|
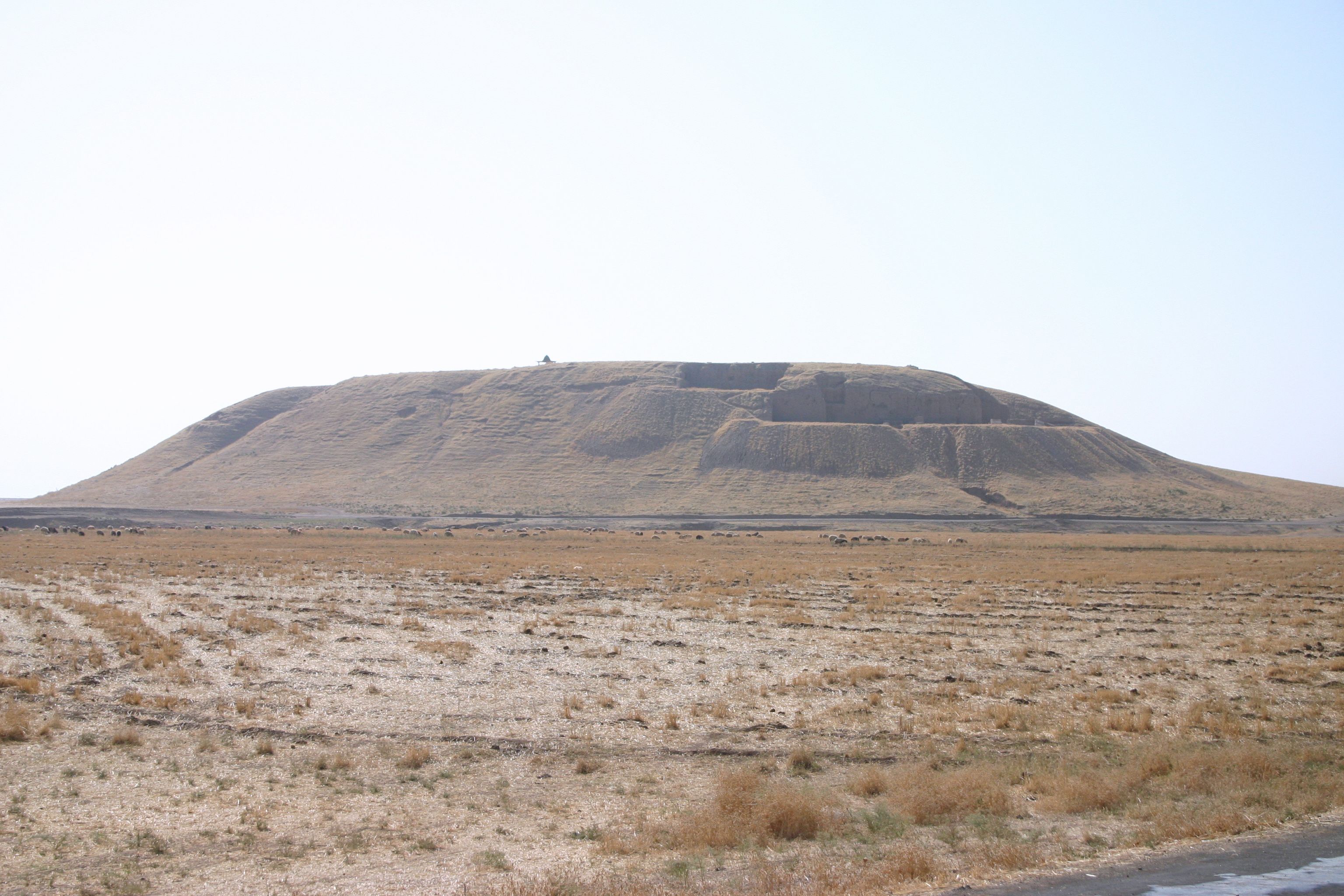
Tell Ed-Duweir
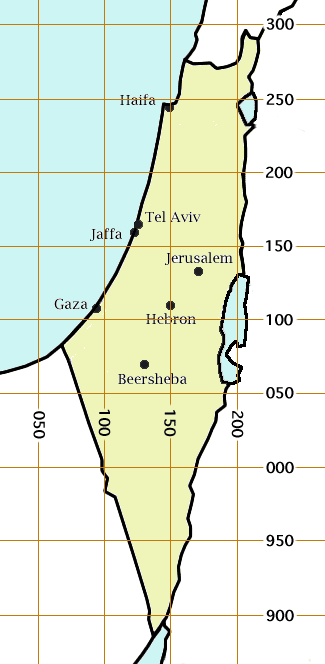
Lachish ( he, לכיש; grc, Λαχίς; la, Lachis) was an ancient Canaanite and Israelite city in the Shephelah ("lowlands of Judea") region of Israel, on the South bank of the Lakhish River, mentioned several times in the Hebrew Bible. The current '' tell'' (ruin) by that name, known as Tel Lachish ( he, תל לכיש) or Tell ed-Duweir (),, has been identified with the biblical Lachish. Today, it is an Israeli national park operated and maintained by the Israel Nature and Parks Authority. The park was established on lands of the depopulated Palestinian village of Qobebet Ibn ‘Awwad which was north of the Tel. It lies near the present-day moshav of Lakhish. Lachish was first mentioned in the Amarna letters. In the Book of Joshua, Lachish is mentioned as one of the cities destroyed by the Israelites for joining the league against the Gibeonites (). The territory was later assigned to the tribe of Judah () and became part of the United Kingdom of Israel. Following the k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palestine Grid
The Palestine grid was the geographic coordinate system used by the Survey Department of Palestine. The system was chosen by the Survey Department of the Government of Palestine in 1922. The projection used was the Cassini-Soldner projection. The central meridian (the line of longitude along which there is no local distortion) was chosen as that passing through a marker on the hill of Mar Elias Monastery south of Jerusalem. The false origin (zero point) of the grid was placed 100 km to the south and west of the Ali el-Muntar hill that overlooks Gaza city. The unit length for the grid was the kilometre; the British units were not even considered. At the time the grid was established, there was no intention of mapping the lower reaches of the Negev Desert, but this did not remain true. Those southern regions having a negative north-south coordinate then became a source of confusion, which was solved by adding 1000 to the northern coordinate in that case. For some military pu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tell (archaeology)
In archaeology, a tell or tel (borrowed into English from ar, تَلّ, ', 'mound' or 'small hill'), is an artificial topographical feature, a species of mound consisting of the accumulated and stratified debris of a succession of consecutive settlements at the same site, the refuse of generations of people who built and inhabited them, and of natural sediment. (Very limited snippet view).Matthews (2020)Introduction and Definition/ref> Tells are most commonly associated with the ancient Near East, but they are also found elsewhere, such as Southern and parts of Central Europe, from Greece and Bulgaria to Hungary and SpainBlanco-González & Kienlin, eds (2020), 6th page of chapter 1, see map. and in North Africa. Within the Near East, they are concentrated in less arid regions, including Upper Mesopotamia, the Southern Levant, Anatolia and Iran, which had more continuous settlement. Eurasian tells date to the Neolithic,Blanco-González & Kienlin, eds (2020), 2nd page of chapter 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. is a city in Western Asia. Situated on a plateau in the Judaean Mountains between the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and the Dead Sea, it is one of the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest cities in the world and is considered to be a holy city for the three major Abrahamic religions: Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. Both Israelis and Palestinians claim Jerusalem as their Capital city, capital, as Israel maintains its primary governmental institutions there and the State of Palestine ultimately foresees it as its seat of power. Because of this dispute, Status of Jerusalem, neither claim is widely recognized internationally. Throughout History of Jerusalem, its long history, Jerusalem has been destroyed at least twice, Sie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Israel (united Monarchy)
The United Monarchy () in the Hebrew Bible refers to History of ancient Israel and Judah, Israel and Judah under the reigns of Saul, David, and Solomon. It is traditionally dated to have lasted between and . According to the biblical account, on the succession of Solomon's son Rehoboam, the United Monarchy would have split into two separate kingdoms: the Kingdom of Israel (Samaria), Kingdom of Israel in the north, containing the cities of Shechem and Samaria (ancient city), Samaria; and the Kingdom of Judah in the south, containing the city of Jerusalem and the Temple in Jerusalem, Jewish Temple. However, whether or not the United Monarchy actually existed is a matter of ongoing academic debate. In the 1990s, Israeli archaeologist Israel Finkelstein contested that existing archaeological evidence for the United Monarchy in the 10th century BCE should actually be dated to the 9th century BCE. This model placed the biblical kingdom in Iron Age, Iron Age I, suggesting that it was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tribe Of Judah
According to the Hebrew Bible, the tribe of Judah (, ''Shevet Yehudah'') was one of the twelve Tribes of Israel, named after Judah, the son of Jacob. Judah was the first tribe to take its place in the Land of Israel, occupying the southern part of the territory. Jesse and his sons, including King David, belonged to this tribe. Biblical account The tribe of Judah, its conquests, and the centrality of its capital in Jerusalem for the worship of the god Yahweh figure prominently in the Deuteronomistic history, encompassing the books of Deuteronomy through II Kings, which most scholars agree was reduced to written form, although subject to exilic and post-exilic alterations and emendations, during the reign of the Judahite reformer Josiah from 641–609 BCE. According to the account in the Book of Joshua, following a partial conquest of Canaan by the Israelite tribes (the Jebusites still held Jerusalem),Kitchen, Kenneth A. (2003), ''On the Reliability of the Old Testament'' ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gibeon (ancient City)
Gibeon ( he, , ''Gīḇəʻōn''; grc-gre, Γαβαων, ''Gabaōn'') was a Canaanite and, later, an Israelite city which was located north of Jerusalem. According to and , the pre-Israelite-conquest inhabitants, the Gibeonites, were Hivites; according to they were Amorites. The remains of Gibeon are located in the southern portion of the Palestinian village of al-Jib. Biblical account Canaanite city After the destruction of Jericho and Ai, the Hivite people of Gibeon sent ambassadors to trick Joshua and the Israelites into making a treaty with them. According to the Bible, the Israelites were commanded to destroy all non-Israelite Canaanites in Palestine. The Gibeonites presented themselves as ambassadors from a distant, powerful land. Without consulting God (), the Israelites entered into a covenant or peace treaty with the Gibeonites. The Israelites soon found out that the Gibeonites were actually their neighbors, living within three days walk of them ( Joshua 9:17) and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Book Of Joshua
The Book of Joshua ( he, סֵפֶר יְהוֹשֻׁעַ ', Tiberian: ''Sēp̄er Yŏhōšūaʿ'') is the sixth book in the Hebrew Bible and the Christian Old Testament, and is the first book of the Deuteronomistic history, the story of Israel from the conquest of Canaan to the Babylonian exile. It tells of the campaigns of the Israelites in central, southern and northern Canaan, the destruction of their enemies, and the division of the land among the Twelve Tribes, framed by two set-piece speeches, the first by God commanding the conquest of the land, and, at the end, the second by Joshua warning of the need for faithful observance of the Law (''torah'') revealed to Moses. Almost all scholars agree that the Book of Joshua holds little historical value for early Israel and most likely reflects a much later period. The earliest parts of the book are possibly chapters 2–11, the story of the conquest; these chapters were later incorporated into an early form of Joshua likely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amarna Letters
The Amarna letters (; sometimes referred to as the Amarna correspondence or Amarna tablets, and cited with the abbreviation EA, for "El Amarna") are an archive, written on clay tablets, primarily consisting of diplomatic correspondence between the Ancient Egypt, Egyptian administration and its representatives in Canaan and Amurru kingdom, Amurru, or neighboring kingdom leaders, during the New Kingdom, spanning a period of no more than thirty years between c. 1360–1332 BC (see Amarna letters#Chronology, here for dates).Moran, p.xxxiv The letters were found in Upper Egypt at el-Amarna, the modern name for the ancient Egyptian capital of ''Akhetaten'', founded by pharaoh Akhenaten (1350s–1330s BC) during the Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt. The Amarna letters are unusual in Egyptological research, because they are written not in the language of ancient Egypt, but in cuneiform, the writing system of ancient Mesopotamia. Most are in a variety of Akkadian language, Akkadian sometim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lakhish, Israel
Lakhish ( he, לָכִישׁ) is a moshav in the northern Negev in south-central Israel. Located south-east of Kiryat Gat, it falls under the jurisdiction of Lakhish Regional Council. In it had a population of . History The moshav was founded as a Nahal settlement in 1955 on the land of the depopulated Palestinian village of al-Qubayba. Named after Lachish Lachish ( he, לכיש; grc, Λαχίς; la, Lachis) was an ancient Canaanite and Israelite city in the Shephelah ("lowlands of Judea") region of Israel, on the South bank of the Lakhish River, mentioned several times in the Hebrew Bible. Th ..., the ancient town of the same name, which is now an archaeological tel, just north of the moshav. Economy The economy of Lakhish is based on the cultivation and sale of grapes. In 2006, the moshav built a large reservoir with a capacity of 1.25 million cubic meters to irrigate its 6,000 dunams of vineyards. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moshav
A moshav ( he, מוֹשָׁב, plural ', lit. ''settlement, village'') is a type of Israeli town or settlement, in particular a type of cooperative agricultural community of individual farms pioneered by the Labour Zionists between 1904 and 1914, during what is known as the second wave of ''aliyah''. A resident or a member of a moshav can be called a "moshavnik" (). The moshavim are similar to kibbutzim with an emphasis on community labour. They were designed as part of the Zionist state-building programme following the green revolution Yishuv ("settlement") in the British Mandate of Palestine during the early 20th century, but in contrast to the collective farming kibbutzim, farms in a moshav tended to be individually owned but of fixed and equal size. Workers produced crops and other goods on their properties through individual or pooled labour with the profit and foodstuffs going to provide for themselves. Moshavim are governed by an elected council ( he, ועד, ''va'a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Qubayba, Hebron
al-Qubayba ( ar, القبيبة, قبيبة ابن عوّاد ), also known as Gbebah, Qubeiba or Qobebet Ibn 'Awwad, was a Palestinian village, located 24 kilometers northwest of Hebron. It was depopulated in the 1948 Arab–Israeli War. Name The eponym of the village, "Ibn 'Awwad" or "Ibn 'Awadh", was named after the clan residing therein. History Known in Crusader times as Deirelcobebe, the ruins of the ancient Canaanite and Judean city of Lachish lay adjacent to the village, which was subject to extensive archaeological excavations by the British Mandatory authorities in Palestine, and by Israeli authorities subsequent to its capture during the 1948 Arab-Israeli war. In 1136 the King of Jerusalem, Fulk confirmed ''Deirelcobebe'' as a casale under the Knights Hospitallers. Ottoman period In 1517, Al-Qubayba was incorporated into the Ottoman Empire with the rest of Palestine, and in 1596 it appeared in the tax registers as being in the ''nahiya'' (subdistrict) of Ga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nature And Parks Authority (Israel)
The Israel Nature and Parks Authority ( he, רשות הטבע והגנים ''Rashut Hateva Vehaganim''; ar, سلطة الطبيعة والحدائق) is an Israeli government organization that manages nature reserves and national parks in Israel, the Golan Heights and parts of the West Bank. The organization was founded in April 1998, merging two organizations (The National Parks Authority and the Nature Reserves Authority) that had managed the National parks and nature reserves of Israel, nature reserves and national parks separately since 1964. The director of the Authority is Shaul Goldstein.Israel Declares Five New National Parks and Nature Reserves Haaretz. Zafrir Rinat. 27/06/17. Retrieved 16/05/18 The symbol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





%2C_cisterns_(marked_Cis)_and_Caves.png)




