|
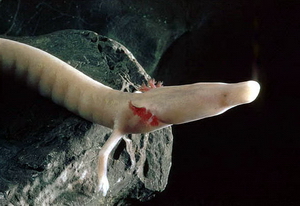
Texas Blind Salamander
The Texas blind salamander (''Eurycea rathbuni'') is a rare cave-dwelling troglobite amphibian native to San Marcos, Hays County, Texas, specifically the San Marcos Pool of the Edwards Aquifer. Description The species has a broad, flat, snout and head, and vestigial eyes beneath that are covered by skin. Like other neotenous salamanders, it has external gills for absorbing oxygen from the water. The salamander's mature length is around . The forelimbs carry four digits and the hind limbs possess five digits. Its diet varies by what flows into its cave, and includes blind shrimp (''Palaemonetes antrorum''), snails, and amphipods. Distribution and habitat Specimens have been collected at seven localities in the Purgatory Creek system and along the San Marcos Fault near San Marcos, Texas. Adults and immature larvae are well-adapted for living in underground streams in caves, and many probably inhabit deep recesses that are not accessible to collectors. Specimens have been ta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edwards Aquifer
The Edwards Aquifer is one of the most prolific artesian aquifers in the world. Located on the eastern edge of the Edwards Plateau in the U.S. state of Texas, it is the source of drinking water for two million people, and is the primary water supply for agriculture and industry in the aquifer's region. Additionally, the Edwards Aquifer feeds the Comal and San Marcos springs, provides springflow for recreational and downstream uses in the Nueces, San Antonio, Guadalupe, and San Marcos river basins, and is home to several unique and endangered species. Basin characteristics Geography Located in South Central Texas, the Edwards Aquifer encompasses an area of approximately that extends into parts of 11 counties. The aquifer's boundaries begin at the groundwater divide in Kinney County, East of Brackettville, and extend Eastward through the San Antonio area and then Northeast where the aquifer boundary ends at the Leon River in Bell County.Tremallo, Robin; Hamiton, Mark; Johns ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leonhard Hess Stejneger
Leonhard Hess Stejneger (30 October 1851 – 28 February 1943) was a Norwegian-born American ornithologist, herpetologist and zoologist. Stejneger specialized in vertebrate natural history studies. He gained his greatest reputation with reptiles and amphibians. Wetmore, Alexander (1945). "Leonhard Hess Stejneger (1851-1943)". ''Biographical Memoir. Nat. Acad. Sci.'' 24: 145-195PDF/ref> Early life and family Stejneger was born in Bergen, Norway. His father was Peter Stamer Steineger, a merchant and auditor; his mother was Ingeborg Catharine (née Hess). Leonhard was the eldest of seven children. His sister Agnes Steineger was a Norwegian artist. Until 1880, the Steineger family had been one of the wealthy families in Bergen; at that time business reverses led to the father declaring bankruptcy. Stejneger attended the Smith Theological School in Bergen from 1859 to 1860, and Bergen Latin School until 1869. His interests in zoology developed early. By age sixteen he had a pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spermatheca
The spermatheca (pronounced plural: spermathecae ), also called receptaculum seminis (plural: receptacula seminis), is an organ of the female reproductive tract in insects, e.g. ants, bees, some molluscs, oligochaeta worms and certain other invertebrates and vertebrates. Its purpose is to receive and store sperm from the male or, in the case of hermaphrodites, the male component of the body. Spermathecae can sometimes be the site of fertilization when the oocytes are sufficiently developed. Some species of animal have multiple spermathecae. For example, certain species of earthworms have four pairs of spermathecae—one pair each in the 6th, 7th, 8th, and 9th segments. The spermathecae receive and store the spermatozoa of another earthworm during copulation. They are lined with epithelium and are variable in shape: some are thin, heavily coiled tubes, while others are vague outpocketings from the main reproductive tract. It is one of the many variations in sexual reproduct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endemic Fauna Of Texas
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found elsewhere. For example, the Cape sugarbird is found exclusively in southwestern South Africa and is therefore said to be ''endemic'' to that particular part of the world. An endemic species can be also be referred to as an ''endemism'' or in scientific literature as an ''endemite''. For example '' Cytisus aeolicus'' is an endemite of the Italian flora. '' Adzharia renschi'' was once believed to be an endemite of the Caucasus, but it was later discovered to be a non-indigenous species from South America belonging to a different genus. The extreme opposite of an endemic species is one with a cosmopolitan distribution, having a global or widespread range. A rare alternative term for a species that is endemic is "precinctive", which applies to s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphibians Of The United States
Amphibians are four-limbed and ectothermic vertebrates of the class Amphibia. All living amphibians belong to the group Lissamphibia. They inhabit a wide variety of habitats, with most species living within terrestrial, fossorial, arboreal or freshwater aquatic ecosystems. Thus amphibians typically start out as larvae living in water, but some species have developed behavioural adaptations to bypass this. The young generally undergo metamorphosis from larva with gills to an adult air-breathing form with lungs. Amphibians use their skin as a secondary respiratory surface and some small terrestrial salamanders and frogs lack lungs and rely entirely on their skin. They are superficially similar to reptiles like lizards but, along with mammals and birds, reptiles are amniotes and do not require water bodies in which to breed. With their complex reproductive needs and permeable skins, amphibians are often ecological indicators; in recent decades there has been a dramatic decline ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cave Salamanders
A cave salamander is a type of salamander that primarily or exclusively inhabits caves, a group that includes several species. Some of these animals have developed special, even extreme, adaptations to their subterranean environments. Some species have only rudimentary (or even absent) eyes (''blind salamanders''). Others lack pigmentation, rendering them a pale yellowish or pinkish color (e.g., ''Eurycea rathbuni''). With the notable exception of ''Proteus anguinus'', all "cave salamanders" are members of the family Plethodontidae ("lungless salamanders"). History The first dedicated scientific study of a cave animal was focused upon a cave salamander, ''Proteus anguinus''. It was originally identified as a "dragon's larva" by Johann Weikhard von Valvasor in 1689. Later, the Austrian naturalist Joseph Nicolaus Lorenz described it scientifically in 1768. Another early scientific description of a cave salamander was undertaken by Constantine Samuel Rafinesque in 1822 while he w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ESA Endangered Species
, owners = , headquarters = Paris, Île-de-France, France , coordinates = , spaceport = Guiana Space Centre , seal = File:ESA emblem seal.png , seal_size = 130px , image = Views in the Main Control Room (12052189474).jpg , size = , caption = , acronym = , established = , employees = 2,200 , administrator = Director General Josef Aschbacher , budget = €7.2 billion (2022) , language = English and French (working languages) , website = , logo = European Space Agency logo.svg , logo_caption = Logo , image_caption = European Space Operations Centre (ESOC) Main Control Room The European Space Agency (ESA; french: Agence spatiale européenne , it, Agenzia Spaziale Europea, es, Agencia Espacial Europea ASE; german: Europäische Weltraumorganisation) is an intergovernmental organisation of 22 member states dedicated to the exploration of space. Established in 1975 and headquartered in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blanco Blind Salamander
The Blanco blind salamander (''Eurycea robusta'') is a species of aquatic, lungless salamander native to the United States. It is endemic to a small region of the Blanco River near San Marcos in Hays County, Texas. Its habitat, deep in limestone karst, makes collecting specimens for research particularly problematic. It is known from only a single specimen, collected in the 1950s. The Blanco blind salamander is considered a lost species, as it is unknown whether it is still alive or not. Four specimens were discovered in 1951 by a gravel company digging in the dry bed of the Blanco River. Two were eaten by a heron, one was lost and the final specimen was sent to the University of Texas at Austin for research. Any extant members of the species are believed to live in the Edwards Aquifer. Researchers are using environmental DNA analysis to assess whether it still lives, but are hampered by the fact that no extant viable DNA samples exist. For that reason, they are using similar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axolotl
The axolotl (; from nci, āxōlōtl ), ''Ambystoma mexicanum'', is a paedomorphic salamander closely related to the tiger salamander. Axolotls are unusual among amphibians in that they reach adulthood without undergoing metamorphosis. Instead of taking to the land, adults remain aquatic and gilled. The species was originally found in several lakes underlying what is now Mexico City, such as Lake Xochimilco and Lake Chalco. These lakes were drained by Spanish settlers after the conquest of the Aztec Empire, leading to the destruction of much of the axolotl’s natural habitat. Axolotls should not be confused with the larval stage of the closely related tiger salamander (''A. tigrinum''), which are widespread in much of North America and occasionally become paedomorphic. Neither should they be confused with mudpuppies (''Necturus'' spp.), fully aquatic salamanders from a different family that are not closely related to the axolotl but bear a superficial resemblance. , wild ax ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cloaca
In animal anatomy, a cloaca ( ), plural cloacae ( or ), is the posterior orifice that serves as the only opening for the digestive, reproductive, and urinary tracts (if present) of many vertebrate animals. All amphibians, reptiles and birds, and a few mammals ( monotremes, tenrecs, golden moles, and marsupial moles), have this orifice, from which they excrete both urine and feces; this is in contrast to most placental mammals, which have two or three separate orifices for evacuation. Excretory openings with analogous purpose in some invertebrates are also sometimes referred to as cloacae. Mating through the cloaca is known as cloacal copulation, commonly referred to as cloacal kiss. The cloacal region is also often associated with a secretory organ, the cloacal gland, which has been implicated in the scent-marking behavior of some reptiles, marsupials, amphibians, and monotremes. Etymology The word is from the Latin verb ''cluo'', "(I) cleanse", thus the noun ''cloaca'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorsum (anatomy)
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals, including humans. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position provides a definition of what is at the front ("anterior"), behind ("posterior") and so on. As part of defining and describing terms, the body is described through the use of anatomical planes and anatomical axes. The meaning of terms that are used can change depending on whether an organism is bipedal or quadrupedal. Additionally, for some animals such as invertebrates, some terms may not have any meaning at all; for example, an animal that is radially symmetrical will have no anterior surface, but can still have a description that a part is close to the middle ("proximal") or further from the middle ("distal"). International organisations have determined vocabularies that are often used as standard vocabularies for subdisciplines of anatom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)
.png)