|
Terbium Phosphide
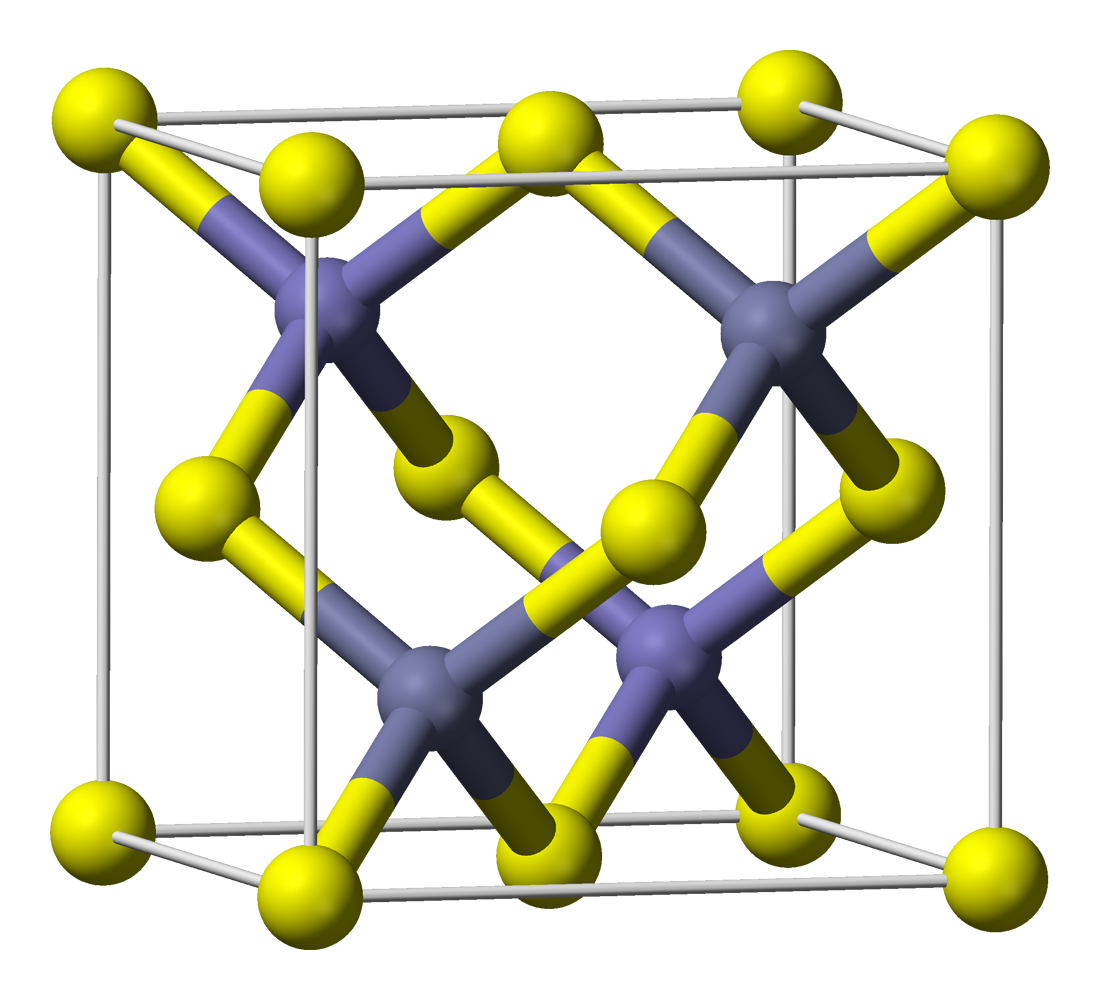
Terbium phosphide is an inorganic compound of terbium and phosphorus with the chemical formula TbP. Synthesis TbP can be obtained by the reaction of terbium and red phosphorus at 800–1000 °C: ::4 Tb + P4 → 4 TbP The compound can also be obtained by the reaction of sodium phosphide and anhydrous terbium chloride at 700~800 °C. Physical properties TbP undergoes a phase transition at 40 GPa from a NaCl-structure to a CsCl-structure. The compound can be sintered with zinc sulfide to make a green phosphor layer. TbP forms crystals of a cubic system, space group ''Fm''3''m''. Uses The compound is a semiconductor used in high power, high frequency applications and in laser diodes and other photo diode A photodiode is a light-sensitive semiconductor diode. It produces current when it absorbs photons. The package of a photodiode allows light (or infrared or ultraviolet radiation, or X-rays) to reach the sensitive part of the device. The packa ...s. References {{Phosph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inorganic Compound
In chemistry, an inorganic compound is typically a chemical compound that lacks carbon–hydrogen bonds, that is, a compound that is not an organic compound. The study of inorganic compounds is a subfield of chemistry known as '' inorganic chemistry''. Inorganic compounds comprise most of the Earth's crust, although the compositions of the deep mantle remain active areas of investigation. Some simple carbon compounds are often considered inorganic. Examples include the allotropes of carbon (graphite, diamond, buckminsterfullerene, etc.), carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, carbides, and the following salts of inorganic anions: carbonates, cyanides, cyanates, and thiocyanates. Many of these are normal parts of mostly organic systems, including organisms; describing a chemical as inorganic does not necessarily mean that it does not occur within living things. History Friedrich Wöhler's conversion of ammonium cyanate into urea in 1828 is often cited as the starting point of modern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physics Letters A
''Physics Letters'' was a scientific journal published from 1962 to 1966, when it split in two series now published by Elsevier: *''Physics Letters A'': condensed matter physics, theoretical physics, nonlinear science, statistical physics, mathematical and computational physics, general and cross-disciplinary physics (including foundations), atomic, molecular and cluster physics, plasma and fluid physics, optical physics, biological physics and nanoscience. *''Physics Letters B'': nuclear physics, theoretical nuclear physics, experimental high-energy physics, theoretical high-energy physics, and astrophysics. ''Physics Letters B'' is part of the SCOAP3 initiative. References See also * List of periodicals published by Elsevier This is a list of scientific, technical and general interest periodicals published by Elsevier or one of its imprints or subsidiary companies. Both printed items and electronic publications are included in this list. A B C D E F G ... ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terbium Compounds
Terbium compounds are compounds formed by the lanthanide metal terbium (Tb). Terbium generally exhibits the +3 oxidation state in these compounds, such as in TbCl3, Tb(NO3)3 and Tb(CH3COO)3. Compounds with terbium in the +4 oxidation state are also known, such as TbO2 and BaTbF6. Terbium can also form compounds in the 0, +1 and +2 oxidation states. The trivalent terbium ion is generally colorless in aqueous solution, and when it is irradiated by certain wavelengths of ultraviolet light (such as 254 nm or 365 nm) in solution or crystal form, it will emit green fluorescence. This property has given rise to applications in fields such as optics. Properties of terbium compounds Chalcogenides Oxides Terbium has a variety of oxides. The most easily obtained is terbium(III,IV) oxide, which can be produced by the decomposition of terbium compounds such as the hydroxide,Chen Shouchun. Important Inorganic Chemical Reactions. Shanghai Science and Technology Press, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphides
In chemistry, a phosphide is a compound containing the ion or its equivalent. Many different phosphides are known, with widely differing structures. Most commonly encountered on the binary phosphides, i.e. those materials consisting only of phosphorus and a less electronegative element. Numerous are polyphosphides, which are solids consisting of anionic chains or clusters of phosphorus. Phosphides are known with the majority of less electronegative elements with the exception of Hg, Pb, Sb, Bi, Te, and Po.Von Schnering, H.G. and Hönle , W. (1994) "Phosphides - Solid-state Chemistry" in ''Encyclopedia of Inorganic Chemistry''. R. Bruce King (ed.). John Wiley & Sons Finally, some phosphides are molecular. Binary phosphides Binary phosphides include phosphorus and one other element. An example of a group 1 phosphide is sodium phosphide (). Other notable examples include aluminium phosphide () and calcium phosphide (), which are used as pesticides, exploiting their tendenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photo Diode
A photodiode is a light-sensitive semiconductor diode. It produces current when it absorbs photons. The package of a photodiode allows light (or infrared or ultraviolet radiation, or X-rays) to reach the sensitive part of the device. The package may include lenses or optical filters. Devices designed for use specially as a photodiode use a PIN junction rather than a p–n junction, to increase the speed of response. Photodiodes usually have a slower response time as their surface area increases. A photodiode is designed to operate in reverse bias. A solar cell used to generate electric solar power is a large area photodiode. Photodiodes are used in scientific and industrial instruments to measure light intensity, either for its own sake or as a measure of some other property (density of smoke, for example). A photodiode can be used as the receiver of data encoded on an infrared beam, as in household remote controls. Photodiodes can be used to form an optocoupler, allowing tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laser Diode
file:Laser diode chip.jpg, The laser diode chip removed and placed on the eye of a needle for scale A laser diode (LD, also injection laser diode or ILD, or diode laser) is a semiconductor device similar to a light-emitting diode in which a diode pumped directly with electrical current can create active laser medium, lasing conditions at the diode's p–n junction, junction. Driven by voltage, the doped p–n-transition allows for Carrier generation and recombination, recombination of an electron with a Electron hole, hole. Due to the drop of the electron from a higher energy level to a lower one, radiation, in the form of an emitted photon is generated. This is spontaneous emission. Stimulated emission can be produced when the process is continued and further generates light with the same phase, coherence and wavelength. The choice of the semiconductor material determines the wavelength of the emitted beam, which in today's laser diodes range from infra-red to the UV spectrum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material which has an electrical resistivity and conductivity, electrical conductivity value falling between that of a electrical conductor, conductor, such as copper, and an insulator (electricity), insulator, such as glass. Its electrical resistivity and conductivity, resistivity falls as its temperature rises; metals behave in the opposite way. Its conducting properties may be altered in useful ways by introducing impurities ("doping (semiconductor), doping") into the crystal structure. When two differently doped regions exist in the same crystal, a semiconductor junction is created. The behavior of charge carriers, which include electrons, ions, and electron holes, at these junctions is the basis of diodes, transistors, and most modern electronics. Some examples of semiconductors are silicon, germanium, gallium arsenide, and elements near the so-called "metalloid staircase" on the periodic table. After silicon, gallium arsenide is the second-most common s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Group
In mathematics, physics and chemistry, a space group is the symmetry group of an object in space, usually in three dimensions. The elements of a space group (its symmetry operations) are the rigid transformations of an object that leave it unchanged. In three dimensions, space groups are classified into 219 distinct types, or 230 types if chiral copies are considered distinct. Space groups are discrete cocompact groups of isometries of an oriented Euclidean space in any number of dimensions. In dimensions other than 3, they are sometimes called Bieberbach groups. In crystallography, space groups are also called the crystallographic or Fedorov groups, and represent a description of the symmetry of the crystal. A definitive source regarding 3-dimensional space groups is the ''International Tables for Crystallography'' . History Space groups in 2 dimensions are the 17 wallpaper groups which have been known for several centuries, though the proof that the list was complete was only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cubic System
In crystallography, the cubic (or isometric) crystal system is a crystal system where the unit cell is in the shape of a cube. This is one of the most common and simplest shapes found in crystals and minerals. There are three main varieties of these crystals: *Primitive cubic (abbreviated ''cP'' and alternatively called simple cubic) *Body-centered cubic (abbreviated ''cI'' or bcc) *Face-centered cubic (abbreviated ''cF'' or fcc, and alternatively called ''cubic close-packed'' or ccp) Each is subdivided into other variants listed below. Although the ''unit cells'' in these crystals are conventionally taken to be cubes, the primitive unit cells often are not. Bravais lattices The three Bravais lattices in the cubic crystal system are: The primitive cubic lattice (cP) consists of one lattice point on each corner of the cube; this means each simple cubic unit cell has in total one lattice point. Each atom at a lattice point is then shared equally between eight adjacent cubes, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zinc Sulfide
Zinc sulfide (or zinc sulphide) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula of ZnS. This is the main form of zinc found in nature, where it mainly occurs as the mineral sphalerite. Although this mineral is usually black because of various impurities, the pure material is white, and it is widely used as a pigment. In its dense synthetic form, zinc sulfide can be transparent, and it is used as a window for visible optics and infrared optics. Structure ZnS exists in two main crystalline forms. This dualism is an example of polymorphism. In each form, the coordination geometry at Zn and S is tetrahedral. The more stable cubic form is known also as zinc blende or sphalerite. The hexagonal form is known as the mineral wurtzite, although it also can be produced synthetically.. The transition from the sphalerite form to the wurtzite form occurs at around 1020 °C. A tetragonal form is also known as the very rare mineral called polhemusite, with the formula . Applicatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CsCl China.
{{disambig ...
CSCL can refer to: * Caesium chloride (CsCl), a chemical compound. * Computer Supported Collaborative Learning, a research topic on supporting collaborative learning with the assistance of computer artifacts. * China Shipping Container Lines, a containerized marine shipping company, based in Shanghai Shanghai (; , , Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ) is one of the four direct-administered municipalities of the People's Republic of China (PRC). The city is located on the southern estuary of the Yangtze River, with the Huangpu River flow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |