|
Texas Vampires
The Texas Vampires were a name given to a group of researchers from Baylor College of Medicine who in 1998 conducted a study on arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia (ARVD) among the population of Grand Falls-Windsor, Newfoundland and Labrador, Canada. The study team was led by Dr. Robert Roberts (cardiologist), who was president and CEO of the University of Ottawa Heart Institute from 2004–2014. Because of the settlement pattern and isolation of the province's population, Newfoundland has clusters of certain genetic conditions, making it a focus of research in genetics. In 1998, one such cluster emerged in the community of Grand Falls-Windsor, where a number of people were found to have ARVD and some died of the condition. A group of researchers from the Baylor College of Medicine arrived in Newfoundland to study the community. The group collected blood samples, family histories and electrocardiographs (EKGs) from community members in order to test for a particular biom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Roberts (cardiologist)
Robert Roberts (born in Grole, Newfoundland, Canada), is a cardiologist, geneticist, speaker and educator, who is regarded as one of the founders of molecular cardiology, pioneering the genetic causes of heart disease He is currently the chief executive officer of RDS Inc., executive director of the Heart and Vascular Institute and Director of Cardiovascular Genetics and Genomics at Dignity Health at St Joseph's Hospital & Medical Center, Chair of the International Society of Cardiovascular Translational Research at the University of Arizona College of Medicine, and a Professor of Medicine at the University of Arizona College of Medicine. Dr. Roberts’ accomplished career as a geneticist and cardiologist also includes leading the cardiology department at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston for 23 years, serving as the President and CEO of the University of Ottawa Heart Institute, and working with NASA as a cardiology consultant where he cleared astronaut, John Glenn, to take f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newfoundland And Labrador Map
Newfoundland and Labrador (; french: Terre-Neuve-et-Labrador; frequently abbreviated as NL) is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region of Labrador, having a total size of 405,212 square kilometres (156,500 sq mi). In 2021, the population of Newfoundland and Labrador was estimated to be 521,758. The island of Newfoundland (and its smaller neighbouring islands) is home to around 94 per cent of the province's population, with more than half residing in the Avalon Peninsula. Labrador borders the province of Quebec, and the French overseas collectivity of Saint Pierre and Miquelon lies about 20 km west of the Burin Peninsula. According to the 2016 census, 97.0 per cent of residents reported English as their native language, making Newfoundland and Labrador Canada's most linguistically homogeneous province. A majority of the population is descended from English and Irish set ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baylor College Of Medicine
Baylor College of Medicine (BCM) is a medical school and research center in Houston, Texas, within the Texas Medical Center, the world's largest medical center. BCM is composed of four academic components: the School of Medicine, the Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences; the School of Health Professions, and the National School of Tropical Medicine. The school is part owner, alongside Catholic Health Initiatives (CHI), of St. Luke's Episcopal Hospital, Baylor St. Luke's Medical Center, the flagship hospital of the CHI St. Luke's Health system. Other affiliated teaching hospitals and research institutes include Harris Health System, Harris Health System's Ben Taub Hospital, Texas Children's Hospital, The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, TIRR Memorial Hermann, the Menninger Clinic, the Michael E. DeBakey Veterans Affairs Medical Center in Houston, Michael E. DeBakey VA Medical Center, and the Christus Santa Rosa Health System, Children's Hospital of San Antonio. On ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia
Arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy (ACM), arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia (ARVD), or arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC), most commonly is an inherited heart disease. ACM is caused by genetic defects of the parts of heart muscle (also called ''myocardium'' or ''cardiac muscle'') known as desmosomes, areas on the surface of heart muscle cells which link the cells together. The desmosomes are composed of several proteins, and many of those proteins can have harmful mutations. ARVC can also develop in intense endurance athletes in the absence of desmosomal abnormalities. Exercise-induced ARVC cause possibly is a result of excessive right ventricular wall stress during high intensity exercise. The disease is a type of non-ischemic cardiomyopathy that primarily involves the right ventricle, though cases of exclusive left ventricular disease have been reported. It is characterized by hypokinetic areas involving the free wall of the ventricle, with fibrofatt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Falls-Windsor, Newfoundland And Labrador
Grand Falls-Windsor is a town located in the central region of the island of Newfoundland in the province of Newfoundland and Labrador, Canada, with a population of 13,853 at the 2021 census. The town is the largest in the central region, the sixth largest in the province, and is home to the annual Exploits Valley Salmon Festival. Grand Falls-Windsor was incorporated in 1991, when the two former towns of Grand Falls and Windsor amalgamated. Grand Falls-Windsor is one of two major population centres in Central Newfoundland. The town is known as "''Qapskuk''" in the Mi'kmaq language. History In 1768, Lieutenant John Cartwright, while following the Exploits River through the Exploits Valley, named the waterfall he found "Grand Falls". The land remained undeveloped until 1905, except for the Newfoundland Railway which ran about north of Grand Falls. The railway offered development potential. In 1905, the town of Grand Falls was established as a company town using Garden City ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Ottawa Heart Institute
The University of Ottawa Heart Institute (UOHI) ''(French: Institut de cardiologie de l'Université d'Ottawa (ICUO))'' is Canada's largest cardiovascular health centre. It is located in Ottawa, Ontario, Canada. It began as a department in The Ottawa Hospital, and since has evolved into Canada's only complete cardiac centre, encompassing prevention, diagnosis, treatment, rehabilitation, research, and education. UOHI cares for more than 100,000 cardiac patients each year, and patient satisfaction is among the highest in Ontario, averaging 98 percent. The Heart Institute is affiliated with the Ottawa Hospital and the University of Ottawa, specifically the Faculty of Medicine. The institute also provides training to more than 100 physicians annually and runs an extensive cardiovascular research program, with 60 principal investigators and research funding of approximately $65 million a year. History UOHI was founded in 1976 by Dr. Wilbert Keon, with financial support from the Ontario ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Informed Consent
Informed consent is a principle in medical ethics and medical law, that a patient must have sufficient information and understanding before making decisions about their medical care. Pertinent information may include risks and benefits of treatments, alternative treatments, the patient's role in treatment, and their right to refuse treatment. In most systems, healthcare providers have a legal and ethical responsibility to ensure that a patient's consent is informed. This principle applies more broadly than healthcare intervention, for example to conduct research and to disclosing a person's medical information. Definitions of informed consent vary, and the standard required is generally determined by the state. Informed consent requires a clear appreciation and understanding of the facts, implications, and consequences of an action. To give informed consent, the individual concerned must have adequate reasoning faculties and possess all relevant facts. Impairments to reasoning an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
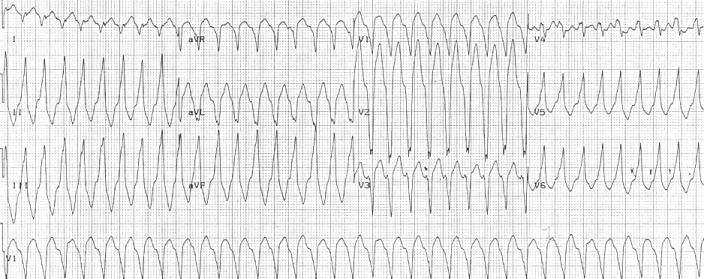
Electrocardiography
Electrocardiography is the process of producing an electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG), a recording of the heart's electrical activity. It is an electrogram of the heart which is a graph of voltage versus time of the electrical activity of the heart using electrodes placed on the skin. These electrodes detect the small electrical changes that are a consequence of cardiac muscle depolarization followed by repolarization during each cardiac cycle (heartbeat). Changes in the normal ECG pattern occur in numerous cardiac abnormalities, including cardiac rhythm disturbances (such as atrial fibrillation and ventricular tachycardia), inadequate coronary artery blood flow (such as myocardial ischemia and myocardial infarction), and electrolyte disturbances (such as hypokalemia and hyperkalemia). Traditionally, "ECG" usually means a 12-lead ECG taken while lying down as discussed below. However, other devices can record the electrical activity of the heart such as a Holter monitor but also s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian Broadcasting Corporation
The Canadian Broadcasting Corporation (french: Société Radio-Canada), branded as CBC/Radio-Canada, is a Canadian public broadcaster for both radio and television. It is a federal Crown corporation that receives funding from the government. The English- and French-language service units of the corporation are commonly known as CBC and Radio-Canada, respectively. Although some local stations in Canada predate the CBC's founding, CBC is the oldest existing broadcasting network in Canada. The CBC was established on November 2, 1936. The CBC operates four terrestrial radio networks: The English-language CBC Radio One and CBC Music, and the French-language Ici Radio-Canada Première and Ici Musique. (International radio service Radio Canada International historically transmitted via shortwave radio, but since 2012 its content is only available as podcasts on its website.) The CBC also operates two terrestrial television networks, the English-language CBC Television and the Frenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circulation (journal)
''Circulation'' is a scientific journal published by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins for the American Heart Association. The journal publishes articles related to research in and the practice of cardiovascular diseases, including observational studies, clinical trials, epidemiology, health services and outcomes studies, and advances in applied (translational) and basic research. Its 2020 impact factor is 29.690, ranking it third among journals in the Cardiac and Cardiovascular Systems category and first in the Peripheral Vascular Disease category.2020 Journal Citation Reports (Clarivate Analytics, 2021) Articles become open access after a 12-month embargo period. 2008 saw the appearance of six subspecialty journals. The first edition of ''Circulation: Arrhythmia and Electrophysiology'' appeared in April 2008, followed by an edition dedicated to heart failure in May titled ''Circulation: Heart Failure''. The remaining four journals launched once per month from July through October ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Ethics
Medical ethics is an applied branch of ethics which analyzes the practice of clinical medicine and related scientific research. Medical ethics is based on a set of values that professionals can refer to in the case of any confusion or conflict. These values include the respect for autonomy, non-maleficence, beneficence, and justice. Such tenets may allow doctors, care providers, and families to create a treatment plan and work towards the same common goal. It is important to note that these four values are not ranked in order of importance or relevance and that they all encompass values pertaining to medical ethics. However, a conflict may arise leading to the need for hierarchy in an ethical system, such that some moral elements overrule others with the purpose of applying the best moral judgement to a difficult medical situation. Medical ethics is particularly relevant in decisions regarding involuntary treatment and involuntary commitment. There are several codes of conduct. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Subject Research In Canada
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, and language. Humans are highly social and tend to live in complex social structures composed of many cooperating and competing groups, from families and kinship networks to political states. Social interactions between humans have established a wide variety of values, social norms, and rituals, which bolster human society. Its intelligence and its desire to understand and influence the environment and to explain and manipulate phenomena have motivated humanity's development of science, philosophy, mythology, religion, and other fields of study. Although some scientists equate the term ''humans'' with all members of the genus '' Homo'', in common usage, it generally refers to ''Homo sapiens'', the only extant member. Anatom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |