|
The Age Of Reptiles
''The Age of Reptiles'' is a mural depicting the period of ancient history when reptiles were the dominant creatures on the earth, painted by Rudolph Zallinger. The fresco sits in the Yale Peabody Museum in New Haven, Connecticut, and was completed in 1947 after five years of work. ''The Age of Reptiles'' was at one time the largest painting in the world, and depicts a span of nearly 350 million years in Earth's history. Painted in the Renaissance ''fresco secco'' technique, ''The Age of Reptiles'' showcases the contemporary view of dinosaurs as slow, sluggish creatures (a view that has been gradually replaced by more active dinosaurs). Zallinger received the Addison Emery Verrill medal in 1980 for the mural. Background Zallinger was an art student who in the early 1940s had been painting seaweed drawings for the Peabody museum. Dr. Albert E. Parr, then director of the Peabody Museum, had been unhappy with the appearance of the Great Hall of the museum, which he felt w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rudolph Zallinger
Rudolph Franz Zallinger (; November 12, 1919 – August 1, 1995) was an American-based Austrian-Russian artist. His most notable works include his mural '' The Age of Reptiles'' (1947) at Yale University's Peabody Museum of Natural History, and the ''March of Progress'' (1965) with numerous parodies and versions. His painting of a ''Tyrannosaurus'' heavily influenced the creature design of Toho Studios' ''Godzilla'' (1954). Two of Zallinger's dinosaurs—the ''T. rex'' and ''Brontosaurus—''are seen in that film as part of a slide demonstration during a lecture in the National Diet Building. Born in Russia, he was raised in Seattle and became a prominent member of Yale University after painting his murals, gaining him awards and honors. He made illustrations for Life magazine and illustrations for dinosaur books, which made more people aware of his mural work. Because of the time in which they were painted, his murals have errors that are noticeable today but still remain a larg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eusthenopteron
''Eusthenopteron'' (from el, εὖ , 'good', el, σθένος , 'strength', and el, πτερόν 'wing' or 'fin') is a genus of prehistoric sarcopterygian (often called lobe-finned fishes) which has attained an iconic status from its close relationships to tetrapods. Early depictions of this animal show it emerging onto land; however, paleontologists now widely agree that it was a strictly aquatic animal.M. Laurin, F. J. Meunier, D. Germain, and M. Lemoine 2007A microanatomical and histological study of the paired fin skeleton of the Devonian sarcopterygian ''Eusthenopteron foordi'' ''Journal of Paleontology'' 81: 143–153. The genus ''Eusthenopteron'' is known from several species that lived during the Late Devonian period, about 385 million years ago. ''Eusthenopteron'' was first described by J. F. Whiteaves in 1881, as part of a large collection of fishes from Miguasha, Quebec. Some 2,000 ''Eusthenopteron'' specimens have been collected from Miguasha, one of which was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Varanosaurus
''Varanosaurus'' (' monitor lizard') is an extinct genus of early pelycosaur synapsid that lived during the Kungurian. Description As its name implies, ''Varanosaurus'' may have looked superficially similar to present-day monitor lizards, though not related at all. ''Varanosaurus'' had a flattened, elongated skull and a pointed snout with a row of sharp teeth, including two pairs of conspicuous pseudocanines, implying that it was an active predator. ''Varanosaurus'' probably lived in swamps, competing with the larger '' Ophiacodon'' for food. Classification Below is a cladogram modified from the analysis of Benson (2012): See also * List of pelycosaurs This list of pelycosaurs is an attempt to create a comprehensive listing of all genera that have ever been included in the synapsida excluding therapsida and purely vernacular terms. The list includes all commonly accepted genera, but also genera t ... References Further reading *Benes, Josef. Prehistoric Animals and P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limnoscelis
''Limnoscelis'' (\ limˈnäsələ̇s \, meaning "marsh footed") was a genus of large diadectomorph tetrapods from the Late Carboniferous of western North America. It includes two species: the type species ''Limnoscelis paludis'' from New Mexico, and ''Limnoscelis dynatis'' from Colorado, both of which are thought to have lived concurrently. No specimens of ''Limnoscelis'' are known from outside of North America. ''Limnoscelis'' was carnivorous, and likely semiaquatic, though it may have spent a significant portion of its life on land. ''Limnoscelis'' had a combination of derived amphibian and primitive reptilian features, and its placement relative to Amniota has significant implications regarding the origins of the first amniotes. Discovery and naming The type species ''Limnoscelis paludis'' was collected by the fossil hunter David Baldwin between 1877 and 1880 from the El Cobre Canyon beds of the Cutler Formation, New Mexico. Baldwin was collecting fossils in service of the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
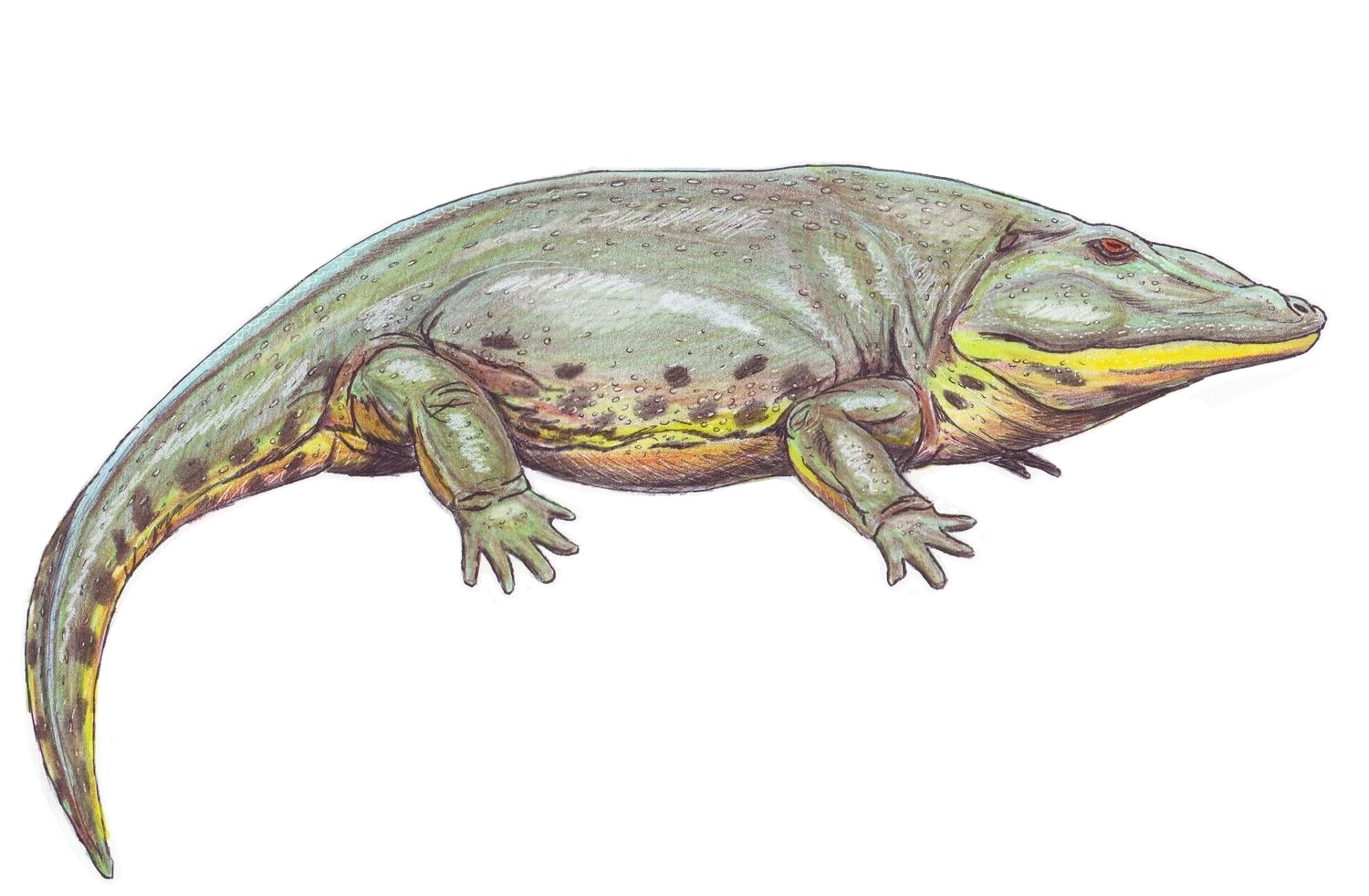
Seymouria
''Seymouria'' is an extinct genus of seymouriamorph from the Early Permian of North America and Europe. Although they were amphibians (in a biological sense), ''Seymouria'' were well-adapted to life on land, with many reptilian features—so many, in fact, that ''Seymouria'' was first thought to be a primitive reptile. It is primarily known from two species, ''Seymouria baylorensis'' and ''Seymouria sanjuanensis''. The type species, ''S. baylorensis'', is more robust and specialized, though its fossils have only been found in Texas. On the other hand, ''Seymouria sanjuanensis'' is more abundant and widespread. This smaller species is known from multiple well-preserved fossils, including a block of six skeletons found in the Cutler Formation of New Mexico, and a pair of fully grown skeletons from the Tambach Formation of Germany, which were fossilized lying next to each other. For the first half of the 20th century, ''Seymouria'' was considered one of the oldest and most "prim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Permian
The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.9 Mya. It is the last period of the Paleozoic Era; the following Triassic Period belongs to the Mesozoic Era. The concept of the Permian was introduced in 1841 by geologist Sir Roderick Murchison, who named it after the region of Perm in Russia. The Permian witnessed the diversification of the two groups of amniotes, the synapsids and the sauropsids ( reptiles). The world at the time was dominated by the supercontinent Pangaea, which had formed due to the collision of Euramerica and Gondwana during the Carboniferous. Pangaea was surrounded by the superocean Panthalassa. The Carboniferous rainforest collapse left behind vast regions of desert within the continental interior. Amniotes, which could better cope with these drier conditions, rose to dominance in place of their am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sigillaria
''Sigillaria'' is a genus of extinct, spore-bearing, arborescent (tree-like) plants. It was a lycopodiophyte, and is related to the lycopsids, or club-mosses, but even more closely to quillworts, as was its associate ''Lepidodendron''. Fossil records This genus is known in the fossil records from as early as the Middle Devonian or the Late Carboniferous period but dwindled to extinction in the Cisuralian, Early Permian period (age range: from 383.7 to 254.0 million years ago). Fossils are found in Great Britain, United States, Canada, China, Korea, Tanzania and Zimbabwe. Species Species within this genus include: *''S.alveolaris'' Brongniart (1828) *''S.barbata'' Weiss (1887) *''S.bicostata'' Weiss (1887) *''S.boblayi'' Brongniart (1828) *''S.brardii'' Brongniart (1828) *''S.cancriformis'' Weiss (1887) *''S.cristata'' Sauveur (1848) *''S.cumulata'' Weiss (1887) *''S.davreuxii'' Brongniart (1828) *''S.densifolia'' Brongniart (1836) *''S.elegans'' Sternberg (1825) *''S.elonga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lepidodendron
''Lepidodendron'' is an extinct genus of primitive vascular plants belonging to the family Lepidodendraceae, part of a group of Lycopodiopsida known as scale trees or arborescent lycophytes, related to Isoetes, quillworts and Lycopodiopsida, lycopsids (club mosses). They were part of the coal forest flora. They sometimes reached heights of , and the trunks were often over in diameter. They thrived during the Carboniferous Period (358.9 to 298.9 million years ago). Sometimes erroneously called "giant club mosses", the genus was actually more closely related to modern quillworts than to modern club mosses. Within the form classification system used within paleobotany, ''Lepidodendron'' is both used for the whole plant as well as specifically the stems and leaves. Etymology The name ''Lepidodendron'' comes from the Greek language, Greek wikt:λεπίς, λεπίς ', scale, and wikt:δένδρον, δένδρον ''dendron'', tree. Growth During the early stages of growth, ''L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eryops
''Eryops'' (; from Greek , , 'drawn-out' + , , 'face', because most of its skull was in front of its eyes) is a genus of extinct, amphibious temnospondyls. It contains the single species , the fossils of which are found mainly in early Permian (about 295 million years ago) rocks of the Texas Red Beds, located in Archer County, Texas. Fossils have also been found in late Carboniferous period rocks from New Mexico. Several complete skeletons of ''Eryops'' have been found in lower Permian rocks, but skull bones and teeth are its most common fossils. Description ''Eryops'' averaged a little over long and could grow up to , making them among the largest land animals of their time. Adults weighed between . The skull was proportionately large, being broad and flat and reaching lengths of . It had an enormous mouth with many curved teeth like the frog. Its teeth had enamel with a folded pattern, leading to its early classification as a "labyrinthodont" ("maze toothed"). The sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meganeuropsis
