|
Thalassocalycida
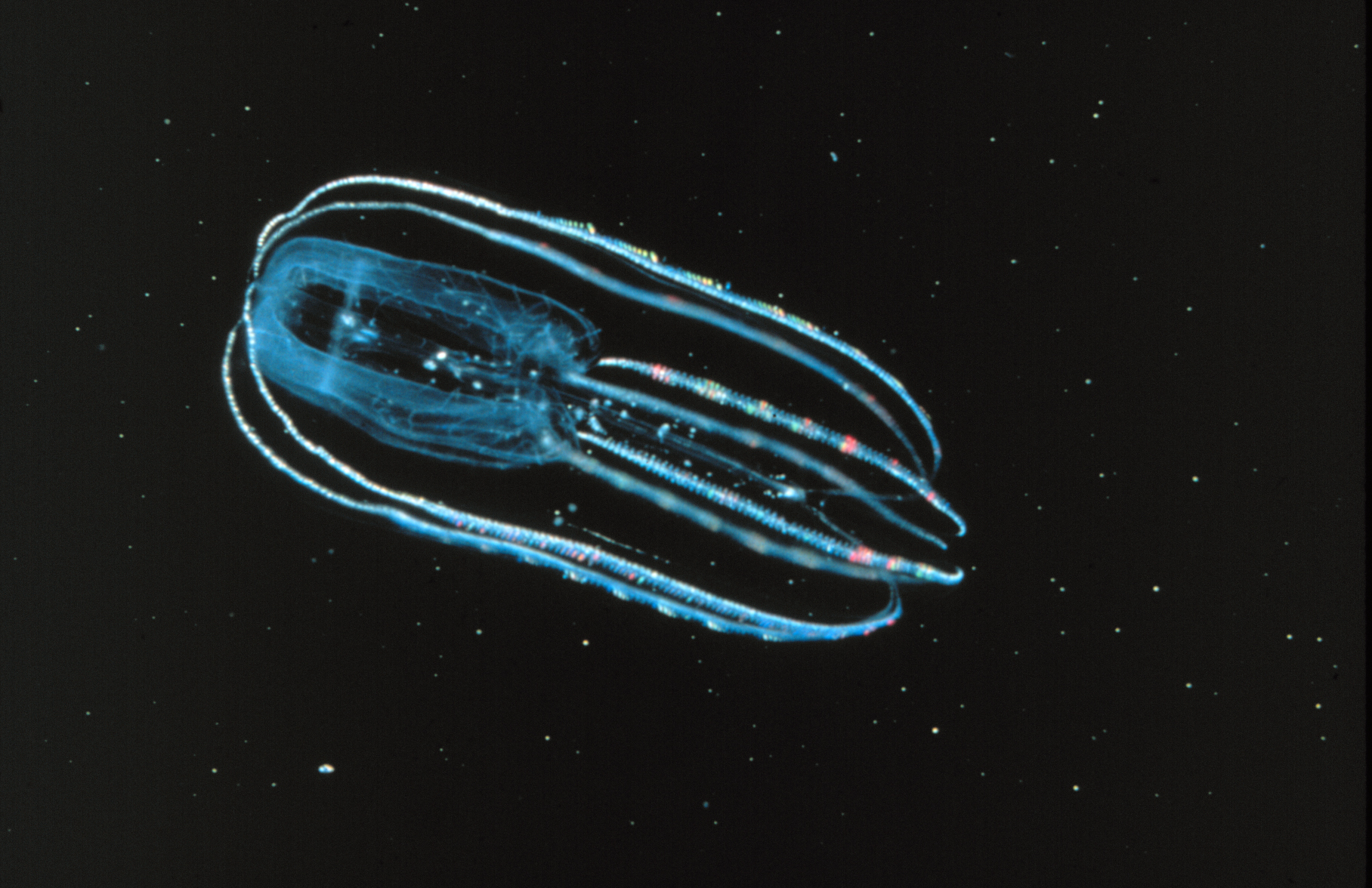
''Thalassocalyce'' is a genus of ctenophore, or comb jellies, known from the California Coast, Gulf of Mexico, and west north Atlantic. It is represented by a single species, ''Thalassocalyce inconstans'', which is the only species in the family Thalassocalycidae and the order Thalassocalycida.Madin, L. P., and G. R. Harbison. "Thalassocalyce inconstans, new genus and species, an enigmatic ctenophore representing a new family and order." ''Bulletin of Marine Science'' 28.4 (1978): 680-687. ''T. inconstans'' is a pelagic ctenophore typically occurring in upper-mesopelagic depths, but has been observed at depths up to 3,500 m in Monterey Canyon.Swift, H. F., Hamner, W. M., Robison, B. H., & Madin, L. P. (2009). Feeding behavior of the ctenophore Thalassocalyce inconstans: revision of anatomy of the order Thalassocalycida. ''Marine biology'', ''156''(5), 1049-1056. Due to their fragility, gelatinous zooplankton are inherently difficult to sample by traditional m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ctenophora
Ctenophora (; ctenophore ; ) comprise a phylum of marine invertebrates, commonly known as comb jellies, that inhabit sea waters worldwide. They are notable for the groups of cilia they use for swimming (commonly referred to as "combs"), and they are the largest animals to swim with the help of cilia. Depending on the species, adult ctenophores range from a few millimeters to in size. Only 100 to 150 species have been validated, and possibly another 25 have not been fully described and named. The textbook examples are cydippids with egg-shaped bodies and a pair of retractable tentacles fringed with tentilla ("little tentacles") that are covered with colloblasts, sticky cells that capture prey. Their bodies consist of a mass of jelly, with a layer two cells thick on the outside, and another lining the internal cavity. The phylum has a wide range of body forms, including the egg-shaped cydippids with retractable tentacles that capture prey, the flat generally combless plat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tentaculata
Tentaculata is a class of comb jellies. The common feature of this class is a pair of long, feathery, contractile tentacles, which can be retracted into specialised ciliated sheaths. In some species, the primary tentacles are reduced and they have smaller, secondary tentacles. The tentacles have colloblasts, which are sticky-tipped cells that trap small prey. Body size and shape varies widely. The group includes the small, oval sea gooseberries found on both Atlantic and Pacific coasts. The more flattened species of the genus ''Mnemiopsis'', about long, are common on the upper Atlantic coast; it has a large mouth and mainly feeds on larval molluscs and copepods. This species is brilliantly luminescent. The similar, but larger, genus ''Leucothea In Greek mythology, Leucothea (; grc-gre, Λευκοθέα, Leukothéa, white goddess), sometimes also called Leucothoe ( grc-gre, Λευκοθόη, Leukothóē), was one of the aspects under which an ancient sea goddess was recogni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cydippida
