|
Tham Sang Triangle
The Tham Sang Triangle refer to a group of four caves in close proximity, located roughly north of Vang Vieng, Laos, to the northwest of the village of Ban Pakpo. The four caves are Tham Sang, Tham Hoi, Tham Loup, and Tham Nam. The name "Tham Sang" refers to the stalactites within them which are said to resemble elephants, a characteristic in particular of the Tham Sang cave. The entrance has a grey boulder on the right side with a red flower bush beyond that. Tham Hoi is considered the most sacred to locals, with a larger Buddha Siddhartha Gautama, most commonly referred to as the Buddha, was a śramaṇa, wandering ascetic and religious teacher who lived in South Asia during the 6th or 5th century BCE and founded Buddhism. According to Buddhist tradition, he was ... head in the entrance, whilst Tham Loup is noted for its stalactites. Tham Nam, meaning "water cave", is located roughly south of Tham Hoi. References {{coord missing, Laos Buddhist caves in Laos Geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cave
A cave or cavern is a natural void in the ground, specifically a space large enough for a human to enter. Caves often form by the weathering of rock and often extend deep underground. The word ''cave'' can refer to smaller openings such as sea caves, rock shelters, and grottos, that extend a relatively short distance into the rock and they are called ''exogene'' caves. Caves which extend further underground than the opening is wide are called ''endogene'' caves. Speleology is the science of exploration and study of all aspects of caves and the cave environment. Visiting or exploring caves for recreation may be called ''caving'', ''potholing'', or ''spelunking''. Formation types The formation and development of caves is known as ''speleogenesis''; it can occur over the course of millions of years. Caves can range widely in size, and are formed by various geological processes. These may involve a combination of chemical processes, erosion by water, tectonic forces, microorgani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vang Vieng
Vang may refer to: People Vang is a common surname among Hmong Americans, including *Vang Pao (1929–2011), Lieutenant General in the Royal Lao Army and a leader of the Hmong American community in the United States *Ka Vang (born 1975), writer *Chai Vang (born 1968), convicted murderer *Bee Vang (born 1991), actor, best known as Thao Vang Lor in ''Gran Torino'' *Katie Ka Vang, artist, playwright *Bora Vang (born 1987), Chinese-born Turkish table tennis player Places *Vang, Bornholm, a village on the island of Bornholm, Denmark *Vang, Innlandet, a municipality in Innlandet county, Norway **Vang i Valdres, a village in the municipality of Vang in Innlandet county, Norway *Vang, Hedmark, a former municipality in the old Hedmark county, Norway *Vang, a village in Ka Choun, Cambodia *Vəng (other), a list of similarly-named places in Azerbaijan Other * Vang (spritsail), a sailing part *Boom vang, a sailing part *Gaff vang, a sailing part *D-alanine—D-serine ligase D-Alan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laos
Laos (, ''Lāo'' )), officially the Lao People's Democratic Republic ( Lao: ສາທາລະນະລັດ ປະຊາທິປະໄຕ ປະຊາຊົນລາວ, French: République démocratique populaire lao), is a socialist state and the only landlocked country in Southeast Asia. At the heart of the Indochinese Peninsula, Laos is bordered by Myanmar and China to the northwest, Vietnam to the east, Cambodia to the southeast, and Thailand to the west and southwest. Its capital and largest city is Vientiane. Present-day Laos traces its historic and cultural identity to Lan Xang, which existed from the 14th century to the 18th century as one of the largest kingdoms in Southeast Asia. Because of its central geographical location in Southeast Asia, the kingdom became a hub for overland trade and became wealthy economically and culturally. After a period of internal conflict, Lan Xang broke into three separate kingdoms: Luang Phrabang, Vientiane and Champasak. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ban Pakpo
Ban Pakpo, also Pak Pok or Pakpo, is a village in Vientiane Province, Laos. It is located north along Route 13 from Vang Vieng, not far from the eastern bank of the Nam Song River. To the northwest of the village is the Tham Pha Thao cave and the Tham Sang Triangle The Tham Sang Triangle refer to a group of four caves in close proximity, located roughly north of Vang Vieng, Laos, to the northwest of the village of Ban Pakpo. The four caves are Tham Sang, Tham Hoi, Tham Loup, and Tham Nam. The name "Tham Sang ... of four caves. References {{Laos-geo-stub Populated places in Vientiane Province ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
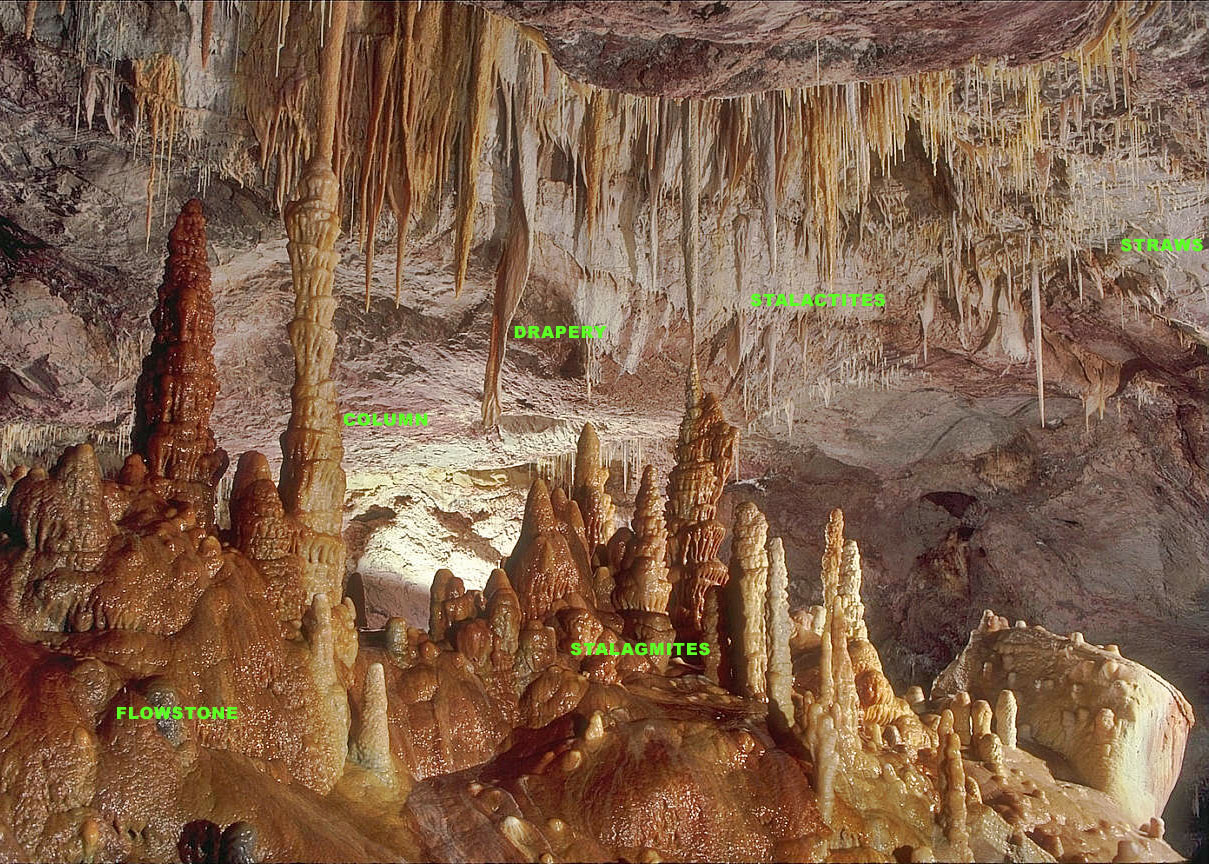
Stalactite
A stalactite (, ; from the Greek 'stalaktos' ('dripping') via ''stalassein'' ('to drip') is a mineral formation that hangs from the ceiling of caves, hot springs, or man-made structures such as bridges and mines. Any material that is soluble and that can be deposited as a colloid, or is in suspension, or is capable of being melted, may form a stalactite. Stalactites may be composed of lava, minerals, mud, peat, pitch, sand, sinter, and amberat (crystallized urine of pack rats). A stalactite is not necessarily a speleothem, though speleothems are the most common form of stalactite because of the abundance of limestone caves. The corresponding formation on the floor of the cave is known as a stalagmite. Mnemonics have been developed for which word refers to which type of formation; one is that ''stalactite'' has a C for "ceiling", and ''stalagmite'' has a G for "ground". Another example is that ''stalactites'' "hang on ''T''ight" and ''stalagmites'' "''M''ight grow up" � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elephant
Elephants are the largest existing land animals. Three living species are currently recognised: the African bush elephant, the African forest elephant, and the Asian elephant. They are the only surviving members of the family Elephantidae and the order Proboscidea. The order was formerly much more diverse during the Pleistocene, but most species became extinct during the Late Pleistocene epoch. Distinctive features of elephants include a long proboscis called a trunk, tusks, large ear flaps, pillar-like legs, and tough but sensitive skin. The trunk is used for breathing, bringing food and water to the mouth, and grasping objects. Tusks, which are derived from the incisor teeth, serve both as weapons and as tools for moving objects and digging. The large ear flaps assist in maintaining a constant body temperature as well as in communication. African elephants have larger ears and concave backs, whereas Asian elephants have smaller ears, and convex or level backs. Elephants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boulder
In geology, a boulder (or rarely bowlder) is a rock fragment with size greater than in diameter. Smaller pieces are called cobbles and pebbles. While a boulder may be small enough to move or roll manually, others are extremely massive. In common usage, a boulder is too large for a person to move. Smaller boulders are usually just called rocks or stones. The word ''boulder'' derives from ''boulder stone'', from the Middle English ''bulderston'' or Swedish ''bullersten''. Online Etymology Dictionary. Retrieved December 9, 2011, from Dictionary.com website. In places covered by s during s, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddha
Siddhartha Gautama, most commonly referred to as the Buddha, was a śramaṇa, wandering ascetic and religious teacher who lived in South Asia during the 6th or 5th century BCE and founded Buddhism. According to Buddhist tradition, he was born in Lumbini, in what is now Nepal, to royal parents of the Shakya clan, but Great Renunciation, renounced his Householder (Buddhism), home life to live as a wandering ascetic ( sa, śramaṇa). After leading a life of begging, asceticism, and meditation, he attained Enlightenment in Buddhism, enlightenment at Bodh Gaya in what is now India. The Buddha thereafter wandered through the lower Indo-Gangetic Plain, teaching and building a Sangha, monastic order. He taught a Middle Way between sensual indulgence and severe asceticism, leading to Nirvana (Buddhism), Nirvana, that is, Vimutti, freedom from Avidyā (Buddhism), ignorance, Upādāna, craving, Saṃsāra (Buddhism), rebirth, and suffering. His teachings are summarized in the Noble ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddhist Caves In Laos
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and gradually spread throughout much of Asia via the Silk Road. It is the world's fourth-largest religion, with over 520 million followers (Buddhists) who comprise seven percent of the global population. The Buddha taught the Middle Way, a path of spiritual development that avoids both extreme asceticism and hedonism. It aims at liberation from clinging and craving to things which are impermanent (), incapable of satisfying ('), and without a lasting essence (), ending the cycle of death and rebirth (). A summary of this path is expressed in the Noble Eightfold Path, a training of the mind with observance of Buddhist ethics and meditation. Other widely observed practices include: monasticism; "taking refuge" in the Buddha, the , and the ; and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_colourised.png)
.jpg)