|
The Balochistani Princely States
The princely states of Pakistan ( ur, ; sd, پاڪستان جون نوابي رياستون) were princely states of the British Indian Empire which acceded to the new Dominion of Pakistan between 1947 and 1948, following the partition of British India and its independence. At the time of the withdrawal of British forces from the subcontinent on 15 August 1947, West Pakistan was less than half of its ultimate size. It took a year of negotiations and accidents to bring the princely states into Pakistan, and a long process of integration followed. Options of the Princes With the withdrawal of the British from the Indian subcontinent, in 1947, the Indian Independence Act provided that the hundreds of princely states which had existed alongside but outside British India were released from all their subsidiary alliances and other treaty obligations to the British, while at the same time the British withdrew from their treaty obligations to defend the states and keep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Princely States Of Pakistan Map
A prince is a male ruler (ranked below a king, grand prince, and grand duke) or a male member of a monarch's or former monarch's family. ''Prince'' is also a title of nobility (often highest), often hereditary, in some European states. The female equivalent is a princess. The English word derives, via the French word ''prince'', from the Latin noun , from (first) and (head), meaning "the first, foremost, the chief, most distinguished, noble ruler, prince". Historical background The Latin word (older Latin *prīsmo-kaps, literally "the one who takes the first lace/position), became the usual title of the informal leader of the Roman senate some centuries before the transition to empire, the ''princeps senatus''. Emperor Augustus established the formal position of monarch on the basis of principate, not dominion. He also tasked his grandsons as summer rulers of the city when most of the government were on holiday in the country or attending religious rituals, and, for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ghulam Moinuddin Khanji
Ghulam Moinuddin Khanji (22 December 1911 – 13 February 2003) was the ruler of Manavadar State, one of the princely states associated with British India. Although Khanji chose to accede to Pakistan after the partition of India, the state was soon annexed by India and a subsequent referendum resulted in a massive Indian victory. An able sportsman, Khanji played first-class cricket for Western India and in his later life, was also the president of the Pakistan Hockey Federation. Early life Khanji was born as Ghulam Moinuddin Khanji at Manavadar, Bantva Manavadar (in present-day Gujarat, India) on 22 December 1911. He was the eldest son of Nawab Fatehuddin Khanji. His mother, Fatima Siddiqa Begum was the second wife of Fatehuddin. Moinuddin graduated from Rajkumar College, Rajkot.''Who's Who in India, Burma & Ceylon'' (Who's Who Publishers (India) Limited, 1936), p. 541 Reign Khanji ascended the throne of Manavadar on 19 October 1918 after the death of his father. Since h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
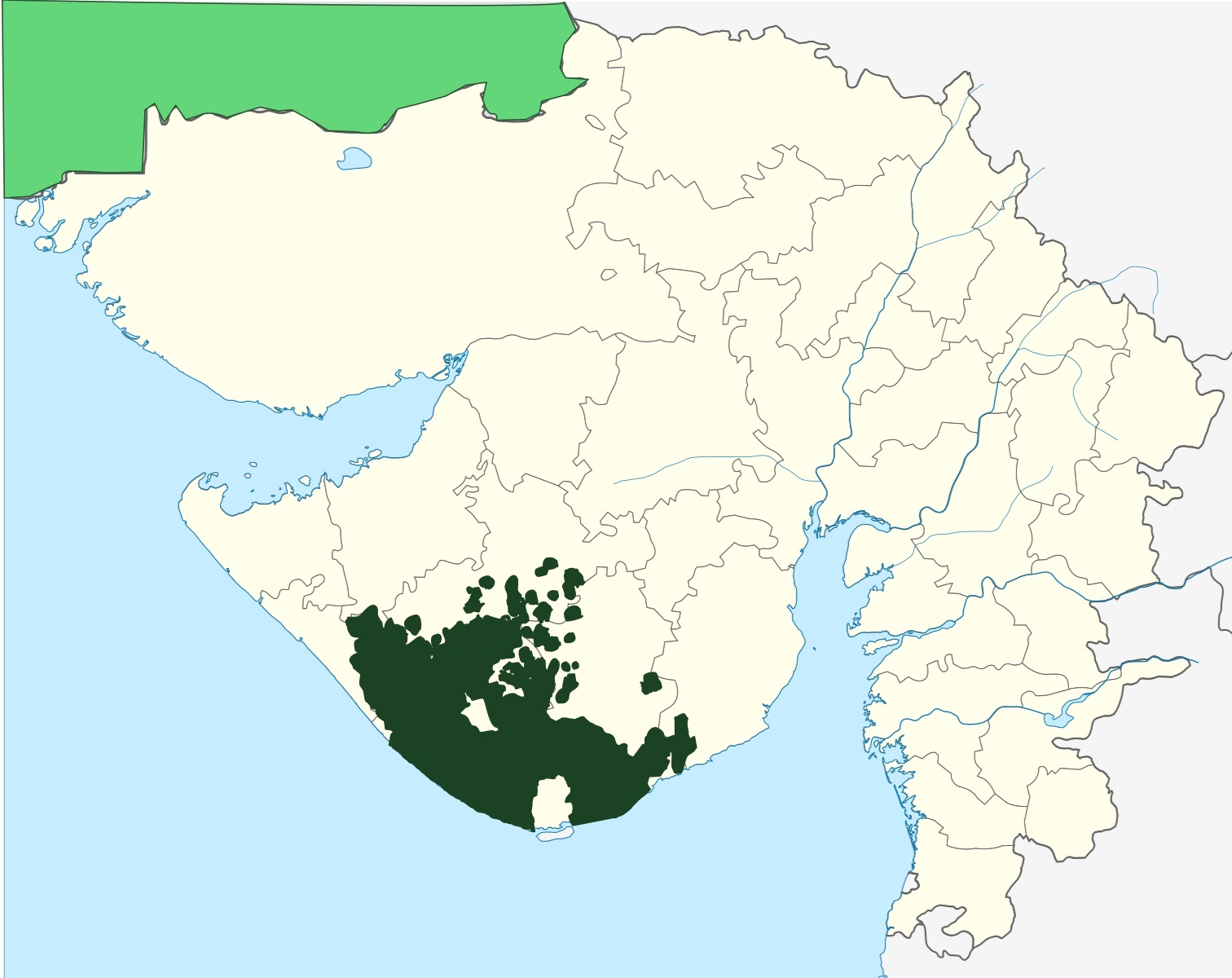
Indian Integration Of Junagadh
Junagarh State, Junagadh was a princely state of the British Raj, located in what is now Gujarat, outside but under the suzerainty of British India. In the independence and partition of British India of 1947, the 565 princely states were given a choice to either join the new Dominion of India or the newly formed state of dominion of Pakistan, Pakistan. The Nawab of Junagadh, Muhammad Mahabat Khanji III, a Muslim whose ancestors had ruled Junagadh and small principalities for some two hundred years, decided that Junagadh should become part of Pakistan, much to the displeasure of many of the people of the state, an overwhelming majority of whom were Hindus, about 80%. The Nawab acceded to the Dominion of Pakistan on 15 August 1947, against the advice of Lord Mountbatten, arguing that Junagadh joined Pakistan by sea. The principality of Babariawad and Sheikh of Mangrol State, Mangrol reacted by claiming independence from Junagadh and accession to India, although the Sheikh of Man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Referendum
A referendum (plural: referendums or less commonly referenda) is a direct vote by the electorate on a proposal, law, or political issue. This is in contrast to an issue being voted on by a representative. This may result in the adoption of a new policy or specific law, or the referendum may be only advisory. In some countries, it is synonymous with or commonly known by other names including plebiscite, votation, popular consultation, ballot question, ballot measure, or proposition. Some definitions of 'plebiscite' suggest it is a type of vote to change the constitution or government of a country. The word, 'referendum' is often a catchall, used for both legislative referrals and initiatives. Etymology 'Referendum' is the gerundive form of the Latin verb , literally "to carry back" (from the verb , "to bear, bring, carry" plus the inseparable prefix , here meaning "back"Marchant & Charles, Cassell's Latin Dictionary, 1928, p. 469.). As a gerundive is an adjective,A gerundiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindu
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism.Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for people living in the Indian subcontinent. The term ''"Hindu"'' traces back to Old Persian which derived these names from the Sanskrit name ''Sindhu'' (सिन्धु ), referring to the river Indus. The Greek cognates of the same terms are "''Indus''" (for the river) and "''India''" (for the land of the river). The term "''Hindu''" also implied a geographic, ethnic or cultural identifier for people living in the Indian subcontinent around or beyond the Sindhu (Indus) River. By the 16th century CE, the term began to refer to residents of the subcontinent who were not Turkic or Muslims. Hindoo is an archaic spelling variant, whose use today is considered derogatory. The historical development of Hindu self-identity within the local In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jinnah
Muhammad Ali Jinnah (, ; born Mahomedali Jinnahbhai; 25 December 1876 – 11 September 1948) was a barrister, politician, and the founder of Pakistan. Jinnah served as the leader of the All-India Muslim League from 1913 until the inception of Pakistan on 14 August 1947, and then as the Dominion of Pakistan's first governor-general until his death. Born at Wazir Mansion in Karachi, Jinnah was trained as a barrister at Lincoln's Inn in London. Upon his return to India, he enrolled at the Bombay High Court, and took an interest in national politics, which eventually replaced his legal practice. Jinnah rose to prominence in the Indian National Congress in the first two decades of the 20th century. In these early years of his political career, Jinnah advocated Hindu–Muslim unity, helping to shape the 1916 Lucknow Pact between the Congress and the All-India Muslim League, in which Jinnah had also become prominent. Jinnah became a key leader in the All-India Home R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)
