|
Tham Phra Wang Daeng
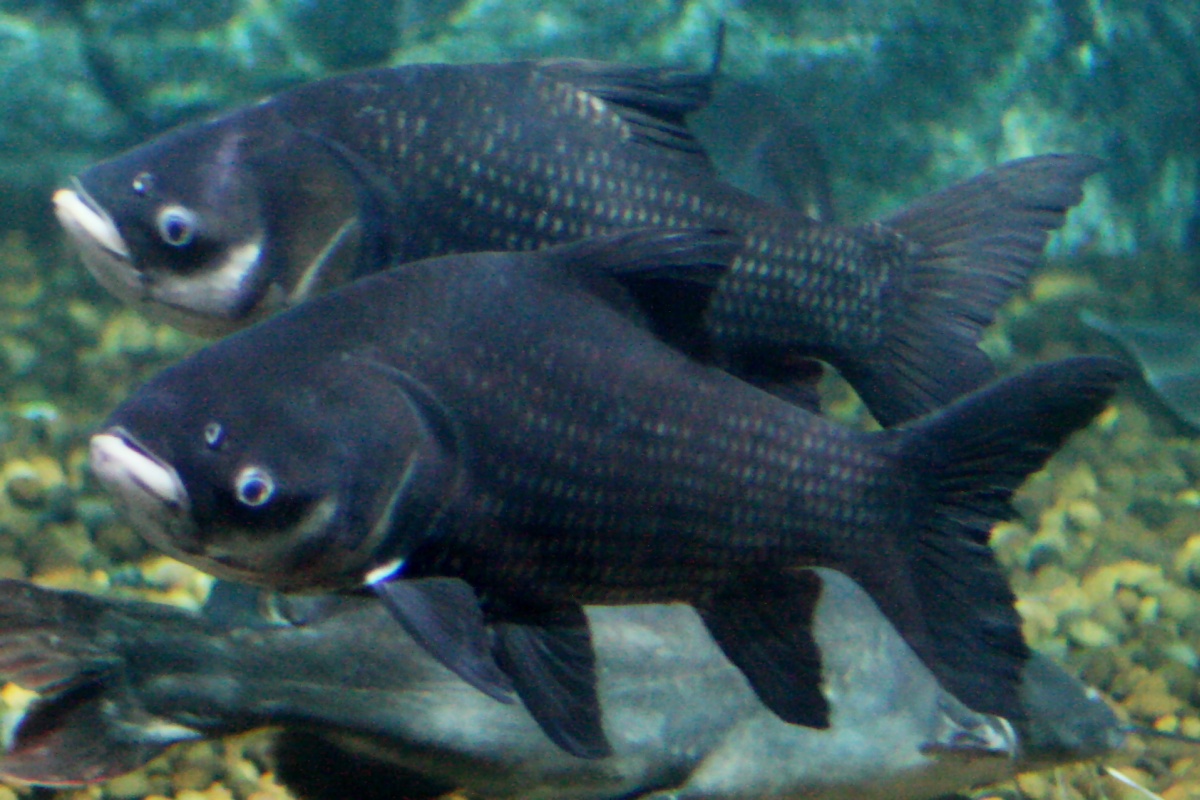
Tham Phra Wang Daeng, also known as the Cave of the Monk ( th, ถ้ำพระวังแดง), is a deep cave located in Thung Salaeng Luang National Park, Amphoe Noen Maprang, Phitsanulok Province, upper central Thailand. It is the longest cave in Thailand, the distance is about 13 kilometers. Buddhist statues and relics, carvings and reliefs, a subterranean river, multiple bat colonies, and a trove of speleothems populate the cave. In 2003, a biological expedition to the cave resulted in the discovery of new fish species, including discoveries in the Balitoridae and Cyprinidae families.https://www.researchgate.net/publication/270508267_Three_new_species_of_fishes_from_Tham_Phra_Wang_Daeng_and_Tham_Phra_Sai_Ngam_caves_in_northern_Thailand_Teleostei_Cyprinidae_and_Balitoridae RGate See also * List of caves * Speleology Speleology is the scientific study of caves and other karst features, as well as their make-up, structure, physical properties, history, life forms, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thung Salaeng Luang National Park
Thung Salaeng Luang National Park ( th, อุทยานแห่งชาติทุ่งแสลงหลวง, ) is a national park in Phitsanulok and Phetchabun Provinces of Thailand. It encompasses substantial portions of Wang Thong and Lom Sak Districts. Topography The park consists of limestone hills, slate and hardpan at altitudes ranging from , Khao Khae is the highest point in the park. Thung Salaeng Luang is inlaid with meadows, especially in the southern portions of the park. The park is the source of numerous streams. There are large salt licks at Pong Sai in the northwest and Pong Thung Phaya in the southwest. The Wang Thong River flows through the park. History Thung Salaeng Luang was proposed for inclusion in the national parks system In 1959. Thung Salaeng Luang was declared the 3rd national park in 1963, covering an area of . At the request of the Thai Army were withdrawn from the national park. That is why a "new" national park area was created in 1972. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphoe Noen Maprang
Noen Maprang ( th, เนินมะปราง, ) is the southernmost district (''amphoe'') of Phitsanulok province, central Thailand. History To better cope with the problems caused by communist insurgents in northern Thailand in the 1970s, the government separated Tambon Noen Maprang from Wang Thong district to create a minor district (''king amphoe'') on 6 September 1976. It was upgraded to a full district on 1 April 1983. Geography Neighboring districts are (from the north clockwise) Wang Thong of Phitsanulok Province, Khao Kho, Mueang Phetchabun, and Wang Pong of Phetchabun province, Thap Khlo, Wang Sai Phun, and Sak Lek of Phichit province. Noen Maprang lies within the Nan Basin, which is part of the Chao Phraya Watershed. Within the district is the source of the Chomphu River.Google Earth The Ban Mung (Thai: คลองบ้านมุง) and Sai Yoi (คลองไทรย้อย) Rivers also flow through the district. Administration The distr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Thailand
Central Thailand (Central plain) or more specifically Siam (also known as Suvarnabhumi and Dvaravati) is one of the regions of Thailand, covering the broad alluvial plain of the Chao Phraya River. It is separated from northeast Thailand (Isan) by the Phetchabun mountain range. The Tenasserim Hills separate it from Myanmar to the west. In the north it is bounded by the Phi Pan Nam Range, one of the hilly systems of northern Thailand. The area was the heartland of the Ayutthaya Kingdom (at times referred to as Siam), and is still the dominant area of Thailand, containing as it does, the world's most primate city, Bangkok. Definition The grouping of Thai provinces into regions follow two major systems, in which Thailand is divided into either four or six regions. In the six-region system, commonly used in geographical studies, central Thailand extends from Sukhothai and Phitsanulok Provinces in the north to the provinces bordering the Gulf of Thailand in the south, excluding the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
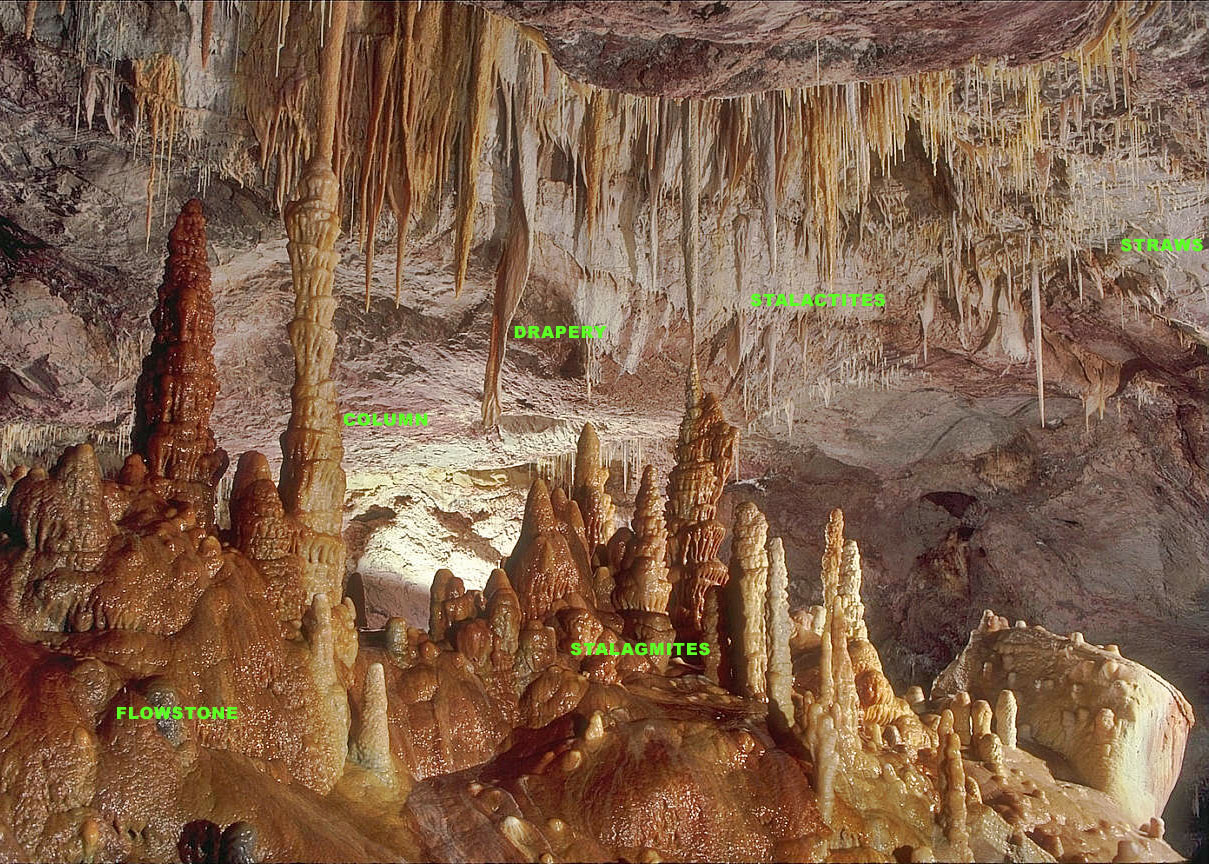
Speleothem
A speleothem (; ) is a geological formation by mineral deposits that accumulate over time in natural caves. Speleothems most commonly form in calcareous caves due to carbonate dissolution reactions. They can take a variety of forms, depending on their depositional history and environment. Their chemical composition, gradual growth, and preservation in caves make them useful paleoclimatic proxies. Chemical and physical characteristics More than 300 variations of cave mineral deposits have been identified. The vast majority of speleothems are calcareous, composed of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) minerals (calcite or aragonite). Less commonly, speleothems are made of calcium sulfate (gypsum or mirabilite) or opal. Speleothems of pure calcium carbonate or calcium sulfate are translucent and colorless. The presence of iron oxide or copper provides a reddish brown color. The presence of manganese oxide can create darker colors such as black or dark brown. Speleothems can also be brown d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balitoridae
The hillstream loaches or river loaches are a family, the Balitoridae, of small fish from South, Southeast and East Asia. The family includes about 202 species. They are sometimes sold as "lizardfish" or (in Germany) "flossensaugers". Many of the species are popular for aquaria, species in the genus ''Sewellia'' are most commonly sold in the aquaria trade. They have a number of similarities with the Cobitidae, their sibling family of "loaches", such as multiple barbels around the mouth. They should not be confused with the loricariids, which look similar but are a family of catfish. Most species are rheophilic, living in swift, clear and well-oxygenated streams. Several species of the family live in fast-flowing streams or torrents and have modified ventral fins used for clinging to rocks. The subfamily Nemacheilinae has recently been separated as a distinct family, Nemacheilidae (stone loaches) and several genera have been separated into the family Gastromyzontidae The Gast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyprinidae
Cyprinidae is a family of freshwater fish commonly called the carp or minnow family. It includes the carps, the true minnows, and relatives like the barbs and barbels. Cyprinidae is the largest and most diverse fish family and the largest vertebrate animal family in general with about 3,000 species, of which only 1,270 remain extant, divided into about 370 genera. Cyprinids range from about 12 mm in size to the giant barb (''Catlocarpio siamensis''). By genus and species count, the family makes up more than two-thirds of the ostariophysian order Cypriniformes. The family name is derived from the Greek word ( 'carp'). Biology and ecology Cyprinids are stomachless fish with toothless jaws. Even so, food can be effectively chewed by the gill rakers of the specialized last gill bow. These pharyngeal teeth allow the fish to make chewing motions against a chewing plate formed by a bony process of the skull. The pharyngeal teeth are unique to each species and are used by scient ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Caves
This is a list of caves of the world that have articles or that are properly cited. They are sorted by continent and then country. Caves which are in overseas territories on a different continent than the home country are sorted by the territory's continent and name. Africa File:Cango Caves, Western Cape (6253225986).jpg, The Cango caves in western cape. File:African cave paintings.jpg, African cave paintings. File:Lithic Industries at Blombos Cave, Southern Cape, South Africa (c. 105 – 90 Ka).jpg, Lithic Industries at Blombos Cave, Southern Cape, South Africa. File:Wonder Caves Praying Mary.JPG, Wonder Caves Praying Mary. Algeria * Aïn Taïba * Anou Achra Lemoun * Anou Boussouil * Anou Ifflis * Anou Timedouine * Gueldaman caves * Ghar Boumâaza * Grotte de Cervantes * Kef Al Kaous * Rivière De La Tafna Botswana * Gcwihaba * Rhino Cave Cameroon * Gouffre de Mbilibekon * Grottes de Linté * Grotte de Loung * Grotte de Mfouda * Grotte Fovu [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speleology
Speleology is the scientific study of caves and other karst features, as well as their make-up, structure, physical properties, history, life forms, and the processes by which they form (speleogenesis) and change over time (speleomorphology). The term ''speleology'' is also sometimes applied to the recreational activity of exploring caves, but this is more properly known as ''caving'', ''potholing'' (British English), or ''spelunking''. Speleology and caving are often connected, as the physical skills required for ''in situ'' study are the same. Speleology is a cross-disciplinary field that combines the knowledge of chemistry, biology, geology, physics, meteorology, and cartography to develop portraits of caves as complex, evolving systems. History Before modern speleology developed, John Beaumont wrote detailed descriptions of some Mendip caves in the 1680s. The term speleology was coined by Émile Rivière in 1890. Prior to the mid-nineteenth century the scientific valu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caves Of Thailand
A cave or cavern is a natural void in the ground, specifically a space large enough for a human to enter. Caves often form by the weathering of rock and often extend deep underground. The word ''cave'' can refer to smaller openings such as sea caves, rock shelters, and grottos, that extend a relatively short distance into the rock and they are called ''exogene'' caves. Caves which extend further underground than the opening is wide are called ''endogene'' caves. Speleology is the science of exploration and study of all aspects of caves and the cave environment. Visiting or exploring caves for recreation may be called ''caving'', ''potholing'', or ''spelunking''. Formation types The formation and development of caves is known as ''speleogenesis''; it can occur over the course of millions of years. Caves can range widely in size, and are formed by various geological processes. These may involve a combination of chemical processes, erosion by water, tectonic forces, microorganism ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_Photograph_by_Shantanu_Kuveskar.jpg)