427, during which Vietnam was ruled by the Chinese Ming dynasty as the province of Jiaozhi (Giao Chỉ). Ming rule was established in Vietnam following its conquest of the Hồ dynasty. The previous periods of Chinese rule, collectively known as ''Bắc thuộc'', lasted much longer and amounted to around 1000 years. The fourth period of Chinese rule over Vietnam was eventually ended with the establishment of the Later Lê dynasty. History Ming conquest of Vietnam In mid-late 14th century, the kingdom of Đại Việt (north Vietnam) faced a series of troubles resulting in an ecological breakdown. This led to the rising of a radical intellectual and reformer, Hồ Quý Ly (c. 1336 – 1408). In 1400, Hồ Quý Ly deposed and massacred the Trần house before usurping the throne. After taking the throne, Hồ Quý Ly renamed the country from Đại Việt to Đại Ngu. In 1402, he abdicated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thành Hoàng
Thành hoàng ( Chữ Hán: 城隍) or Thần hoàng (神隍), Thần Thành hoàng (神城隍) refers to the gods that is enshrined in each village's communal temple in Vietnam. The gods is believed to guard the village against disasters and bring it fortune. Etymology ' is a Sino-Vietnamese word, literally referring to the city wall and the moat that surrounds it. It is also the Vietnamese pronunciation of Chinese ''Chénghuáng'' (or City God), which was adopted from Taoism. Origin No later than Đinh dynasty, each locality started to worship the mountain and river gods that ruled over a domain which encompassed their village. Later on, the government decreed the deification of late national heroes, righteous officials and loyal subjects, and specific localities were chosen to exalt these gods. Gradually other common folks took up the practice and worshipped their own gods to be blessed with protection and fortune. Ranking Generally each village worships only one Thành ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quốc Oai District
Quốc is a Vietnamese given name. Notable people with the name include: * Nguyễn Quốc Cường (born 1982), Vietnamese politician * Quốc Thiên (born 1988), Vietnamese singer * Trần Quốc Khang (1237–1300), Vietnamese prince * Trần Quốc Tảng (died 1313), Vietnamese general * Trần Quốc Toản Marquis Hoài Văn Trần Quốc Toản ( vi-hantu, , born 1267, fl. 1267–1285) was a marquis of the Trần Dynasty who was well known for his active role in the second war of resistance of Đại Việt against the Mongol invasion. Alth ... (1267–1285), Vietnamese marquis * Trần Quốc Tuấn (1228–1300), Vietnamese general {{DEFAULTSORT:Quoc Vietnamese names ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trùng Quang Đế
Trùng Quang Emperor ( vi, Trùng Quang Đế, vi-hantu, 重光帝, ?–1414), real name Trần Quý Khoáng (陳季擴), was the second and last emperor of Later Trần dynasty. He was a son of prince Trần Ngạc. As the second son of Trần Nghệ Tông, Ngạc was appointed as Prime Minister with the title ''Trang Định vương'' (莊定王, "Prince Trang Định"), but was later killed by an order of Co-Prime Minister Hồ Quý Ly in 1392. Giản Định revolted against Ming China in September 1408. Trùng Quang was appointed as a Palace Attendant (''thị trung'' 侍中). In the next year, he was installed as the new emperor by Đặng Dung and Nguyễn Cảnh Dị in Chi La (modern Đức Thọ District, Hà Tĩnh Province). Giản Định was arrested by Nguyễn Suý, a general of Trùng Quang, then transferred to Nghệ An Province. Trùng Quang granted him the title ''thái thượng hoàng'' ("Retired Emperor"). Trùng Quang came to Bình Than to fight again ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |