Shellfish on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 Shellfish, in colloquial and
Shellfish, in colloquial and
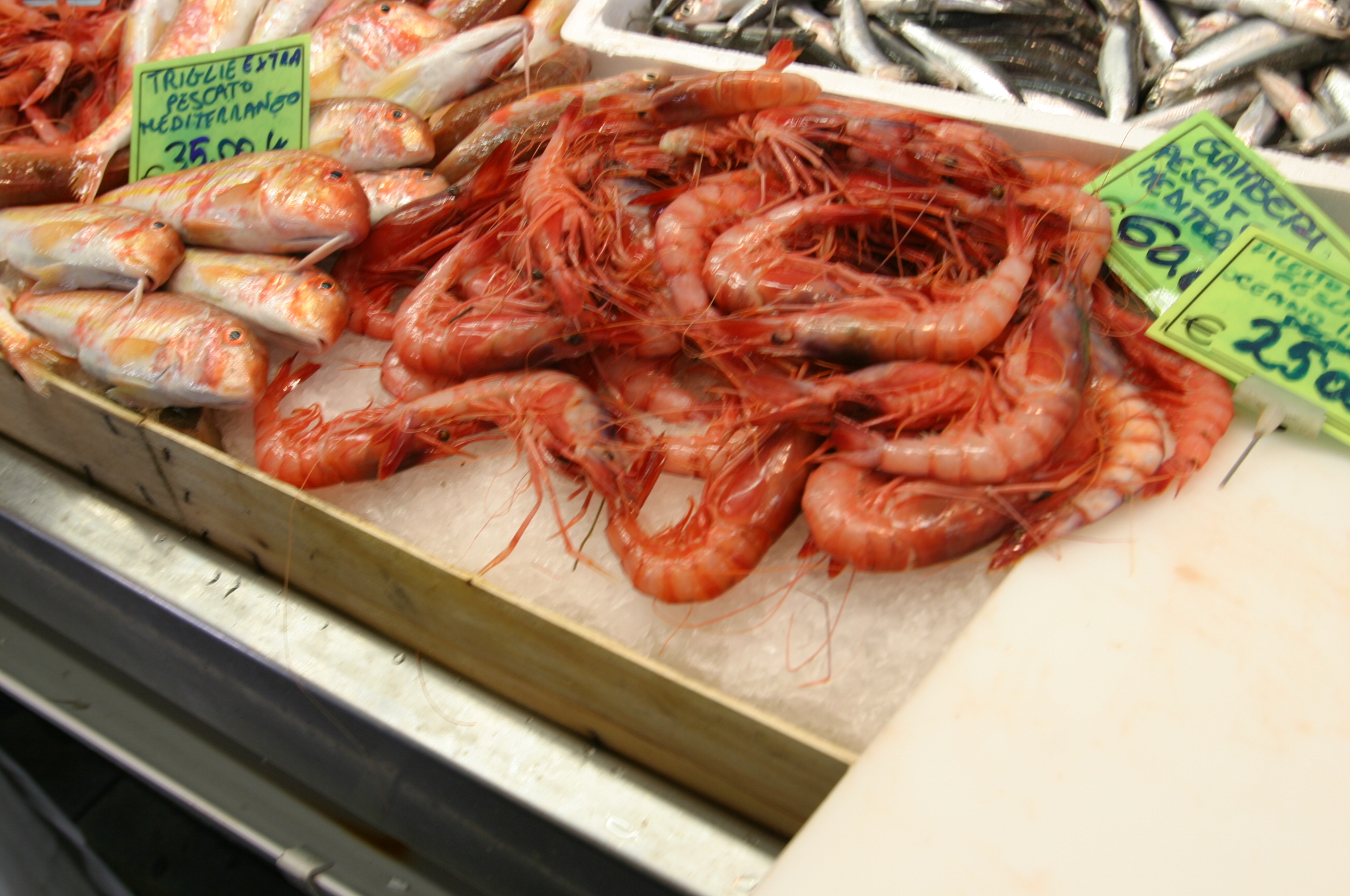
 The term "shellfish" is used both broadly and specifically. In common parlance, as in "having shellfish for dinner", it can refer to anything from clams and oysters to lobster and shrimp. For regulatory purposes it is often narrowly defined as filter-feeding
The term "shellfish" is used both broadly and specifically. In common parlance, as in "having shellfish for dinner", it can refer to anything from clams and oysters to lobster and shrimp. For regulatory purposes it is often narrowly defined as filter-feeding


 Some popular dishes using shellfish:
* Ceviche
* Cioppino
*
Some popular dishes using shellfish:
* Ceviche
* Cioppino
*
"Are crustaceans shellfish? A whiff of scandal in English lexicography"
''Australian Style'', 12 (1): 1–3.
BC Shellfish Growers Association
East Coast Shellfish Growers Association
Pacific Coast Shellfish Growers Association
Shellfish Gallery
at the University of Washington Libraries, Digital Collection * ttp://www.healthaliciousness.com/nutritionfacts/nutrition-comparison.php?o=90240&t=15169&h=15159&s=100&e=100&r=100 Nutrition Facts for Various Shellfish {{Authority control Seafood Fish products

 Shellfish, in colloquial and
Shellfish, in colloquial and fisheries
Fishery can mean either the enterprise of raising or harvesting fish and other aquatic life or, more commonly, the site where such enterprise takes place ( a.k.a., fishing grounds). Commercial fisheries include wild fisheries and fish farm ...
usage, are exoskeleton
An exoskeleton () . is a skeleton that is on the exterior of an animal in the form of hardened integument, which both supports the body's shape and protects the internal organs, in contrast to an internal endoskeleton (e.g. human skeleton, that ...
-bearing aquatic invertebrate
Invertebrates are animals that neither develop nor retain a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''spine'' or ''backbone''), which evolved from the notochord. It is a paraphyletic grouping including all animals excluding the chordata, chordate s ...
s used as food
Food is any substance consumed by an organism for Nutrient, nutritional support. Food is usually of plant, animal, or Fungus, fungal origin and contains essential nutrients such as carbohydrates, fats, protein (nutrient), proteins, vitamins, ...
, including various species of mollusc
Mollusca is a phylum of protostome, protostomic invertebrate animals, whose members are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 76,000 extant taxon, extant species of molluscs are recognized, making it the second-largest animal phylum ...
s, crustacean
Crustaceans (from Latin meaning: "those with shells" or "crusted ones") are invertebrate animals that constitute one group of arthropods that are traditionally a part of the subphylum Crustacea (), a large, diverse group of mainly aquatic arthrop ...
s, and echinoderm
An echinoderm () is any animal of the phylum Echinodermata (), which includes starfish, brittle stars, sea urchins, sand dollars and sea cucumbers, as well as the sessile sea lilies or "stone lilies". While bilaterally symmetrical as ...
s. Although most kinds of shellfish are harvested from saltwater environments, some are found in freshwater
Fresh water or freshwater is any naturally occurring liquid or frozen water containing low concentrations of dissolved salts and other total dissolved solids. The term excludes seawater and brackish water, but it does include non-salty mi ...
. In addition, a few species of land crabs are eaten, for example '' Cardisoma guanhumi'' in the Caribbean
The Caribbean ( , ; ; ; ) is a region in the middle of the Americas centered around the Caribbean Sea in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, mostly overlapping with the West Indies. Bordered by North America to the north, Central America ...
. Shellfish are among the most common food allergens.
Despite the name, shell''fish'' are not fish
A fish (: fish or fishes) is an aquatic animal, aquatic, Anamniotes, anamniotic, gill-bearing vertebrate animal with swimming fish fin, fins and craniate, a hard skull, but lacking limb (anatomy), limbs with digit (anatomy), digits. Fish can ...
. Most shellfish are low on the food chain
A food chain is a linear network of links in a food web, often starting with an autotroph (such as grass or algae), also called a producer, and typically ending at an apex predator (such as grizzly bears or killer whales), detritivore (such as ...
and eat a diet composed primarily of phytoplankton
Phytoplankton () are the autotrophic (self-feeding) components of the plankton community and a key part of ocean and freshwater Aquatic ecosystem, ecosystems. The name comes from the Greek language, Greek words (), meaning 'plant', and (), mea ...
and zooplankton
Zooplankton are the heterotrophic component of the planktonic community (the " zoo-" prefix comes from ), having to consume other organisms to thrive. Plankton are aquatic organisms that are unable to swim effectively against currents. Consequent ...
. Many varieties of shellfish, and crustacean
Crustaceans (from Latin meaning: "those with shells" or "crusted ones") are invertebrate animals that constitute one group of arthropods that are traditionally a part of the subphylum Crustacea (), a large, diverse group of mainly aquatic arthrop ...
s in particular, are actually closely related to insects
Insects (from Latin ') are hexapod invertebrates of the class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body (head, thorax and abdomen), three pairs of jointed ...
and arachnids; crustaceans make up one of the main subphyla of the phylum Arthropoda
Arthropods ( ) are invertebrates in the phylum Arthropoda. They possess an exoskeleton with a cuticle made of chitin, often mineralised with calcium carbonate, a body with differentiated ( metameric) segments, and paired jointed appendages. ...
. Molluscs
Mollusca is a phylum of protostome, protostomic invertebrate animals, whose members are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 76,000 extant taxon, extant species of molluscs are recognized, making it the second-largest animal phylum ...
include cephalopods
A cephalopod is any member of the molluscan Taxonomic rank, class Cephalopoda (Greek language, Greek plural , ; "head-feet") such as a squid, octopus, cuttlefish, or nautilus. These exclusively marine animals are characterized by bilateral symm ...
(squids, octopuses, cuttlefish) and bivalves
Bivalvia () or bivalves, in previous centuries referred to as the Lamellibranchiata and Pelecypoda, is a class of aquatic molluscs (marine and freshwater) that have laterally compressed soft bodies enclosed by a calcified exoskeleton consis ...
(clams, oysters), as well as gastropods
Gastropods (), commonly known as slugs and snails, belong to a large taxonomic class of invertebrates within the phylum Mollusca called Gastropoda ().
This class comprises snails and slugs from saltwater, freshwater, and from the land. Ther ...
(aquatic species such as whelks and winkles; land species such as snails and slugs).
Molluscs used as a food source by humans include many species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), ...
of clam
Clam is a common name for several kinds of bivalve mollusc. The word is often applied only to those that are deemed edible and live as infauna, spending most of their lives halfway buried in the sand of the sea floor or riverbeds. Clams h ...
s, mussel
Mussel () is the common name used for members of several families of bivalve molluscs, from saltwater and Freshwater bivalve, freshwater habitats. These groups have in common a shell whose outline is elongated and asymmetrical compared with other ...
s, oyster
Oyster is the common name for a number of different families of salt-water bivalve molluscs that live in marine or brackish habitats. In some species, the valves are highly calcified, and many are somewhat irregular in shape. Many, but no ...
s, winkles, and scallop
Scallop () is a common name that encompasses various species of marine bivalve molluscs in the taxonomic family Pectinidae, the scallops. However, the common name "scallop" is also sometimes applied to species in other closely related famili ...
s. Some crustaceans that are commonly eaten are shrimp
A shrimp (: shrimp (American English, US) or shrimps (British English, UK)) is a crustacean with an elongated body and a primarily Aquatic locomotion, swimming mode of locomotion – typically Decapods belonging to the Caridea or Dendrobranchi ...
, lobster
Lobsters are Malacostraca, malacostracans Decapoda, decapod crustaceans of the family (biology), family Nephropidae or its Synonym (taxonomy), synonym Homaridae. They have long bodies with muscular tails and live in crevices or burrows on th ...
s, crayfish
Crayfish are freshwater crustaceans belonging to the infraorder Astacidea, which also contains lobsters. Taxonomically, they are members of the superfamilies Astacoidea and Parastacoidea. They breathe through feather-like gills. Some spe ...
, crab
Crabs are decapod crustaceans of the infraorder Brachyura (meaning "short tailed" in Greek language, Greek), which typically have a very short projecting tail-like abdomen#Arthropoda, abdomen, usually hidden entirely under the Thorax (arthropo ...
s and barnacle
Barnacles are arthropods of the subclass (taxonomy), subclass Cirripedia in the subphylum Crustacean, Crustacea. They are related to crabs and lobsters, with similar Nauplius (larva), nauplius larvae. Barnacles are exclusively marine invertebra ...
s. Echinoderm
An echinoderm () is any animal of the phylum Echinodermata (), which includes starfish, brittle stars, sea urchins, sand dollars and sea cucumbers, as well as the sessile sea lilies or "stone lilies". While bilaterally symmetrical as ...
s are not as frequently harvested for food as molluscs and crustaceans; however, sea urchin
Sea urchins or urchins () are echinoderms in the class (biology), class Echinoidea. About 950 species live on the seabed, inhabiting all oceans and depth zones from the intertidal zone to deep seas of . They typically have a globular body cove ...
gonads
A gonad, sex gland, or reproductive gland is a mixed gland and sex organ that produces the gametes and sex hormones of an organism. Female reproductive cells are egg cells, and male reproductive cells are sperm. The male gonad, the testicle, ...
are quite popular in many parts of the world, where the live delicacy is harder to transport.
Though some shellfish harvesting has been unsustainable, and shrimp farming has been destructive in some parts of the world, shellfish farming can be important to environmental restoration, by developing reefs, filtering water and eating biomass.
Terminology
 The term "shellfish" is used both broadly and specifically. In common parlance, as in "having shellfish for dinner", it can refer to anything from clams and oysters to lobster and shrimp. For regulatory purposes it is often narrowly defined as filter-feeding
The term "shellfish" is used both broadly and specifically. In common parlance, as in "having shellfish for dinner", it can refer to anything from clams and oysters to lobster and shrimp. For regulatory purposes it is often narrowly defined as filter-feeding molluscs
Mollusca is a phylum of protostome, protostomic invertebrate animals, whose members are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 76,000 extant taxon, extant species of molluscs are recognized, making it the second-largest animal phylum ...
such as clams, mussels, and oyster to the exclusion of crustacean
Crustaceans (from Latin meaning: "those with shells" or "crusted ones") are invertebrate animals that constitute one group of arthropods that are traditionally a part of the subphylum Crustacea (), a large, diverse group of mainly aquatic arthrop ...
s and all else.
Although the term is primarily applied to marine species, edible freshwater
Fresh water or freshwater is any naturally occurring liquid or frozen water containing low concentrations of dissolved salts and other total dissolved solids. The term excludes seawater and brackish water, but it does include non-salty mi ...
invertebrates such as crayfish
Crayfish are freshwater crustaceans belonging to the infraorder Astacidea, which also contains lobsters. Taxonomically, they are members of the superfamilies Astacoidea and Parastacoidea. They breathe through feather-like gills. Some spe ...
and river mussels
Mussel () is the common name used for members of several families of bivalve molluscs, from saltwater and freshwater habitats. These groups have in common a shell whose outline is elongated and asymmetrical compared with other edible clams, whic ...
are also sometimes grouped under the umbrella term "shellfish".
Although their shells may differ, all shellfish are invertebrates. As non-mammalian animals that spend their entire lives in water they are "fish" in an informal sense; however, the term ”finfish" is sometimes used to distinguish fish
A fish (: fish or fishes) is an aquatic animal, aquatic, Anamniotes, anamniotic, gill-bearing vertebrate animal with swimming fish fin, fins and craniate, a hard skull, but lacking limb (anatomy), limbs with digit (anatomy), digits. Fish can ...
, animals defined by having vertebrae
Each vertebra (: vertebrae) is an irregular bone with a complex structure composed of bone and some hyaline cartilage, that make up the vertebral column or spine, of vertebrates. The proportions of the vertebrae differ according to their spinal ...
, from shellfish in modern terminology.
The word "shellfish" is both singular and plural; the rarely used "shellfishes" is sometimes employed to distinguish among various types of shellfish.
Shellfish in various cuisines
Archaeological finds have shown that humans have been making use of shellfish as a food item for hundreds of thousands of years. In the present, shellfish dishes are a feature of almost all thecuisine
A cuisine is a style of cooking characterized by distinctive ingredients, List of cooking techniques, techniques and Dish (food), dishes, and usually associated with a specific culture or geographic region. Regional food preparation techniques, ...
s of the world, providing an important source of protein in many cuisines around the world, especially in the countries with coastal areas.

In Japan
InJapanese cuisine
Japanese cuisine encompasses the regional and traditional foods of Japan, which have developed through centuries of political, economic, and social changes. The traditional cuisine of Japan (Japanese language, Japanese: ) is based on rice with m ...
, chefs often use shellfish and their roe
Roe, ( ) or hard roe, is the fully ripe internal egg masses in the ovaries, or the released external egg masses, of fish and certain marine animals such as shrimp, scallop, sea urchins and squid. As a seafood, roe is used both as a cooking, c ...
in different dishes. Sushi
is a traditional Japanese dish made with , typically seasoned with sugar and salt, and combined with a variety of , such as seafood, vegetables, or meat: raw seafood is the most common, although some may be cooked. While sushi comes in n ...
(vinegared rice, topped with other ingredients, including shellfish, fish, meat and vegetables) features both raw and cooked shellfish. Sashimi
is a Japanese cuisine, Japanese delicacy consisting of fresh raw fish or Raw meat, meat sliced into thin pieces and often eaten with soy sauce.
Origin
The word ''sashimi'' means 'pierced body', i.e., "wikt:刺身, 刺身" = ''sashimi'', whe ...
primarily consists of very fresh raw seafood, sliced into thin pieces. Both sushi and sashimi are served with soy sauce and wasabi
Wasabi (Japanese language, Japanese: , , or , ) or Japanese horseradish (''Eutrema japonicum'' syn. ''Wasabia japonica'') is a plant of the family Brassicaceae, which also includes horseradish and Mustard plant, mustard in other genus, genera. ...
paste (a Japanese horseradish
Horseradish (''Armoracia rusticana'', syn. ''Cochlearia armoracia'') is a perennial plant of the family Brassicaceae (which also includes Mustard plant, mustard, wasabi, broccoli, cabbage, and radish). It is a root vegetable, cultivated and us ...
root, a spice with extremely strong, hot flavor), thinly sliced pickled ginger root, and a simple garnish such as shiso (a kitchen herb, member of the mint family) or finely shredded daikon radish, or both.
In the United States

Lobster
Lobsters are Malacostraca, malacostracans Decapoda, decapod crustaceans of the family (biology), family Nephropidae or its Synonym (taxonomy), synonym Homaridae. They have long bodies with muscular tails and live in crevices or burrows on th ...
in particular is a great delicacy in the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
, where families in the Northeast region make them into the centerpiece of a clam bake, usually for special occasions. Lobsters are eaten on much of the East Coast; the American lobster ranges from Newfoundland
Newfoundland and Labrador is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region of Labrador, having a total size of . As of 2025 the population ...
down to about the Carolinas
The Carolinas, also known simply as Carolina, are the U.S. states of North Carolina and South Carolina considered collectively. They are bordered by Virginia to the north, Tennessee to the west, and Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia to the southwes ...
, but is most often associated with Maine
Maine ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the United States, and the northeasternmost state in the Contiguous United States. It borders New Hampshire to the west, the Gulf of Maine to the southeast, and the Provinces and ...
. A typical meal involves boiling the lobster with some slight seasoning and then serving it with drawn butter, baked potato
A baked potato, known in the United Kingdom as a jacket potato, is a preparation of potato. After baking, it may be served with fillings, toppings or condiments, such as butter, cheese, sour cream, gravy, baked beans and tuna.
Some varieties of ...
, and corn on the cob.
Clamming is done both commercially and recreationally along the Northeast coastline of the US. Various type of clams are incorporated into the cuisine of New England. The soft-shelled clam is eaten either fried or steamed (and then called "steamers
Steamer may refer to:
Transportation
* Steamboat, smaller, insular boat on lakes and rivers
* Steamship, ocean-faring ship
* Screw steamer, steamboat or ship that uses "screws" (propellers)
* Steam yacht, luxury or commercial yacht
* Paddle st ...
"). Many types of clams can be used for clam chowder
Clam chowder is any of several chowder soups in American cuisine containing clams. In addition to clams, common ingredients include diced potatoes, salt pork, and onions. It is believed that clams were used in chowder because of the relative ...
, but the quahog, a hard shelled clam also known as a chowder clam, is often used because the long cooking time softens its tougher meat.
The Chesapeake Bay
The Chesapeake Bay ( ) is the largest estuary in the United States. The bay is located in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region and is primarily separated from the Atlantic Ocean by the Delmarva Peninsula, including parts of the Ea ...
and Maryland
Maryland ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It borders the states of Virginia to its south, West Virginia to its west, Pennsylvania to its north, and Delaware to its east ...
region has generally been associated more with crabs, but in recent years the area has been trying to reduce its catch of blue crabs, as wild populations have been depleted. This has not, however, stemmed the demand: Maryland-style crabcakes are still a well known treat in crabhouses all over the bay, though the catch now comes from points farther south.
In the Southeast
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, Radius, radially arrayed compass directions (or Azimuth#In navigation, azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A ''compass rose'' is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, ...
, and particularly the gulf states, shrimping is an important industry. Copious amounts of shrimp are harvested each year in the Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico () is an oceanic basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, mostly surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north, and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United States; on the southw ...
and the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the ...
to satisfy a national demand for shrimp. Locally, prawns and shrimp are often deep fried; in the Cajun and Creole kitchens of Louisiana
Louisiana ( ; ; ) is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It borders Texas to the west, Arkansas to the north, and Mississippi to the east. Of the 50 U.S. states, it ranks 31st in area and 25 ...
, shrimp and prawns are a common addition to traditional recipes like jambalaya and certain stews. Crawfish are a well known and much eaten delicacy there, often boiled in huge pots and heavily spiced.
In many major cities with active fishing ports, raw oyster bars are also a feature of shellfish consumption. When served freshly shucked (opened) and iced, one may find a liquid inside the shell, called the liquor. Some believe that oysters have the properties of an aphrodisiac
An aphrodisiac is a substance that increases libido, sexual desire, sexual attraction, sexual pleasure, or sexual behavior. These substances range from a variety of plants, spices, and foods to synthetic chemicals. Natural aphrodisiacs, such as ...
.
Inter-tidal herbivorous shellfish such as mussels and clams can help people reach a healthy balance of omega-3 and omega-6 fats in their diets, instead of the current Western diets. For this reason, the eating of shellfish is often encouraged by dietitians.

 Some popular dishes using shellfish:
* Ceviche
* Cioppino
*
Some popular dishes using shellfish:
* Ceviche
* Cioppino
* Clam chowder
Clam chowder is any of several chowder soups in American cuisine containing clams. In addition to clams, common ingredients include diced potatoes, salt pork, and onions. It is believed that clams were used in chowder because of the relative ...
* Curanto
* Fruits de mer
* Paella
Paella (, , , , ; ) is a rice dish originally from the Valencian Community. ''Paella'' is regarded as one of the community's identifying symbols. It is one of the best-known dishes in Spanish cuisine.
The dish takes its name from the wide, sha ...
* Sashimi
is a Japanese cuisine, Japanese delicacy consisting of fresh raw fish or Raw meat, meat sliced into thin pieces and often eaten with soy sauce.
Origin
The word ''sashimi'' means 'pierced body', i.e., "wikt:刺身, 刺身" = ''sashimi'', whe ...
and sushi
is a traditional Japanese dish made with , typically seasoned with sugar and salt, and combined with a variety of , such as seafood, vegetables, or meat: raw seafood is the most common, although some may be cooked. While sushi comes in n ...
* Shrimp cocktail
* Lobster
Lobsters are Malacostraca, malacostracans Decapoda, decapod crustaceans of the family (biology), family Nephropidae or its Synonym (taxonomy), synonym Homaridae. They have long bodies with muscular tails and live in crevices or burrows on th ...
bisque
* She-crab soup
Religious dietary restrictions
TheTorah
The Torah ( , "Instruction", "Teaching" or "Law") is the compilation of the first five books of the Hebrew Bible, namely the books of Genesis, Exodus, Leviticus, Numbers and Deuteronomy. The Torah is also known as the Pentateuch () ...
forbids the consumption of shellfish (i.e. the only permitted seafood is fish with fins and scales), in the books of Leviticus and Deuteronomy
Deuteronomy (; ) is the fifth book of the Torah (in Judaism), where it is called () which makes it the fifth book of the Hebrew Bible and Christian Old Testament.
Chapters 1–30 of the book consist of three sermons or speeches delivered to ...
. Jews (of all religious traditions) who fully observe the dietary laws thus do not eat shellfish, neither do Seventh-day Adventists, who also follow Jewish dietary law.
Shia Islam
Shia Islam is the second-largest Islamic schools and branches, branch of Islam. It holds that Muhammad in Islam, Muhammad designated Ali ibn Abi Talib () as both his political Succession to Muhammad, successor (caliph) and as the spiritual le ...
ic schools of thought vary on whether (and which types of) shellfish may be acceptable. Sunni Muslims, except Hanafis, view them as halal
''Halal'' (; ) is an Arabic word that translates to in English. Although the term ''halal'' is often associated with Islamic dietary laws, particularly meat that is slaughtered according to Islamic guidelines, it also governs ethical practices ...
.
Allergy
Approximately 1% of the population is estimated to suffer from shellfish allergy, which is more common in teenage and adult life than very early childhood. There is some evidence that shellfishintolerance
Intolerance may refer to:
* Hypersensitivity or intolerance, undesirable reactions produced by the immune system
* ''Intolerance'' (film), a 1916 film by D. W. Griffith
* ''Intolerance'' (album), the first solo album from Grant Hart, formerly ...
exists in an unknown proportion of the population. The symptoms of this do not include the immune and respiratory symptoms of an allergic reaction, such as hives, hyperventilation, or anaphylaxis, but do involve gastrointestinal distress, such as nausea, abdominal cramps, and diarrhea. Similar symptoms can come from foodborne illness
Foodborne illness (also known as foodborne disease and food poisoning) is any illness resulting from the contamination of food by pathogenic bacteria, viruses, or parasites,
as well as prions (the agents of mad cow disease), and toxins such ...
or as part of a toxic effect.
Toxic content
Some shellfish, such aswhelk
Whelks are any of several carnivorous sea snail species with a swirling, tapered shell. Many are eaten by humans, such as the common whelk of the North Atlantic. Most whelks belong to the family Buccinidae and are known as "true whelks." Othe ...
, contain arsenic
Arsenic is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol As and atomic number 33. It is a metalloid and one of the pnictogens, and therefore shares many properties with its group 15 neighbors phosphorus and antimony. Arsenic is not ...
. A sample of whelk was found to have a total content of arsenic at of which 1% is inorganic arsenic.
Shellfish caught in Alaska
Alaska ( ) is a non-contiguous U.S. state on the northwest extremity of North America. Part of the Western United States region, it is one of the two non-contiguous U.S. states, alongside Hawaii. Alaska is also considered to be the north ...
can cause paralytic shellfish poisoning (PSP). PSP is caused by toxins, namely saxitoxin, released by dinoflagellate
The Dinoflagellates (), also called Dinophytes, are a monophyletic group of single-celled eukaryotes constituting the phylum Dinoflagellata and are usually considered protists. Dinoflagellates are mostly marine plankton, but they are also commo ...
s, a type of protista (also considered algae), which are extremely poisonous (1000 times more potent than cyanide) and can lead to death by paralyzing the breathing muscles. Due to warming oceans, algae blooms have become more widespread, thereby increasing the likelihood of intoxications of various types.
Ecosystem services and reef-building
Shellfish of various kinds contribute to the formation ofreef
A reef is a ridge or shoal of rock, coral, or similar relatively stable material lying beneath the surface of a natural body of water. Many reefs result from natural, abiotic component, abiotic (non-living) processes such as deposition (geol ...
s, such as when millions of oysters or mussels aggregate together. Reefs provide habitat for numerous other species, bury carbon, contributing to climate change mitigation
Climate change mitigation (or decarbonisation) is action to limit the greenhouse gases in the atmosphere that cause climate change. Climate change mitigation actions include energy conservation, conserving energy and Fossil fuel phase-out, repl ...
, and defend the shore against erosion, floods and waves. Conversely, when they are destroyed or exploited, carbon can be released into the atmosphere, simultaneously increasing the likelihood of severe weather while removing the natural defence against its consequences. In addition, some shellfish are known for filtering water, removing suspended particles and contaminants, which contributes to both quality and clarity. These benefits cascade to other species that are helpful to humankind such as seagrasses.
See also
*Aquaculture
Aquaculture (less commonly spelled aquiculture), also known as aquafarming, is the controlled cultivation ("farming") of aquatic organisms such as fish, crustaceans, mollusks, algae and other organisms of value such as aquatic plants (e.g. Nelu ...
* Seafood
Seafood is any form of Marine life, sea life regarded as food by humans, prominently including Fish as food, fish and shellfish. Shellfish include various species of Mollusca, molluscs (e.g., bivalve molluscs such as clams, oysters, and mussel ...
* Seashell
A seashell or sea shell, also known simply as a shell, is a hard, protective outer layer usually created by an animal or organism that lives in the sea. Most seashells are made by Mollusca, mollusks, such as snails, clams, and oysters ...
* Shellfish Association of Great Britain (SAGB)
References
Sources
* Pawley, Andrew (2004"Are crustaceans shellfish? A whiff of scandal in English lexicography"
''Australian Style'', 12 (1): 1–3.
External links
BC Shellfish Growers Association
East Coast Shellfish Growers Association
Pacific Coast Shellfish Growers Association
Shellfish Gallery
at the University of Washington Libraries, Digital Collection * ttp://www.healthaliciousness.com/nutritionfacts/nutrition-comparison.php?o=90240&t=15169&h=15159&s=100&e=100&r=100 Nutrition Facts for Various Shellfish {{Authority control Seafood Fish products