|
Temple Denial
Temple denial is a claim advanced by Palestinian political leaders, religious figures, intellectuals, and authors that the successive Temples in Jerusalem did not exist or were placed other than on the Temple Mount. Yitzhak Reiter describes the growing tendency of Islamic authorities to deny the existence of the Jewish Temples on the Temple Mount, characterizing it as part of a campaign to increase the status of Jerusalem and the Temple Mount in Islam as part of the effort to make Jerusalem a Muslim city under Arab governance. The ''New York Times'' noted that "Temple denial, increasingly common among Palestinian leaders, also has a long history: After Israel became a state in 1948, the Waqf removed from its guidebooks all references to King Solomon's Temple, whose location at the site it had previously said was 'beyond dispute'." David Hazony has described the phenomenon as "a campaign of intellectual erasure y Palestinian leaders, writers, and scholars... aimed at undermining ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
19 Shrine Of The Book 005 (cropped)
Nineteen or 19 may refer to: * 19 (number), the natural number following 18 and preceding 20 * one of the years 19 BC, AD 19, 1919, 2019 Films * 19 (film), ''19'' (film), a 2001 Japanese film * Nineteen (film), ''Nineteen'' (film), a 1987 science fiction film Music * 19 (band), a Japanese pop music duo Albums * 19 (Adele album), ''19'' (Adele album), 2008 * ''19'', a 2003 album by Alsou * ''19'', a 2006 album by Evan Yo * ''19'', a 2018 album by MHD (rapper), MHD * ''19'', one half of the double album ''63/19'' by Kool A.D. * ''Number Nineteen'', a 1971 album by American jazz pianist Mal Waldron * XIX (EP), ''XIX'' (EP), a 2019 EP by 1the9 Songs * 19 (song), "19" (song), a 1985 song by British musician Paul Hardcastle. * "Nineteen", a song by Bad4Good from the 1992 album ''Refugee (Bad4Good album), Refugee'' * "Nineteen", a song by Karma to Burn from the 2001 album ''Almost Heathen''. * Nineteen (song), "Nineteen" (song), a 2007 song by American singer Billy Ray Cyrus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Jerusalem (70 CE)
The siege of Jerusalem of 70 CE was the decisive event of the First Jewish–Roman War (66–73 CE), in which the Roman army led by future emperor Titus besieged Jerusalem, the center of Jewish rebel resistance in the Roman province of Judaea. Following a brutal five-month siege, the Romans destroyed the city and the Second Jewish Temple. In April 70 CE, three days before Passover, the Roman army started besieging Jerusalem. The city had been taken over by several rebel factions following a period of massive unrest and the collapse of a short-lived provisional government. Within three weeks, the Roman army broke the first two walls of the city, but a stubborn rebel standoff prevented them from penetrating the thickest and third wall. According to Josephus, a contemporary historian and the main source for the war, the city was ravaged by murder, famine and cannibalism. On Tisha B'Av, 70 CE (August 30), Roman forces finally overwhelmed the defenders and set fire to the Te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Babylonians
Babylonia (; Akkadian: , ''māt Akkadī'') was an ancient Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Syria). It emerged as an Amorite-ruled state c. 1894 BCE. During the reign of Hammurabi and afterwards, Babylonia was called "the country of Akkad" (''Māt Akkadī'' in Akkadian), a deliberate archaism in reference to the previous glory of the Akkadian Empire. It was often involved in rivalry with the older state of Assyria to the north and Elam to the east in Ancient Iran. Babylonia briefly became the major power in the region after Hammurabi ( fl. c. 1792–1752 BCE middle chronology, or c. 1696–1654 BCE, short chronology) created a short-lived empire, succeeding the earlier Akkadian Empire, Third Dynasty of Ur, and Old Assyrian Empire. The Babylonian Empire rapidly fell apart after the death of Hammurabi and reverted to a small kingdom. Like Assyria, the Babylonian state retained t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moriah
Moriah ( Hebrew: , ''Mōrīyya''; Arabic: ﻣﺮﻭﻩ, ''Marwah'') is the name given to a mountainous region in the Book of Genesis, where the binding of Isaac by Abraham is said to have taken place. Jews identify the region mentioned in Genesis and the specific mountain in which the near-sacrifice is said to have occurred with "Mount Moriah", mentioned in the Book of Chronicles as the place where Solomon's Temple is said to have been built, and both these locations are also identified with the current Temple Mount in Jerusalem. The Samaritan Torah, on the other hand, transliterates the place mentioned for the binding of Isaac as Moreh, a name for the region near modern-day Nablus. It is believed by the Samaritans that the near-sacrifice actually took place on Mount Gerizim, near Nablus in the West Bank. Many Muslims, in turn, believe the place mentioned in the first book of the Bible, rendered as Marwa in Arabic in the Quran, is actually located close to the Kaaba in Mecca, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solomon In Islam
Sulaimān ibn Dāwūd ( ar, سُلَيْمَان بْن دَاوُوْد, ) was, according to the Quran, a '' malik'' (, ) and '' nabī'' (, ) of the Israelites. Generally, Islamic tradition holds that he was the third king of the Jewish people and a wise ruler of Israel. In Islam, Solomon is regarded as one of the prophets of God who was bestowed with many divine gifts, including the ability to speak to both animals and ''jinn''; he is also said to have enslaved the '' shayāṭīn'' (, ) and the '' dīv'' (, ) with the support of a staff given to him by God. Muslims further maintain that he remained a faithful monotheist throughout his life; reigned justly over the whole of the Israelite nation; was blessed with a level of kingship that was given to none before him nor after him; and fulfilled all of his commandments, being promised nearness to God in ''Jannah'' (, ) at the end of his life. Since the rise of Islam, various Arab historians have regarded Solomon as one of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foundation Stone
The cornerstone (or foundation stone or setting stone) is the first stone set in the construction of a masonry foundation. All other stones will be set in reference to this stone, thus determining the position of the entire structure. Over time a cornerstone became a ceremonial masonry stone, or replica, set in a prominent location on the outside of a building, with an inscription on the stone indicating the construction dates of the building and the names of architect, builder, and other significant individuals. The rite of laying a cornerstone is an important cultural component of eastern architecture and metaphorically in sacred architecture generally. Some cornerstones include time capsules from, or engravings commemorating, the time a particular building was built. History The ceremony typically involved the placing of offerings of grain, wine and oil on or under the stone. These were symbolic of the produce and the people of the land and the means of their subsistence. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
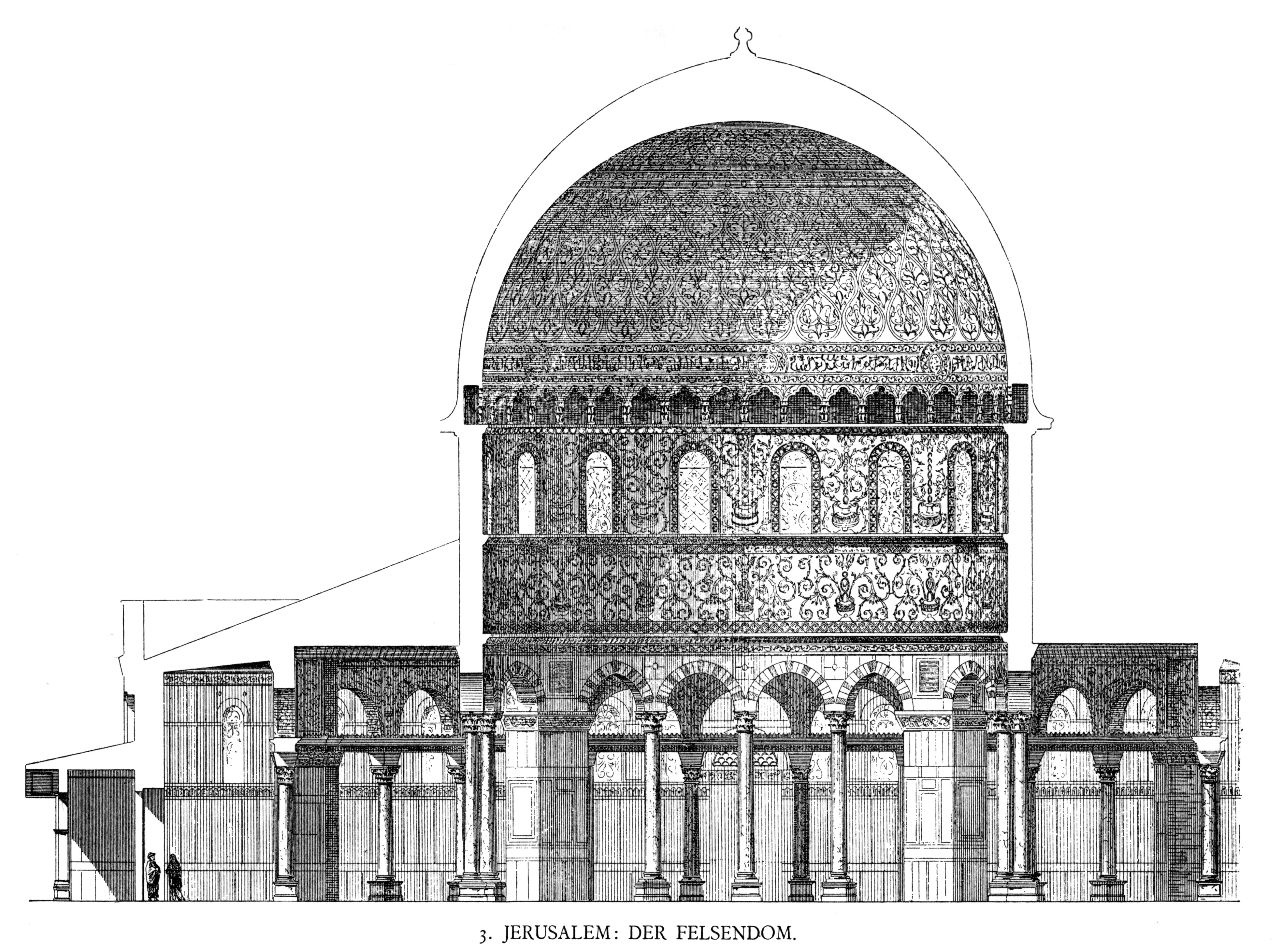
Dome Of The Rock
The Dome of the Rock ( ar, قبة الصخرة, Qubbat aṣ-Ṣakhra) is an Islamic shrine located on the Temple Mount in the Old City of Jerusalem, a site also known to Muslims as the ''al-Haram al-Sharif'' or the Al-Aqsa Compound. Its initial construction was undertaken by the Umayyad Caliphate on the orders of Abd al-Malik during the Second Fitna in 691–692 CE, and it has since been situated on top of the site of the Second Jewish Temple (built in to replace the destroyed Solomon's Temple), which was destroyed by the Romans in 70 CE. The original dome collapsed in 1015 and was rebuilt in 1022–23. The Dome of the Rock is the world's oldest surviving work of Islamic architecture. Its architecture and mosaics were patterned after nearby Byzantine churches and palaces, although its outside appearance was significantly changed during the Ottoman period and again in the modern period, notably with the addition of the gold-plated roof, in 1959–61 and again in 1993. The oc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qibli Mosque
Al-Aqsa Mosque (, ), also known as Jami' Al-Aqsa () or as the Qibli Mosque ( ar, المصلى القبلي, translit=al-Muṣallā al-Qiblī, label=none), and also is a congregational mosque located in the Old City of Jerusalem. It is situated on the Temple Mount, known from its Arabic-language name as the Al-Aqsa Mosque compound or simply as Al-Aqsa Mosque, which serves as a namesake for the structure. * * * * * PEF Survey of Palestine, 1883, volume III Jerusalem, p.119: "The Jamia el Aksa, or 'distant mosque' (that is, distant from Mecca), is on the south, reaching to the outer wall. The whole enclosure of the Haram is called by Moslem writers Masjid el Aksa, 'praying-place of the Aksa,' from this mosque." * Yitzhak Reiter: "This article deals with the employment of religious symbols for national identities and national narratives by using the sacred compound in Jerusalem (The Temple Mount/al-Aqsa) as a case study. The narrative of The Holy Land involves three concen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Umayyad Caliphate
The Umayyad Caliphate (661–750 CE; , ; ar, ٱلْخِلَافَة ٱلْأُمَوِيَّة, al-Khilāfah al-ʾUmawīyah) was the second of the four major caliphates established after the death of Muhammad. The caliphate was ruled by the Umayyad dynasty ( ar, ٱلْأُمَوِيُّون, ''al-ʾUmawīyūn'', or , ''Banū ʾUmayyah'', "Sons of Umayyah"). Uthman ibn Affan (r. 644–656), the third of the Rashidun caliphs, was also a member of the clan. The family established dynastic, hereditary rule with Muawiya ibn Abi Sufyan, long-time governor of Greater Syria, who became the sixth caliph after the end of the First Fitna in 661. After Mu'awiyah's death in 680, conflicts over the succession resulted in the Second Fitna, and power eventually fell into the hands of Marwan I from another branch of the clan. Greater Syria remained the Umayyads' main power base thereafter, with Damascus serving as their capital. The Umayyads continued the Muslim conquests, incorpo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rashidun
, image = تخطيط كلمة الخلفاء الراشدون.png , caption = Calligraphic representation of Rashidun Caliphs , birth_place = Mecca, Hejaz, Arabia present-day Saudi Arabia , known_for = Companions of the Prophet , title = Ar-Rashidun , family = Quraysh The Rashidun Caliphs ( ar, الخلفاء الراشدون, translit=al-Khulafāʾ al-Rāshidūn, ), often simply called the Rashidun, are the first four caliphs (lit.: 'successors') who led the Muslim community following the death of the Islamic prophet Muhammad: Abu Bakr (), Umar (), Uthman (), and Ali (). The reign of these caliphs, called the Rashidun Caliphate (632–661), is considered in Sunni Islam to have been 'rightly guided' (Arabic: ), meaning that it constitutes a model ( ) to be followed and emulated from a religious point of view. History The first four caliphs who succeeded Muhammad are known as the Rashidun (rightly-guided) Caliphs. # Ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
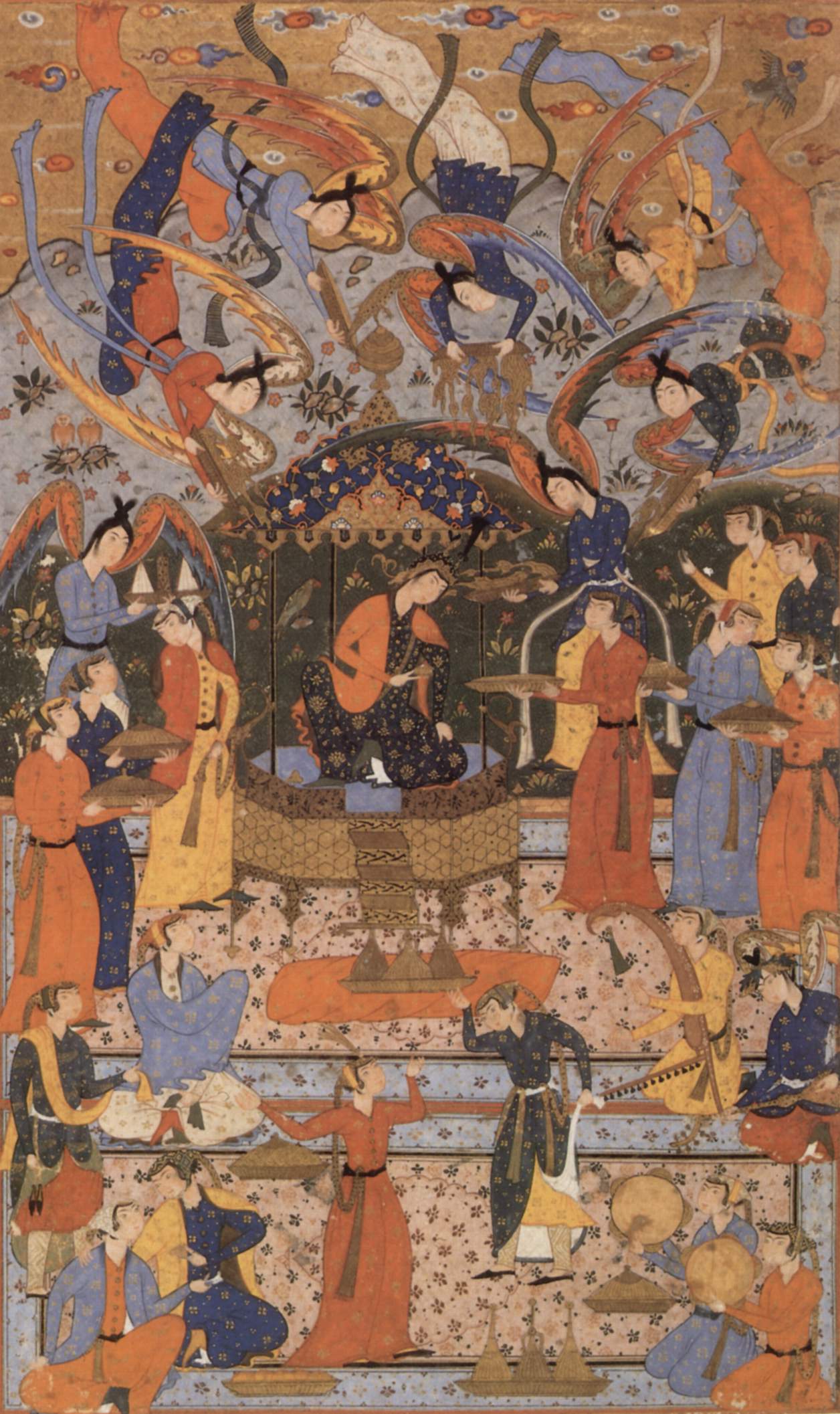
Isra And Mi'raj
The Israʾ and Miʿraj ( ar, الإسراء والمعراج, ') are the two parts of a Night Journey that, according to Islam, the Islamic prophet Muhammad (570–632) took during a single night around the year 621 (1 BH – 0 BH). Within Islam it signifies both a physical and spiritual journey. A brief sketch of the story is in the 17th chapter of the Quran, called ''al-Isra''', while greater detail is found in the ''hadith''; later collections of the reports, teachings, deeds and sayings of Muhammad. In the ''Israʾ'' part of the journey, Muhammad is said to have traveled on the back of Buraq to the Al-Aqsa Mosque (i.e. the Temple Mount) where he leads other prophets in prayer. In the next part of the journey, the ''Miʿraj'', he ascends into heaven where he individually greets the prophets and later, speaks to Allah, who gives Muhammad instructions to take back to the Muslims regarding the details of prayer. The journey and ascent are marked as one of the most cele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muhammad
Muhammad ( ar, مُحَمَّد; 570 – 8 June 632 Common Era, CE) was an Arab religious, social, and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Muhammad in Islam, Islamic doctrine, he was a prophet Divine inspiration, divinely inspired to preach and confirm the tawhid, monotheistic teachings of Adam in Islam, Adam, Abraham in Islam, Abraham, Moses in Islam, Moses, Jesus in Islam, Jesus, and other Prophets and messengers in Islam, prophets. He is believed to be the Seal of the Prophets within Islam. Muhammad united Arabian Peninsula, Arabia into a single Muslim polity, with the Quran as well as his teachings and practices forming the basis of Islamic religious belief. Muhammad was born approximately 570CE in Mecca. He was the son of Abdullah ibn Abd al-Muttalib and Amina bint Wahb. His father Abdullah was the son of Quraysh tribal leader Abd al-Muttalib ibn Hashim, and he died a few months before Muhammad's birth. His mother Amina died when he was six, lea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)



.jpg)

