|
Tendaguripterus
''Tendaguripterus'' was a genus of pterodactyloid pterosaur from the Kimmeridgian to Tithonian-age Upper Jurassic Middle Saurian Beds (Tendaguru Formation) of Tendaguru, Lindi Region, Tanzania. Discovery and naming During the German paleontological expeditions to German East Africa between 1909 and 1913, some pterosaur fossil material was collected that was recognized as such by Hans Reck in 1931. In 1999 David Unwin and Wolf-Dieter Heinrich named a new genus for it. The type species is ''Tendaguripterus recki''. The genus name is derived from Tendaguru and a Latinized Greek ''pteron'', "wing". The specific name honors Reck. Description The genus is based on holotype MB.R.1290, a partial mandible with teeth (the symphyseal region, where the two lower jaws meet and fuse into one element). The top of the back of the symphysis is very concave. The teeth in the posterior section of the jaw fragment point strongly backwards. They are also the longest. The teeth are set relativel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tendaguripteridae
''Tendaguripterus'' was a genus of pterodactyloid pterosaur from the Kimmeridgian to Tithonian-age Upper Jurassic Middle Saurian Beds ( Tendaguru Formation) of Tendaguru, Lindi Region, Tanzania. Discovery and naming During the German paleontological expeditions to German East Africa between 1909 and 1913, some pterosaur fossil material was collected that was recognized as such by Hans Reck in 1931. In 1999 David Unwin and Wolf-Dieter Heinrich named a new genus for it. The type species is ''Tendaguripterus recki''. The genus name is derived from Tendaguru and a Latinized Greek ''pteron'', "wing". The specific name honors Reck. Description The genus is based on holotype MB.R.1290, a partial mandible with teeth (the symphyseal region, where the two lower jaws meet and fuse into one element). The top of the back of the symphysis is very concave. The teeth in the posterior section of the jaw fragment point strongly backwards. They are also the longest. The teeth are set relati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germanodactylidae
Germanodactylidae is a controversial group of pterosaurs within the suborder Pterodactyloidea. It was first named by Yang Zhongjian in 1964, and given a formal phylogenetic definition in 2014 by Brian Andres, James Clark, and Xu Xing. They defined it as the least inclusive clade containing ''Germanodactylus cristatus'' and ''Normannognathus wellnhoferi'', which they considered to be close relatives at the time. However, more recent studies by the same researchers have found that these pterosaurs may be only distantly related. Studies performed in the 2000s suggested this group it contained three genera: ''Germanodactylus'', '' Normannognathus'' and ''Tendaguripterus''. Various studies have since placed these pterosaurs within the larger clades Archaeopterodactyloidea, Eupterodactyloidea, or Dsungaripteroidea, though it has also been recovered within the Ctenochasmatoidea. In several 2010s studies, the supposed "germanodactylid" species were not necessarily found to form a natur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Pterosaur Genera
This list of pterosaurs is a comprehensive listing of all genera that have ever been included in the order Pterosauria, excluding purely vernacular terms. The list includes all commonly accepted genera, but also genera that are now considered invalid, doubtful (''nomen dubium''), or were not formally published (''nomen nudum''), as well as junior synonyms of more established names, and genera that are no longer considered pterosaurian. The list currently includes 263 genera. Scope and terminology There is no official, canonical list of pterosaur genera, but the most thorough attempts can be found at the Pterosauria section of Mikko Haaramo's ''Phylogeny Archive'', the Genus Index at Mike Hanson's ''The Pterosauria'', supplemented by the Pterosaur Species List, and in the fourth supplement of Donald F. Glut's ''Dinosaurs: The Encyclopedia'' series. Authors and year The authors column lists the authors of the formal description responsible for the erection of the genus listed. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
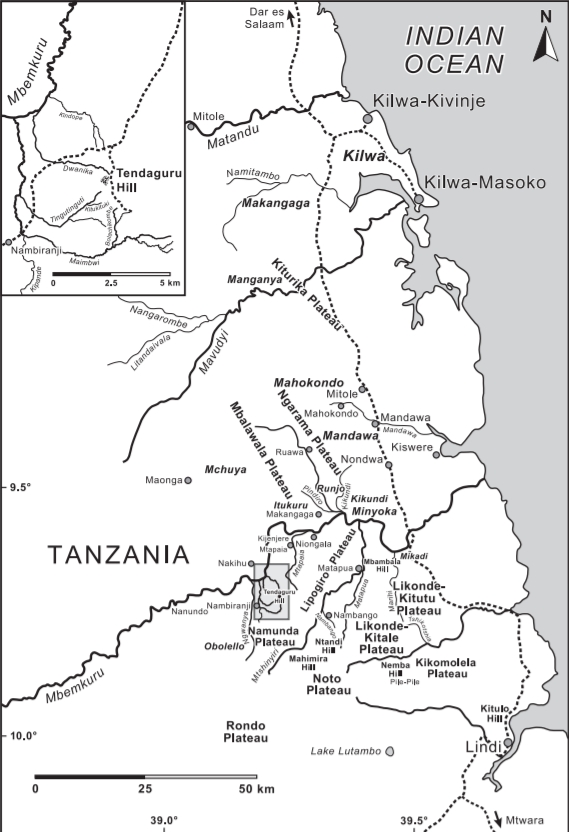
Tendaguru Formation
The Tendaguru Formation, or Tendaguru Beds are a highly fossiliferous formation and Lagerstätte located in the Lindi Region of southeastern Tanzania. The formation represents the oldest sedimentary unit of the Mandawa Basin, overlying Neoproterozoic basement, separating by a long hiatus and unconformity. The formation reaches a total sedimentary thickness of more than . The formation ranges in age from the late Middle Jurassic to the Early Cretaceous, Oxfordian to Hauterivian stages, with the base of the formation possibly extending into the Callovian. The Tendaguru Formation is subdivided into six members; from oldest to youngest Lower Dinosaur Member, the ''Nerinella'' Member, the Middle Dinosaur Member, ''Indotrigonia africana'' Member, the Upper Dinosaur Member, and the ''Rutitrigonia bornhardti-schwarzi'' Member. The succession comprises a sequence of sandstones, shales, siltstones, conglomerates with minor oolitic limestones, deposited in an overall shallow marine to c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandible
In anatomy, the mandible, lower jaw or jawbone is the largest, strongest and lowest bone in the human facial skeleton. It forms the lower jaw and holds the lower tooth, teeth in place. The mandible sits beneath the maxilla. It is the only movable bone of the skull (discounting the ossicles of the middle ear). It is connected to the temporal bones by the temporomandibular joints. The bone is formed prenatal development, in the fetus from a fusion of the left and right mandibular prominences, and the point where these sides join, the mandibular symphysis, is still visible as a faint ridge in the midline. Like other symphyses in the body, this is a midline articulation where the bones are joined by fibrocartilage, but this articulation fuses together in early childhood.Illustrated Anatomy of the Head and Neck, Fehrenbach and Herring, Elsevier, 2012, p. 59 The word "mandible" derives from the Latin word ''mandibula'', "jawbone" (literally "one used for chewing"), from ''wikt:mandere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clade
A clade (), also known as a monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that are monophyletic – that is, composed of a common ancestor and all its lineal descendants – on a phylogenetic tree. Rather than the English term, the equivalent Latin term ''cladus'' (plural ''cladi'') is often used in taxonomical literature. The common ancestor may be an individual, a population, or a species (extinct or extant). Clades are nested, one in another, as each branch in turn splits into smaller branches. These splits reflect evolutionary history as populations diverged and evolved independently. Clades are termed monophyletic (Greek: "one clan") groups. Over the last few decades, the cladistic approach has revolutionized biological classification and revealed surprising evolutionary relationships among organisms. Increasingly, taxonomists try to avoid naming taxa that are not clades; that is, taxa that are not monophyletic. Some of the relationships between organisms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pterodactyloidea
Pterodactyloidea (derived from the Greek words ''πτερόν'' (''pterón'', for usual ''ptéryx'') "wing", and ''δάκτυλος'' (''dáktylos'') "finger" meaning "winged finger", "wing-finger" or "finger-wing") is one of the two traditional suborders of pterosaurs ("wing lizards"), and contains the most derived members of this group of flying reptiles. They appeared during the middle Jurassic Period, and differ from the basal (though paraphyletic) rhamphorhynchoids by their short tails and long wing metacarpals (hand bones). The most advanced forms also lack teeth, and by the late Cretaceous, all known pterodactyloids were toothless. Many species had well-developed crests on the skull, a form of display taken to extremes in giant-crested forms like ''Nyctosaurus'' and ''Tupandactylus''. Pterodactyloids were the last surviving pterosaurs when the order became extinct at the end of the Cretaceous Period, together with the non-avian dinosaurs and most marine reptiles. "Pteroda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dsungaripterus
''Dsungaripterus'' is a genus of dsungaripterid pterosaur with an average wingspan of . ''Dsungaripterus'' lived during the Early Cretaceous in what is now China, and its first fossil was found in the Junggar Basin. Description ''Dsungaripterus weii'' had a wing span of . Like most dsungaripteroids it had a rather robust skeleton with thick walls and stouty bodily proportions, suggesting a mostly terrestrial lifestyle. The flight style of these animals is unclear, but it was probably punctuated by abrupt landings and extensive flapping. The skull of ''Dsungaripterus'', long, bore a low bone crest that ran down from the base of the skull to halfway to the beak. ''Dsungaripteruss head and neck were together almost long. Its most notable feature are its long, narrow, upcurved jaws with a pointed tip. It had no teeth in the front part of its jaws, which were probably used to remove prey from cracks in rocks and/or the sandy, muddy inland environments it inhabited. It had knobbly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germanodactylus
''Germanodactylus'' ("German finger") is a genus of germanodactylid pterodactyloid pterosaur from Upper Jurassic-age rocks of Germany, including the Solnhofen Limestone. Its specimens were long thought to pertain to '' Pterodactylus''. The head crest of ''Germanodactylus'' is a distinctive feature. History ''G. cristatus'' is based on specimen BSP 1892.IV.1, from the Solnhofen limestone of Eichstätt, Germany. It was originally described by Plieninger in 1901 as a specimen of ''Pterodactylus kochi'', and was given its current specific name by Carl Wiman in 1925, meaning "crested" in Latin. Yang Zhongjian determined that it deserved its own genus in 1964. A second species called ''G. ramphastinus'' (in 1858 accidentally revised to ''rhamphastinus'' by Christian Erich Hermann von Meyer) was named as a distinct species long before ''G. cristatus'', described by Johann Andreas Wagner in 1851 as a species of the now deprecated genus '' Ornithocephalus''. The specific name refe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Kellner
Alexander Wilhelm Armin Kellner (born September 26, 1961) is a Brazilian geologist and paleontologist who is a leading expert in the field of studying pterosaurs. His research has focused mainly on fossil reptiles from the Cretaceous Period, including extinct dinosaurs and crocodylomorphs. Kellner has over 500 publications to his name, has published more than 160 primary studies and two science books. He has participated in paleontological expeditions to many locations including Brazil, Chile, Iran, the United States, Argentina, China, and Antarctica. His scientific achievements include the description of more than thirty species. For his work he has received several honors and prizes, including the TWAS Prize for Earth Sciences from The World Academy of Sciences and admission to the National Order of Scientific Merit (class Comendador), one Brazil's most prestigious awards. Biography Kellner was born in Vaduz, Liechtenstein, son of a German father and Austrian mother. In hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shellfish
Shellfish is a colloquial and fisheries term for exoskeleton-bearing aquatic invertebrates used as food, including various species of molluscs, crustaceans, and echinoderms. Although most kinds of shellfish are harvested from saltwater environments, some are found in freshwater. In addition, a few species of land crabs are eaten, for example ''Cardisoma guanhumi'' in the Caribbean. Shellfish are among the most common food allergens. Despite the name, ''shellfish'' are not fish. Most shellfish are low on the food chain and eat a diet composed primarily of phytoplankton and zooplankton. Many varieties of shellfish, and crustaceans in particular, are actually closely related to insects and arachnids; crustaceans make up one of the main subphyla of the phylum Arthropoda. Molluscs include cephalopods (squids, octopuses, cuttlefish) and bivalves (clams, oysters), as well as gastropods (aquatic species such as whelks and winkles; land species such as snails and slugs). M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crab
Crabs are decapod crustaceans of the infraorder Brachyura, which typically have a very short projecting "tail" (abdomen) ( el, βραχύς , translit=brachys = short, / = tail), usually hidden entirely under the thorax. They live in all the world's oceans, in freshwater, and on land, are generally covered with a thick exoskeleton, and have a single pair of pincers. They first appeared during the Jurassic Period. Description Crabs are generally covered with a thick exoskeleton, composed primarily of highly mineralized chitin, and armed with a pair of chelae (claws). Crabs vary in size from the pea crab, a few millimeters wide, to the Japanese spider crab, with a leg span up to . Several other groups of crustaceans with similar appearances – such as king crabs and porcelain crabs – are not true crabs, but have evolved features similar to true crabs through a process known as carcinisation. Environment Crabs are found in all of the world's oceans, as well as in fresh w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |







.jpg)