|
Ternary Signal
In telecommunication, a ternary signal is a signal that can assume, at any given instant, one of three states or significant conditions, such as power level, phase position, pulse duration, or frequency. Examples of ternary signals are (a) a pulse that can have a positive, zero, or negative voltage value at any given instant ( PAM-3), (b) a sine wave that can assume phases of 0°, 120°, or 240° relative to a clock A clock or a timepiece is a device used to measure and indicate time. The clock is one of the oldest human inventions, meeting the need to measure intervals of time shorter than the natural units such as the day, the lunar month and the ... pulse (3-phase-shift keying, PSK), and (c) a carrier signal that can assume any one of three different frequencies depending on three different modulation signal significant conditions (3-frequency modulation, FM). Some examples of PAM-3 line codes that use ternary signals are: * hybrid ternary code * bipolar encoding * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telecommunication
Telecommunication is the transmission of information by various types of technologies over wire, radio, optical, or other electromagnetic systems. It has its origin in the desire of humans for communication over a distance greater than that feasible with the human voice, but with a similar scale of expediency; thus, slow systems (such as postal mail) are excluded from the field. The transmission media in telecommunication have evolved through numerous stages of technology, from beacons and other visual signals (such as smoke signals, semaphore telegraphs, signal flags, and optical heliographs), to electrical cable and electromagnetic radiation, including light. Such transmission paths are often divided into communication channels, which afford the advantages of multiplexing multiple concurrent communication sessions. ''Telecommunication'' is often used in its plural form. Other examples of pre-modern long-distance communication included audio messages, such as coded drumb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fast Ethernet
In computer networking, Fast Ethernet physical layers carry traffic at the nominal rate of 100 Mbit/s. The prior Ethernet speed was 10 Mbit/s. Of the Fast Ethernet physical layers, 100BASE-TX is by far the most common. Fast Ethernet was introduced in 1995 as the IEEE 802.3u standard and remained the fastest version of Ethernet for three years before the introduction of Gigabit Ethernet. The acronym ''GE/FE'' is sometimes used for devices supporting both standards. Nomenclature The "100" in the media type designation refers to the transmission speed of 100 Mbit/s, while the "BASE" refers to baseband signaling. The letter following the dash ("T" or "F") refers to the physical medium that carries the signal (twisted pair or fiber, respectively), while the last character ("X", "4", etc.) refers to the line code method used. Fast Ethernet is sometimes referred to as 100BASE-X, where "X" is a placeholder for the FX and TX variants. General design Fast Ethernet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Three-phase Electric Power
Three-phase electric power (abbreviated 3φ) is a common type of alternating current used in electricity generation, transmission, and distribution. It is a type of polyphase system employing three wires (or four including an optional neutral return wire) and is the most common method used by electrical grids worldwide to transfer power. Three-phase electrical power was developed in the 1880s by multiple people. Three-phase power works by the voltage and currents being 120 degrees out of phase on the three wires. As an AC system it allows the voltages to be easily stepped up using transformers to high voltage for transmission, and back down for distribution, giving high efficiency. A three-wire three-phase circuit is usually more economical than an equivalent two-wire single-phase circuit at the same line to ground voltage because it uses less conductor material to transmit a given amount of electrical power. Three-phase power is mainly used directly to power large induction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ternary Computer
A ternary computer, also called trinary computer, is one that uses ternary logic (i.e., base 3) instead of the more common binary system (i.e., base 2) in its calculations. This means it uses trits (instead of bits, as most computers do). Types of states Ternary computing deals with three discrete states, but the ternary digits themselves can be defined differently: Ternary quantum computers use qutrits rather than trits. A qutrit is a quantum state that is a complex unit vector in three dimensions, which can be written as , \Psi\rangle = \alpha, 0\rangle + \beta, 1\rangle + \gamma, 2\rangle in the bra-ket notation. The labels given to the basis vectors (, 0\rangle, , 1\rangle, , 2\rangle) can be replaced with other labels, for example those given above. History One early calculating machine, built entirely from wood by Thomas Fowler in 1840, operated in balanced ternary. The first modern, electronic ternary computer, Setun, was built in 1958 in the Soviet Union at the M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
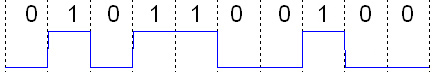
Digital Signal (electronics)
A digital signal is a signal that represents data as a sequence of discrete values; at any given time it can only take on, at most, one of a finite number of values. This contrasts with an analog signal, which represents continuous values; at any given time it represents a real number within a continuous range of values. Simple digital signals represent information in discrete bands of analog levels. All levels within a band of values represent the same information state. In most digital circuits, the signal can have two possible valid values; this is called a binary signal or logic signal. They are represented by two voltage bands: one near a reference value (typically termed as ''ground'' or zero volts), and the other a value near the supply voltage. These correspond to the two values "zero" and "one" (or "false" and "true") of the Boolean domain, so at any given time a binary signal represents one binary digit (bit). Because of this discretization, relatively small chan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balanced Ternary
Balanced ternary is a ternary numeral system (i.e. base 3 with three digits) that uses a balanced signed-digit representation of the integers in which the digits have the values −1, 0, and 1. This stands in contrast to the standard (unbalanced) ternary system, in which digits have values 0, 1 and 2. The balanced ternary system can represent all integers without using a separate minus sign; the value of the leading non-zero digit of a number has the sign of the number itself. The balanced ternary system is an example of a non-standard positional numeral system. It was used in some early computers and also in some solutions of balance puzzles. Different sources use different glyphs used to represent the three digits in balanced ternary. In this article, T (which resembles a ligature of the minus sign and 1) represents −1, while 0 and 1 represent themselves. Other conventions include using '−' and '+' to represent −1 and 1 respectively, or using Greek letter theta (Θ), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
QPSK
Phase-shift keying (PSK) is a digital modulation process which conveys data by changing (modulating) the phase of a constant frequency reference signal (the carrier wave). The modulation is accomplished by varying the sine and cosine inputs at a precise time. It is widely used for wireless LANs, RFID and Bluetooth communication. Any digital modulation scheme uses a finite number of distinct signals to represent digital data. PSK uses a finite number of phases, each assigned a unique pattern of binary digits. Usually, each phase encodes an equal number of bits. Each pattern of bits forms the symbol that is represented by the particular phase. The demodulator, which is designed specifically for the symbol-set used by the modulator, determines the phase of the received signal and maps it back to the symbol it represents, thus recovering the original data. This requires the receiver to be able to compare the phase of the received signal to a reference signal such a system is termed c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BPSK
Phase-shift keying (PSK) is a digital modulation process which conveys Data (computing), data by changing (modulating) the Phase (waves), phase of a constant frequency reference signal (the carrier wave). The modulation is accomplished by varying the sine wave, sine and cosine wave, cosine inputs at a precise time. It is widely used for wireless LANs, RFID and Bluetooth communication. Any digital modulation scheme uses a finite number of distinct signals to represent digital data. PSK uses a finite number of phases, each assigned a unique pattern of bit, binary digits. Usually, each phase encodes an equal number of bits. Each pattern of bits forms the symbol rate, symbol that is represented by the particular phase. The demodulator, which is designed specifically for the symbol-set used by the modulator, determines the phase of the received signal and maps it back to the symbol it represents, thus recovering the original data. This requires the receiver to be able to compare the ph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IEEE
The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) is a 501(c)(3) professional association for electronic engineering and electrical engineering (and associated disciplines) with its corporate office in New York City and its operations center in Piscataway, New Jersey. The mission of the IEEE is ''advancing technology for the benefit of humanity''. The IEEE was formed from the amalgamation of the American Institute of Electrical Engineers and the Institute of Radio Engineers in 1963. Due to its expansion of scope into so many related fields, it is simply referred to by the letters I-E-E-E (pronounced I-triple-E), except on legal business documents. , it is the world's largest association of technical professionals with more than 423,000 members in over 160 countries around the world. Its objectives are the educational and technical advancement of electrical and electronic engineering, telecommunications, computer engineering and similar disciplines. History Origin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DQPSK
Phase-shift keying (PSK) is a digital modulation process which conveys data by changing (modulating) the phase of a constant frequency reference signal (the carrier wave). The modulation is accomplished by varying the sine and cosine inputs at a precise time. It is widely used for wireless LANs, RFID and Bluetooth communication. Any digital modulation scheme uses a finite number of distinct signals to represent digital data. PSK uses a finite number of phases, each assigned a unique pattern of binary digits. Usually, each phase encodes an equal number of bits. Each pattern of bits forms the symbol that is represented by the particular phase. The demodulator, which is designed specifically for the symbol-set used by the modulator, determines the phase of the received signal and maps it back to the symbol it represents, thus recovering the original data. This requires the receiver to be able to compare the phase of the received signal to a reference signal such a system is termed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Return-to-zero
Return-to-zero (RZ or RTZ) describes a line code used in telecommunications signals in which the signal drops (returns) to zero between each pulse. This takes place even if a number of consecutive 0s or 1s occur in the signal. The signal is self-clocking. This means that a separate clock does not need to be sent alongside the signal, but suffers from using twice the bandwidth to achieve the same data-rate as compared to non-return-to-zero format. The "zero" between each bit is a neutral or rest condition, such as a zero amplitude in pulse-amplitude modulation (PAM), zero phase shift in phase-shift keying (PSK), or mid-frequency in frequency-shift keying (FSK). That "zero" condition is typically halfway between the significant condition representing a 1 bit and the other significant condition representing a 0 bit. Although return-to-zero (RZ) contains a provision for synchronization, it still has a DC component resulting in “baseline wander” during long strings of 0 or 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |