|
Gunakadeit Joseeae
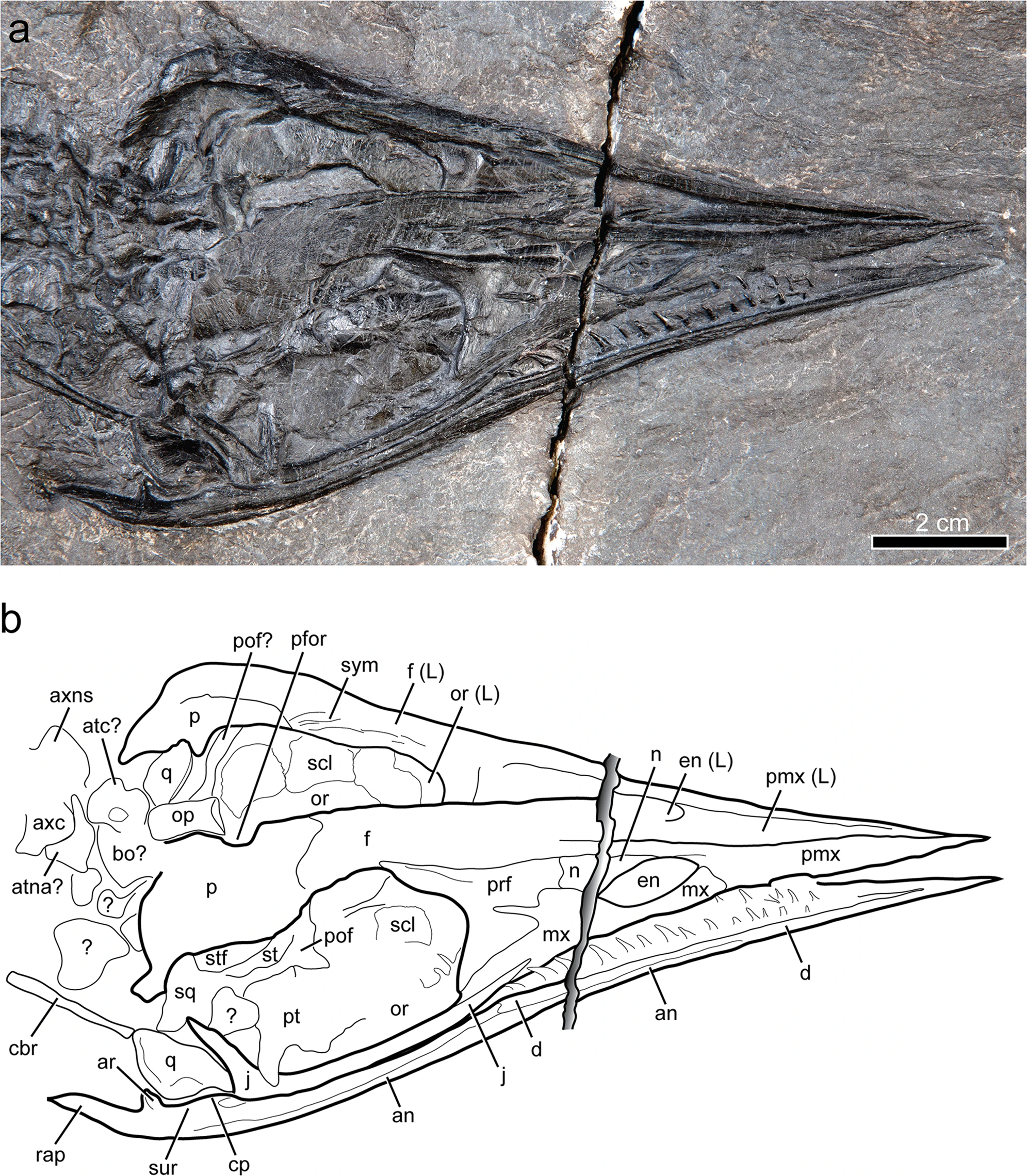
''Gunakadeit'' is an extinct genus of thalattosaur. It is known from a single species, ''Gunakadeit joseeae'', which is based on an articulated and mostly complete skeleton from the late Triassic (middle Norian) Hound Island Volcanics of Alaska. ''Gunakadeit'' possessed a variety of features from the two major suborders of thalattosaurs, Askeptosauroidea and Thalattosauroidea, and it is considered the most basal member of the latter group. Despite this, it is also the youngest known thalattosaur genus, with the group going extinct at the end of the Triassic. ''Gunakadeits basal position and relatively recent occurrence implies a 20-million-year ghost lineage connecting it to the rest of Thalattosauria. The skull ends in a sharply pointed and toothless tip like the askeptosauroid ''Endennasaurus'', but unlike ''Endennasaurus'', ''Gunakadeit'' had poorly developed joints and was likely exclusively aquatic in behavior. Discovery The holotype, UAMES 23258, was discovered by r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triassic
The Triassic ( ) is a geologic period and system which spans 50.6 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.36 Mya. The Triassic is the first and shortest period of the Mesozoic Era. Both the start and end of the period are marked by major extinction events. The Triassic Period is subdivided into three epochs: Early Triassic, Middle Triassic and Late Triassic. The Triassic began in the wake of the Permian–Triassic extinction event, which left the Earth's biosphere impoverished; it was well into the middle of the Triassic before life recovered its former diversity. Three categories of organisms can be distinguished in the Triassic record: survivors from the extinction event, new groups that flourished briefly, and other new groups that went on to dominate the Mesozoic Era. Reptiles, especially archosaurs, were the chief terrestrial vertebrates during this time. A specialized subgroup of archo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patrick Druckenmiller
Patrick S. Druckenmiller is a Mesozoic paleontologist, taxonomist, associate professor of geology, Earth Sciences curator, and museum director of the University of Alaska Museum of the North, where he oversees the largest single collection of Alaskan invertebrate and vertebrate fossils. He has published work on plesiosaurs, ichthyosaurs, mastodons, and dinosaurs in the United States, Svalbard, and Canada. He has co-authored papers on discussions of mass extinctions and biogeography. Much of his work has focused on Arctic species. He is a member of the Spitsbergen Jurassic Research group, which focuses on marine reptiles. Druckenmiller has named many new genera and species, including '' Edgarosaurus muddi, Nichollsia borealis, Athabascasaurus bitumineus, Cryopterygius kristiansenae, Spitrasaurus larseni,'' and ''Spitrasaurus'' ''wensaasi''. Education Druckenmiller has served as a curator and as a faculty member in the University of Alaska, Fairbanks since 2007. Druckenmiller ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coronoid Process Of The Mandible
In human anatomy, the mandible's coronoid process (from Greek ''korōnē'', denoting something hooked) is a thin, triangular eminence, which is flattened from side to side and varies in shape and size. Its anterior border is convex and is continuous below with the anterior border of the ramus. Its ''posterior border'' is concave and forms the anterior boundary of the mandibular notch. The ''lateral surface'' is smooth, and affords insertion to the temporalis and masseter muscles. Its ''medial surface'' gives insertion to the temporalis, and presents a ridge which begins near the apex of the process and runs downward and forward to the inner side of the last molar tooth. Between this ridge and the anterior border is a grooved triangular area, the upper part of which gives attachment to the temporalis, the lower part to some fibers of the buccinator. Clinical significance Fractures of the mandible are common. However, coronoid process fractures are very rare. Isolated fractures of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandibular Symphysis
In human anatomy, the facial skeleton of the skull the external surface of the mandible is marked in the median line by a faint ridge, indicating the mandibular symphysis (Latin: ''symphysis menti'') or line of junction where the two lateral halves of the mandible typically fuse at an early period of life (1-2 years). It is not a true symphysis as there is no cartilage between the two sides of the mandible. This ridge divides below and encloses a triangular eminence, the mental protuberance, the base of which is depressed in the center but raised on either side to form the mental tubercle. The lowest (most inferior) end of the mandibular symphysis — the point of the chin — is called the "menton". It serves as the origin for the geniohyoid and the genioglossus muscles. Other animals Solitary mammalian carnivores that rely on a powerful canine bite to subdue their prey have a strong mandibular symphysis, while pack hunters delivering shallow bites have a weaker one. When filter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supratemporal Bone
The supratemporal bone is a paired cranial bone present in many tetrapods and tetrapodomorph fish. It is part of the temporal region (the portion of the skull roof behind the eyes), usually lying medial (inwards) relative to the squamosal and lateral (outwards) relative to the parietal and/or postparietal. It may also contact the postorbital or intertemporal (which lie forwards), or tabular (which lies backwards), when those bones are present. The supratemporal is a common component of the skull in many extinct amphibians, though it is apparently absent in the lightweight skulls of living lissamphibians (frogs and salamanders). Embryological studies of salamanders suggests that the supratemporal fuses with the squamosal in early development. A separate supratemporal was retained by early synapsids and reptiles, but was strongly reduced in many groups. Squamates (lizards and snakes) still possess a small supratemporal, though archosaurs (crocodilians and birds) and mammals lack i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parietal Bone
The parietal bones () are two bones in the Human skull, skull which, when joined at a fibrous joint, form the sides and roof of the Human skull, cranium. In humans, each bone is roughly quadrilateral in form, and has two surfaces, four borders, and four angles. It is named from the Latin ''paries'' (''-ietis''), wall. Surfaces External The external surface [Fig. 1] is convex, smooth, and marked near the center by an eminence, the parietal eminence (''tuber parietale''), which indicates the point where ossification commenced. Crossing the middle of the bone in an arched direction are two curved lines, the superior and inferior temporal lines; the former gives attachment to the temporal fascia, and the latter indicates the upper limit of the muscular origin of the temporal muscle. Above these lines the bone is covered by a tough layer of fibrous tissue – the epicranial aponeurosis; below them it forms part of the temporal fossa, and affords attachment to the temporal muscle. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supratemporal Fenestra
The skull is a bone protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of four types of bone i.e., cranial bones, facial bones, ear ossicles and hyoid bone. However two parts are more prominent: the cranium and the mandible. In humans, these two parts are the neurocranium and the viscerocranium (facial skeleton) that includes the mandible as its largest bone. The skull forms the anterior-most portion of the skeleton and is a product of cephalisation—housing the brain, and several sensory structures such as the eyes, ears, nose, and mouth. In humans these sensory structures are part of the facial skeleton. Functions of the skull include protection of the brain, fixing the distance between the eyes to allow stereoscopic vision, and fixing the position of the ears to enable sound localisation of the direction and distance of sounds. In some animals, such as horned ungulates (mammals with hooves), the skull also has a defensive function by providing the mount (on the frontal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jugal Bone
The jugal is a skull bone found in most reptiles, amphibians and birds. In mammals, the jugal is often called the malar or zygomatic. It is connected to the quadratojugal and maxilla, as well as other bones, which may vary by species. Anatomy The jugal bone is located on either side of the skull in the circumorbital region. It is the origin of several masticatory muscles in the skull. The jugal and lacrimal bones are the only two remaining from the ancestral circumorbital series: the prefrontal, postfrontal, postorbital, jugal, and lacrimal bones. During development, the jugal bone originates from dermal bone. In dinosaurs This bone is considered key in the determination of general traits in cases in which the entire skull has not been found intact (for instance, as with dinosaurs in paleontology). In some dinosaur genera the jugal also forms part of the lower margin of either the antorbital fenestra or the infratemporal fenestra, or both. Most commonly, this bone articu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbit (anatomy)
In anatomy, the orbit is the cavity or socket of the skull in which the eye and its appendages are situated. "Orbit" can refer to the bony socket, or it can also be used to imply the contents. In the adult human, the volume of the orbit is , of which the eye occupies . The orbital contents comprise the eye, the orbital and retrobulbar fascia, extraocular muscles, cranial nerves II, III, IV, V, and VI, blood vessels, fat, the lacrimal gland with its sac and duct, the eyelids, medial and lateral palpebral ligaments, cheek ligaments, the suspensory ligament, septum, ciliary ganglion and short ciliary nerves. Structure The orbits are conical or four-sided pyramidal cavities, which open into the midline of the face and point back into the head. Each consists of a base, an apex and four walls."eye, human."Encyclopædia Britannica from Encyclopædia Britannica 2006 Ultimate Reference Suite DVD 2009 Openings There are two important foramina, or windows, two important fissu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nasal Bone
The nasal bones are two small oblong bones, varying in size and form in different individuals; they are placed side by side at the middle and upper part of the face and by their junction, form the bridge of the upper one third of the nose. Each has two surfaces and four borders. Structure The two nasal bones are joined at the midline internasal suture and make up the bridge of the nose. Surfaces The ''outer surface'' is concavo-convex from above downward, convex from side to side; it is covered by the procerus and nasalis muscles, and perforated about its center by a foramen, for the transmission of a small vein. The ''inner surface'' is concave from side to side, and is traversed from above downward, by a groove for the passage of a branch of the nasociliary nerve. Articulations The nasal articulates with four bones: two of the cranium, the frontal and ethmoid, and two of the face, the opposite nasal and the maxilla. Other animals In primitive bony fish and tetrapod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Premaxilla
The premaxilla (or praemaxilla) is one of a pair of small cranial bones at the very tip of the upper jaw of many animals, usually, but not always, bearing teeth. In humans, they are fused with the maxilla. The "premaxilla" of therian mammal has been usually termed as the incisive bone. Other terms used for this structure include premaxillary bone or ''os premaxillare'', intermaxillary bone or ''os intermaxillare'', and Goethe's bone. Human anatomy In human anatomy, the premaxilla is referred to as the incisive bone (') and is the part of the maxilla which bears the incisor teeth, and encompasses the anterior nasal spine and alar region. In the nasal cavity, the premaxillary element projects higher than the maxillary element behind. The palatal portion of the premaxilla is a bony plate with a generally transverse orientation. The incisive foramen is bound anteriorly and laterally by the premaxilla and posteriorly by the palatine process of the maxilla. It is formed from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maxilla
The maxilla (plural: ''maxillae'' ) in vertebrates is the upper fixed (not fixed in Neopterygii) bone of the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary bones. In humans, the upper jaw includes the hard palate in the front of the mouth. The two maxillary bones are fused at the intermaxillary suture, forming the anterior nasal spine. This is similar to the mandible (lower jaw), which is also a fusion of two mandibular bones at the mandibular symphysis. The mandible is the movable part of the jaw. Structure In humans, the maxilla consists of: * The body of the maxilla * Four processes ** the zygomatic process ** the frontal process of maxilla ** the alveolar process ** the palatine process * three surfaces – anterior, posterior, medial * the Infraorbital foramen * the maxillary sinus * the incisive foramen Articulations Each maxilla articulates with nine bones: * two of the cranium: the frontal and ethmoid * seven of the face: the nasal, zygomatic, lacrimal, inferior n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)