Cydippida is an order of comb jellies. They are distinguished from other comb jellies by their spherical or oval bodies, and the fact their tentacles are branched, and can be retracted into pouches on either side of the pharynx. The order is not monophyletic, that is, more than one common ancestor is believed to exist. Anatomy Cydippids have bodies that are more or less rounded, sometimes nearly spherical and other times more cylindrical or egg-shaped; the common coastal "sea gooseberry," '' Pleurobrachia'', has an egg-shaped body with the mouth at the narrow end. From opposite sides of the body extends a pair of long, slender tentacles, each housed in a sheath into which it can be withdrawn. Some species of cydippids have bodies that are flattened to various extents, so that they are wider in the plane of the tentacles. The tentacles are typically fringed with tentilla ("little tentacles"), although a few genera have simple tentacles without these side-branches. The tentacles an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lobata
Lobata is an order of Ctenophora in the class Tentaculata with smaller tentacles than other ctenophores, and distinctive flattened lobes extending outwards from their bodies. They grow up to about long. Anatomy The lobates have a pair of lobes, which are muscular, cuplike extensions of the body that project beyond the mouth. Their inconspicuous tentacles originate from the corners of the mouth, running in convoluted grooves and spreading out over the inner surface of the lobes (rather than trailing far behind, as in the Cydippida). Between the lobes on either side of the mouth, many species of lobates have four auricles, gelatinous projections edged with cilia that produce water currents that help direct microscopic prey toward the mouth. This combination of structures enables lobates to feed continuously on suspended planktonic prey. Lobates have eight comb-rows, originating at the aboral pole and usually not extending beyond the body to the lobes; in species with (four) au ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Krill
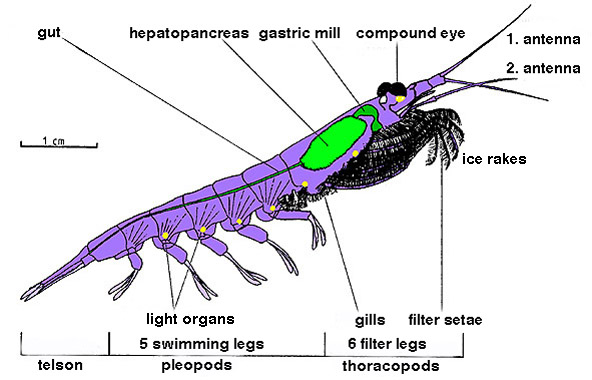
Krill are small crustaceans of the order Euphausiacea, and are found in all the world's oceans. The name "krill" comes from the Norwegian Norwegian, Norwayan, or Norsk may refer to: *Something of, from, or related to Norway, a country in northwestern Europe * Norwegians, both a nation and an ethnic group native to Norway * Demographics of Norway *The Norwegian language, including ... word ', meaning "small fry of fish", which is also often attributed to species of fish. Krill are considered an important trophic level connection – near the bottom of the food chain. They feed on phytoplankton and (to a lesser extent) zooplankton, yet also are the main source of food for many larger animals. In the Southern Ocean, one species, the Antarctic krill, ''Euphausia superba'', makes up an estimated biomass (ecology), biomass of around 379,000,000 tonnes, making it among the species with the largest total biomass. Over half of this biomass is eaten by whales, Pinniped, seals, pen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |