|
Tell Deir
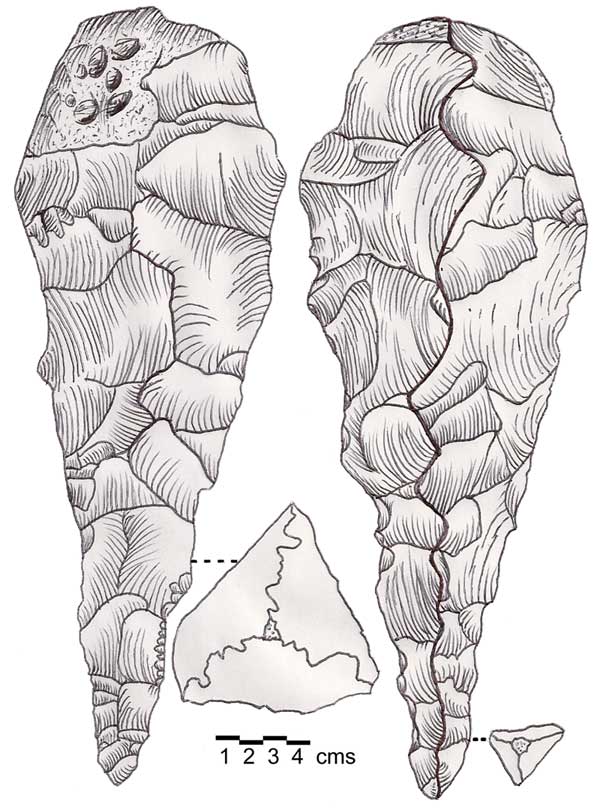
Tell Deir is an archaeological site approximately halfway between Joub Jannine and Chtaura in Lebanon. A large amount of Neolithic material was recovered from the site and it was studied by Lorraine Copeland and Peter Wescombe. The most plentiful types were large axes, adzes, picks, knives and scrapers. Some smaller burins were found along with sickles showing denticulation and segmentation. A few pottery sherds were found with burnishing and red washing. Finds resembled later Neolithic material found nearby and was also suggested to have been occupied in the Bronze Age The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri .... References {{Portal, Lebanon, History, Asia Neolithic settlements Archaeological sites in Lebanon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beqaa Valley
The Beqaa Valley ( ar, links=no, وادي البقاع, ', Lebanese ), also transliterated as Bekaa, Biqâ, and Becaa and known in classical antiquity as Coele-Syria, is a fertile valley in eastern Lebanon. It is Lebanon's most important farming region. Industry also flourishes in Beqaa, especially that related to agriculture. The Beqaa is located about east of Beirut. The valley is situated between Mount Lebanon to the west and the Anti-Lebanon Mountains to the east. It forms the northeasternmost extension of the Great Rift Valley, which stretches from Syria to the Red Sea. Beqaa Valley is long and wide on average. It has a Mediterranean climate of wet, often snowy winters and dry, warm summers. The region receives limited rainfall, particularly in the north, because Mount Lebanon creates a rain shadow that blocks precipitation coming from the sea. The northern section has an average annual rainfall of , compared to in the central valley. Nevertheless, two rivers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lebanon
Lebanon ( , ar, لُبْنَان, translit=lubnān, ), officially the Republic of Lebanon () or the Lebanese Republic, is a country in Western Asia. It is located between Syria to the north and east and Israel to the south, while Cyprus lies to its west across the Mediterranean Sea; its location at the crossroads of the Mediterranean Basin and the Arabian hinterland has contributed to its rich history and shaped a cultural identity of religious diversity. It is part of the Levant region of the Middle East. Lebanon is home to roughly six million people and covers an area of , making it the second smallest country in continental Asia. The official language of the state is Arabic, while French is also formally recognized; the Lebanese dialect of Arabic is used alongside Modern Standard Arabic throughout the country. The earliest evidence of civilization in Lebanon dates back over 7000 years, predating recorded history. Modern-day Lebanon was home to the Phoenicians, a m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tell (archaeology)
In archaeology, a tell or tel (borrowed into English from ar, تَلّ, ', 'mound' or 'small hill'), is an artificial topographical feature, a species of mound consisting of the accumulated and stratified debris of a succession of consecutive settlements at the same site, the refuse of generations of people who built and inhabited them, and of natural sediment. (Very limited snippet view).Matthews (2020)Introduction and Definition/ref> Tells are most commonly associated with the ancient Near East, but they are also found elsewhere, such as Southern and parts of Central Europe, from Greece and Bulgaria to Hungary and SpainBlanco-González & Kienlin, eds (2020), 6th page of chapter 1, see map. and in North Africa. Within the Near East, they are concentrated in less arid regions, including Upper Mesopotamia, the Southern Levant, Anatolia and Iran, which had more continuous settlement. Eurasian tells date to the Neolithic,Blanco-González & Kienlin, eds (2020), 2nd page of chapter 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts of the world. This "Neolithic package" included the introduction of farming, domestication of animals, and change from a hunter-gatherer lifestyle to one of settlement. It began about 12,000 years ago when farming appeared in the Epipalaeolithic Near East, and later in other parts of the world. The Neolithic lasted in the Near East until the transitional period of the Chalcolithic (Copper Age) from about 6,500 years ago (4500 BC), marked by the development of metallurgy, leading up to the Bronze Age and Iron Age. In other places the Neolithic followed the Mesolithic (Middle Stone Age) and then lasted until later. In Ancient Egypt, the Neolithic lasted until the Protodynastic period, 3150 BC.Karin Sowada and Peter Grave. Egypt in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lorraine Copeland
Lorraine Copeland (born Elizabeth Lorraine Adie, 1921April 2013) was a British archaeologist specialising in the Palaeolithic period of the Near East. She was a secret agent with the Special Operations Executive during World War II. Early life In 1921, Copeland was born as Elizabeth Lorraine Adie in Edinburgh, Scotland. Her father was a neurosurgeon on Harley Street in London, and she was privately educated at Wycombe Abbey girls' school in Buckinghamshire. Special Operations Executive Copeland worked for British Intelligence during the Second World War, in the Special Operations Executive. She met her American husband, Miles Copeland, Jr., during this period, when he was based in the UK undertaking counter-intelligence for the US Army Counter Intelligence Corps. They married on 25 September 1942 and soon afterwards Miles' work took them to the Near East, particularly Syria, Lebanon and Egypt, and it was whilst in this area that Copeland first developed her interest in archaeo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joub Jannine
Joub Jannine ( / ALA-LC: ''Jub Jannīn'') is located in the Beqaa Valley in Lebanon. Joub Jannine is the capital of West Beqaa. It is a town and the center of the Western Beqaa District, hosting the Grand Serail, Serail, which is a main governmental building serving the area. Joub Jannine is the largest and most populated town in its district with a population of 14,728. All major banks exist in Joub Jannine as well as a trades college, Amusement Park, indoor/outdoor soccer arena, basketball court and the weekly Souk which takes place every Saturday and is a local produce market. Joub Jannine is surrounded by a number of villages. To the south there is the village of Lala, Ghazze to the north, Kamid al lawz to the east, and Kefraya, known for its Grape, wine grape vineyards, to the west. History In 1838, Eli Smith noted ''Jubb Jenin'' as a Sunni Muslim village in the Beqaa Valley. Archaeological sites Joub Jannine I is a small surface site brought to the surface through erosio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chtaura
Chtaura ( ar, شتورا) is a town in Lebanon in the fertile Beqaa Valley, Beqaa valley located between the Mount Lebanon and Syria. It is located halfway on the Beirut - Damascus highway. It is located from Beirut. Chtaura is the valley's hub for banking, transportation, and commerce, with many hotels and restaurants on the main road. From Chtaura, travelers can depart for Zahlé, Baalbek, or Damascus. History On January 29, 1983, the Israeli-run Front for the Liberation of Lebanon from Foreigners detonated a car bomb close to the Fatah HQ at Chtaura (also named Shtura), and another in West Beirut, close to the HQ of the left-wing Mourabitoun. Some sixty people were killed and hundreds wounded. For almost 30 years, during the civil war, the Syrian Army’s military headquarters for the Beqaa Valley was in Chtaura. On 24 November 1989, following the assassination of President René Moawad, his successor, Elias Hrawi, was elected by a hastily gathered assembly of 53 MPs in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter Wescombe
Peter Wescombe (4 January 1932 – 25 November 2014) was a British diplomat, amateur archaeologist, historian and founding member of the Bletchley Park Bletchley Park is an English country house and estate in Bletchley, Milton Keynes ( Buckinghamshire) that became the principal centre of Allied code-breaking during the Second World War. The mansion was constructed during the years following ... Trust. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Wescombe, Peter 1932 births 2014 deaths Amateur archaeologists British diplomats Bletchley Park people ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adze
An adze (; alternative spelling: adz) is an ancient and versatile cutting tool similar to an axe but with the cutting edge perpendicular to the handle rather than parallel. Adzes have been used since the Stone Age. They are used for smoothing or carving wood in hand woodworking, and as a hoe for agriculture and horticulture. Two basic forms of an adze are the hand adze (short hoe)—a short-handled tool swung with one hand—and the foot adze (hoe)—a long-handled tool capable of powerful swings using both hands, the cutting edge usually striking at foot or shin level. A similar tool is called a mattock, which differs by having two blades, one perpendicular to the handle and one parallel. History Africa The adze is depicted in ancient Egyptian art from the Old Kingdom onward. Originally the adze blades were made of stone, but already in the Predynastic Period copper adzes had all but replaced those made of flint. stone blades were fastened to the handle by tying and early ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sickle
A sickle, bagging hook, reaping-hook or grasshook is a single-handed agricultural tool designed with variously curved blades and typically used for harvesting, or reaping, grain crops or cutting succulent forage chiefly for feeding livestock, either freshly cut or dried as hay. Falx was a synonym but was later used to mean any of a number of tools that had a curved blade that was sharp on the inside edge such as a scythe. Since the beginning of the Iron Age hundreds of region-specific variants of the sickle have evolved, initially of iron and later steel. This great diversity of sickle types across many cultures can be divided into smooth or serrated blades, both of which can be used for cutting either green grass or mature cereals using slightly different techniques. The serrated blade that originated in prehistoric sickles still dominates in the reaping of grain and is even found in modern grain-harvesting machines and in some kitchen knives. History Pre-Neolithic The d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pottery
Pottery is the process and the products of forming vessels and other objects with clay and other ceramic materials, which are fired at high temperatures to give them a hard and durable form. Major types include earthenware, stoneware and porcelain. The place where such wares are made by a ''potter'' is also called a ''pottery'' (plural "potteries"). The definition of ''pottery'', used by the ASTM International, is "all fired ceramic wares that contain clay when formed, except technical, structural, and refractory products". In art history and archaeology, especially of ancient and prehistoric periods, "pottery" often means vessels only, and sculpted figurines of the same material are called "terracottas". Pottery is one of the oldest human inventions, originating before the Neolithic period, with ceramic objects like the Gravettian culture Venus of Dolní Věstonice figurine discovered in the Czech Republic dating back to 29,000–25,000 BC, and pottery vessels that were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sherd
In archaeology, a sherd, or more precisely, potsherd, is commonly a historic or prehistoric fragment of pottery, although the term is occasionally used to refer to fragments of stone and glass vessels, as well. Occasionally, a piece of broken pottery may be referred to as a shard. While the spelling shard is generally reserved for referring to fragments of glass vessels, the term does not exclude pottery fragments. The etymology is connected with the idea of breakage, from Old English ''sceard'', related to Old Norse ''skarð'', "notch", and Middle High German ''schart'', "notch". A sherd or potsherd that has been used by having writing painted or inscribed on it can be more precisely referred to as an ostracon An ostracon (Greek: ''ostrakon'', plural ''ostraka'') is a piece of pottery, usually broken off from a vase or other earthenware vessel. In an archaeological or epigraphical context, ''ostraca'' refer to sherds or even small pieces of ston .... The analysis of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.png)
.jpg)