''Meganeuropsis'' is an extinct genus of griffinfly, order Meganisoptera, known from the Early Permian Wellington Formation of North America, and represents the largest known insect of all time. ''Meganeuropsis'' existed during the Artinskian age of the Permian period, 290.1–283.5 mya. The genus includes two described species by Frank Morton Carpenter, fossil insect curator at the Museum of Comparative Zoology at Harvard University: ''Meganeuropsis permiana'' described in 1939 from Elmo, Kansas. It was one of the largest known insects that ever lived, with a reconstructed wing length of , an estimated wingspan of up to , and a body length from head to tail of almost . The holotype is held in the Museum of Comparative Zoology. ''Meganeuropsis americana'', discovered in Noble, Oklahoma Noble is a city in Cleveland County, Oklahoma, United States, and is part of the Oklahoma City Metropolitan Area. The population was 6,481 at the 2010 census. Noble is Cleveland County's thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diplovertebron
''Diplovertebron'' (from el, διπλοῦς , 'double' and la, vertebron, 'vertebra') is an extinct genus of embolomere that lived in the Late Carboniferous period ( Moscovian), about 310 million years ago. ''Diplovertebron'' was a medium-sized animal, around 50 cm in length. Members of the genus inhabited European Carboniferous swamps in what is now the Czech Republic. They were closely related to larger swamp-dwelling tetrapods like ''Proterogyrinus'' and '' Anthracosaurus''. However, ''Diplovertebron'' were much smaller than these large, crocodile-like creatures. Known from a single species, ''Diplovertebron punctatum,'' this genus has had a complicated history closely tied to '' Gephyrostegus'', another genus of small, reptile-like amphibians. History ''Diplovertebron'' was one of many tetrapods found in Czech coal swamps by Antonin Frič in the late 19th century. Its remains were an assortment of disarticulated fossils encased in two slabs of coal, which were d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eogyrinus
''Pholiderpeton'' (from el, φολῐ́δος , 'horny scale' and el, ἑρπετόν , 'creeping thing') is an extinct genus of embolomere amphibian which lived in the Late Carboniferous period ( Bashkirian) of England. The genus was first named by Thomas Henry Huxley in 1869 to include the species ''P. scutigerum'', based on the disarticulated front half of a skeleton discovered near Bradford, Yorkshire. Associated fossil wood suggests that this specimen died inside a ''Lepidodendron'' tree trunk. In 1987, Jennifer A. Clack suggested that a different embolomere, ''Eogyrinus attheyi'' from Newsham, Northumberland, belonged to the same genus as ''Pholiderpeton''. She subsumed the genus ''Eogyrinus'' into ''Pholiderpeton'' and created the new combination ''P. attheyi''. The anatomy of ''"Eogyrinus"'' ''attheyi'' has been described in detail by A.L. Panchen. Some phylogenetic analyses, such as those by Marcello Ruta & Michael Coates (2007) and David Marjanović & Michel Lau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |