|
Thalattosaurs
Thalattosauria (Greek for "sea lizards") is an extinct order of prehistoric marine reptiles that lived in the middle to late Triassic period. Thalattosaurs were diverse in size and shape, and are divided into two superfamilies: Askeptosauroidea and Thalattosauroidea. Askeptosauroids were endemic to the Tethys Ocean, their fossils have been found in Europe and China, and they were likely semiaquatic fish eaters with straight snouts and decent terrestrial abilities. Thalattosauroids were more specialized for aquatic life and most had unusual downturned snouts and crushing dentition. Thalattosauroids lived along the coasts of both Panthalassa and the Tethys Ocean, and were most diverse in China and western North America. The largest species of thalattosaurs grew to over 4 meters (13 feet) in length, including a long, flattened tail utilized in underwater propulsion. Although thalattosaurs bore a superficial resemblance to lizards, their exact relationships are unresolved. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thalattosaurus Alexandrae
''Thalattosaurus'' (pronounced: , "tha-la-to-SORE-us") meaning "sea lizard," from the Attic Greek ' (), "sea," and ' (), "lizard," is an extinct genus of marine reptile in the family Thalattosauroidea. They were aquatic diapsids that are known exclusively from the Triassic period. It was a long shellfish-eating reptile with paddle-like limbs and a down-turned rostrum occurring in the Lower and Middle Triassic Sulphur Mountain Formation of British Columbia as well as the Upper Triassic Hosselkus Limestone of California. It has gained notoriety as a result of studies on general diapsid phylogeny. Although originally described as four distinct species by Merriam in 1905, one was proven to be ''T. alexandrae'' upon further inspection and another has a missing type specimen. Currently it is believed to include two known species; ''Thalattosaurus alexandrae'' and ''T. borealis''. Discovery and naming In the summer of 1903 Annie Alexander led an expedition with Miss Edna Wemple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Askeptosaurus Italicus
''Askeptosaurus'' is an extinct genus of askeptosauroid, a marine reptile from the extinct order Thalattosauria. ''Askeptosaurus'' is known from several well-preserved fossils found in Middle Triassic marine strata in what is now Italy and Switzerland. History of discovery ''Askeptosaurus,'' and its only known species ''Askeptosaurus italicus,'' were first named and described in 1925 by Hungarian paleontologist Franz Nopcsa von Felső-Szilvás. It was most recently redescribed by Dr. Johannes Müller in 2005. ''Askeptosaurus'' is known from several disarticulated and articulated skeletons preserved at the MSNM (Museo Civico di Storia Naturale di Milano) in Milan, Italy, and the PIMUZ ( Paläontologisches Institut und Museum der Universität Zürich) in Zürich, Switzerland. These specimens were discovered in the Grenzbitumenzone of Monte San Giorgio, a UNESCO World Heritage Site on the Swiss-Italian border. Also known as the Besano Formation in Italy, the Grenzbitumenzone has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endennasaurus Acutirostris
''Endennasaurus'' is an extinct genus of thalattosaurian from the Upper Triassic of Italy. It was found in and named after the Endenna cave, composed of Zorzino Limestone in Lombardia. at Fossilworks
Fossilworks is a portal which provides query, download, and analysis tools to facilitate access to the Paleobiology Database
The Paleobiology Database is an online resource for information on the distribution and classification of fossil animals ... .org
Gallery References Thalattosaurs[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
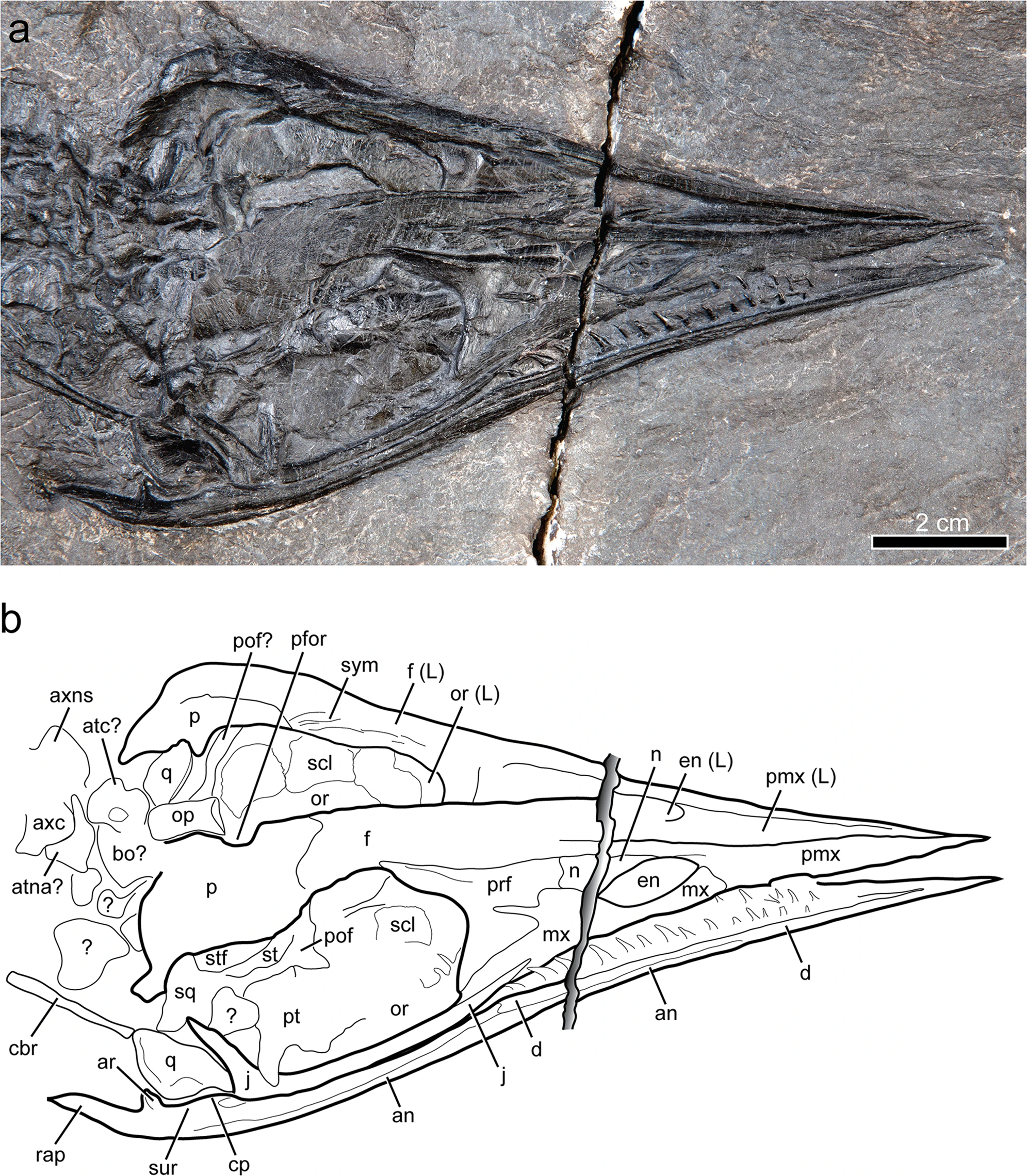
Gunakadeit Joseeae
''Gunakadeit'' is an extinct genus of thalattosaur. It is known from a single species, ''Gunakadeit joseeae'', which is based on an articulated and mostly complete skeleton from the late Triassic (middle Norian) Hound Island Volcanics of Alaska. ''Gunakadeit'' possessed a variety of features from the two major suborders of thalattosaurs, Askeptosauroidea and Thalattosauroidea, and it is considered the most basal member of the latter group. Despite this, it is also the youngest known thalattosaur genus, with the group going extinct at the end of the Triassic. ''Gunakadeits basal position and relatively recent occurrence implies a 20-million-year ghost lineage connecting it to the rest of Thalattosauria. The skull ends in a sharply pointed and toothless tip like the askeptosauroid ''Endennasaurus'', but unlike ''Endennasaurus'', ''Gunakadeit'' had poorly developed joints and was likely exclusively aquatic in behavior. Discovery The holotype, UAMES 23258, was discovered by r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Askeptosauroidea
Askeptosauroidea is a superfamily of thalattosaurs, a Triassic group of marine reptiles. Askeptosauroidea is one of two major subgroups of Thalattosauria, the other being Thalattosauroidea. It includes the family Askeptosauridae and a more basal form called ''Endennasaurus''. Phylogeny Below is a cladogram from Wu ''et al.'' (2009) showing the phylogenetic In biology, phylogenetics (; from Greek φυλή/ φῦλον [] "tribe, clan, race", and wikt:γενετικός, γενετικός [] "origin, source, birth") is the study of the evolutionary history and relationships among or within groups o ... relationships of Askeptosauroidea: References Thalattosaurs Triassic first appearances Triassic extinctions {{triassic-reptile-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Triassic
In the geologic timescale, the Middle Triassic is the second of three epochs of the Triassic period or the middle of three series in which the Triassic system is divided in chronostratigraphy. The Middle Triassic spans the time between Ma and Ma (million years ago). It is preceded by the Early Triassic Epoch and followed by the Late Triassic Epoch. The Middle Triassic is divided into the Anisian and Ladinian ages or stages. Formerly the middle series in the Triassic was also known as Muschelkalk. This name is now only used for a specific unit of rock strata with approximately Middle Triassic age, found in western Europe. Middle Triassic fauna Following the Permian–Triassic extinction event, the most devastating of all mass-extinctions, life recovered slowly. In the Middle Triassic, many groups of organisms reached higher diversity again, such as the marine reptiles (e.g. ichthyosaurs, sauropterygians, thallatosaurs), ray-finned fish and many invertebrate groups like ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ichthyosaur
Ichthyosaurs (Ancient Greek for "fish lizard" – and ) are large extinct marine reptiles. Ichthyosaurs belong to the order known as Ichthyosauria or Ichthyopterygia ('fish flippers' – a designation introduced by Sir Richard Owen in 1842, although the term is now used more for the parent clade of the Ichthyosauria). Ichthyosaurs thrived during much of the Mesozoic era; based on fossil evidence, they first appeared around 250 million years ago ( Ma) and at least one species survived until about 90 million years ago, into the Late Cretaceous. During the Early Triassic epoch, ichthyosaurs and other ichthyosauromorphs evolved from a group of unidentified land reptiles that returned to the sea, in a development similar to how the mammalian land-dwelling ancestors of modern-day dolphins and whales returned to the sea millions of years later, which they gradually came to resemble in a case of convergent evolution. Ichthyosaurs were particularly abundant in the Late Triassic a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squamata
Squamata (, Latin ''squamatus'', 'scaly, having scales') is the largest order of reptiles, comprising lizards, snakes, and amphisbaenians (worm lizards), which are collectively known as squamates or scaled reptiles. With over 10,900 species, it is also the second-largest order of extant (living) vertebrates, after the perciform fish. Members of the order are distinguished by their skins, which bear horny scales or shields, and must periodically engage in molting. They also possess movable quadrate bones, making possible movement of the upper jaw relative to the neurocranium. This is particularly visible in snakes, which are able to open their mouths very wide to accommodate comparatively large prey. Squamata is the most variably sized order of reptiles, ranging from the dwarf gecko (''Sphaerodactylus ariasae'') to the Reticulated python (''Malayopython reticulatus'') and the now-extinct mosasaurs, which reached lengths over . Among other reptiles, squamates are most close ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhynchocephalia
Rhynchocephalia (; ) is an order of lizard-like reptiles that includes only one living species, the tuatara (''Sphenodon punctatus'') of New Zealand. Despite its current lack of diversity, during the Mesozoic rhynchocephalians were a diverse group including a wide array of morphologically distinct forms. The oldest record of the group is dated to the Middle Triassic around 238 to 240 million years ago, and they had achieved a worldwide distribution by the Early Jurassic. Most rhynchocephalians belong to the group Sphenodontia ('wedge-teeth'). Their closest living relatives are lizards and snakes in the order Squamata, with the two orders being grouped together in the superorder Lepidosauria. Many of the niches occupied by lizards today were held by sphenodontians during the Triassic and Jurassic, although lizard diversity began to overtake sphenodontian diversity in the Cretaceous, and they had disappeared almost entirely by the beginning of the Cenozoic. While the modern tuat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archosauromorpha
Archosauromorpha (Greek for "ruling lizard forms") is a clade of diapsid reptiles containing all reptiles more closely related to archosaurs (such as crocodilians and dinosaurs, including birds) rather than lepidosaurs (such as tuataras, lizards, and snakes). Archosauromorphs first appeared during the late Middle Permian or Late Permian, though they became much more common and diverse during the Triassic period. Although Archosauromorpha was first named in 1946, its membership did not become well-established until the 1980s. Currently Archosauromorpha encompasses four main groups of reptiles: the stocky, herbivorous allokotosaurs and rhynchosaurs, the hugely diverse Archosauriformes, and a polyphyletic grouping of various long-necked reptiles including ''Protorosaurus'', tanystropheids, and ''Prolacerta''. Other groups including pantestudines (turtles and their extinct relatives) and the semiaquatic choristoderes have also been placed in Archosauromorpha by some authors. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archosaur
Archosauria () is a clade of diapsids, with birds and crocodilians as the only living representatives. Archosaurs are broadly classified as reptiles, in the cladistic sense of the term which includes birds. Extinct archosaurs include non-avian dinosaurs, pterosaurs, and extinct relatives of crocodilians. Modern paleontologists define Archosauria as a crown group that includes the most recent common ancestor of living birds and crocodilians, and all of its descendants. The base of Archosauria splits into two clades: Pseudosuchia, which includes crocodilians and their extinct relatives, and Avemetatarsalia, which includes birds and their extinct relatives (such as non-avian dinosaurs and pterosaurs). Older definitions of the group Archosauria rely on shared morphological characteristics, such as an antorbital fenestra in the skull, serrated teeth, and an upright stance. Some extinct reptiles, such as proterosuchids and euparkeriids, possessed these features yet originated pri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Femur
The femur (; ), or thigh bone, is the proximal bone of the hindlimb in tetrapod vertebrates. The head of the femur articulates with the acetabulum in the pelvic bone forming the hip joint, while the distal part of the femur articulates with the tibia (shinbone) and patella (kneecap), forming the knee joint. By most measures the two (left and right) femurs are the strongest bones of the body, and in humans, the largest and thickest. Structure The femur is the only bone in the upper leg. The two femurs converge medially toward the knees, where they articulate with the proximal ends of the tibiae. The angle of convergence of the femora is a major factor in determining the femoral-tibial angle. Human females have thicker pelvic bones, causing their femora to converge more than in males. In the condition ''genu valgum'' (knock knee) the femurs converge so much that the knees touch one another. The opposite extreme is ''genu varum'' (bow-leggedness). In the general populatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_601758.jpg)