|
Television Guidance
Television guidance (TGM) is a type of missile guidance system using a television camera in the missile or glide bomb that sends its signal back to the launch platform. There, a weapons officer or bomb aimer watches the image on a television screen and sends corrections to the missile, typically over a radio control link. Television guidance is not a ''seeker'' because it is not automated, although semi-automated systems with autopilots to smooth out the motion are known. They should not be confused with contrast seekers, which also use a television camera but are true automated seeker systems. The concept was first explored by the Germans during World War II as an anti-shipping weapon that would keep the launch aircraft safely out of range of the target's anti-aircraft guns. The best-developed example was the Henschel Hs 293, but the TV guided versions did not see operational use. The US also experimented with similar weapons during the war, notably the GB-4 and Interstate TDR. Onl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Missile Guidance
Missile guidance refers to a variety of methods of guiding a missile or a guided bomb to its intended target. The missile's target accuracy is a critical factor for its effectiveness. Guidance systems improve missile accuracy by improving its Probability of Guidance (Pg). These guidance technologies can generally be divided up into a number of categories, with the broadest categories being "active", "passive", and "preset" guidance. Missiles and guided bombs generally use similar types of guidance system, the difference between the two being that missiles are powered by an onboard engine, whereas guided bombs rely on the speed and height of the launch aircraft for propulsion. History The concept of unmanned guidance originated at least as early as World War I, with the idea of remotely guiding an airplane bomb onto a target, such as the systems developed for the first powered drones by Archibald Low (The Father of Radio Guidance). In World War II, guided missiles were first d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
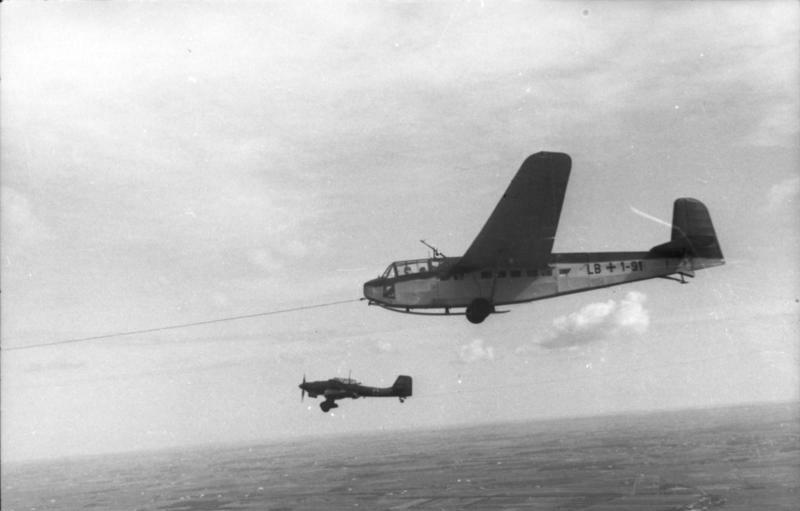
Henschel Hs 293 V4 Pic2
Henschel & Son (german: Henschel und Sohn) was a German company, located in Kassel, best known during the 20th century as a maker of transportation equipment, including locomotives, trucks, buses and trolleybuses, and armoured fighting vehicles and weapons. Georg Christian Carl Henschel founded the factory in 1810 at Kassel. His son Carl Anton Henschel founded another factory in 1837. In 1848, the company began manufacturing locomotives. The factory became the largest locomotive manufacturer in Germany by the 20th century. Henschel built 10 articulated steam trucks, using Doble steam car, Doble steam designs, for Deutsche Reichsbahn-Gesellschaft, Deutsche Reichsbahn railways as delivery trucks. Several cars were built as well, one of which became Hermann Göring's staff car. In 1935 Henschel was able to upgrade its various steam locomotives to a high-speed Streamliner type with a maximum speeds of up to by the addition of a removable shell over the old steam locomotive. In 191 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
US Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage of its active battle fleet alone exceeding the next 13 navies combined, including 11 allies or partner nations of the United States as of 2015. It has the highest combined battle fleet tonnage (4,635,628 tonnes as of 2019) and the world's largest aircraft carrier fleet, with eleven in service, two new carriers under construction, and five other carriers planned. With 336,978 personnel on active duty and 101,583 in the Ready Reserve, the United States Navy is the third largest of the United States military service branches in terms of personnel. It has 290 deployable combat vessels and more than 2,623 operational aircraft . The United States Navy traces its origins to the Continental Navy, which was established during the American Re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wright Patterson Air Force Base
Wright-Patterson Air Force Base (WPAFB) is a United States Air Force base and census-designated place just east of Dayton, Ohio, in Greene County, Ohio, Greene and Montgomery County, Ohio, Montgomery counties. It includes both Wright and Patterson Fields, which were originally Wilbur Wright Field and Fairfield Aviation General Supply Depot. Patterson Field is approximately northeast of Dayton, Ohio, Dayton; Wright Field is approximately northeast of Dayton. The host unit at Wright-Patterson AFB is the 88th Air Base Wing (88 ABW), assigned to the Air Force Life Cycle Management Center and Air Force Materiel Command. The 88 ABW operates the airfield, maintains all infrastructure and provides security, communications, medical, legal, personnel, contracting, finance, transportation, air traffic control, weather forecasting, public affairs, recreation and chaplain services for more than 60 associate units. The base's origins begin with the establishment of Wilbur Wright Field on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry H
Henry may refer to: People *Henry (given name) * Henry (surname) * Henry Lau, Canadian singer and musician who performs under the mononym Henry Royalty * Portuguese royalty ** King-Cardinal Henry, King of Portugal ** Henry, Count of Portugal, Henry of Burgundy, Count of Portugal (father of Portugal's first king) ** Prince Henry the Navigator, Infante of Portugal ** Infante Henrique, Duke of Coimbra (born 1949), the sixth in line to Portuguese throne * King of Germany ** Henry the Fowler (876–936), first king of Germany * King of Scots (in name, at least) ** Henry Stuart, Lord Darnley (1545/6–1567), consort of Mary, queen of Scots ** Henry Benedict Stuart, the 'Cardinal Duke of York', brother of Bonnie Prince Charlie, who was hailed by Jacobites as Henry IX * Four kings of Castile: ** Henry I of Castile ** Henry II of Castile **Henry III of Castile Henry III of Castile (4 October 1379 – 25 December 1406), called the Suffering due to his ill health (, ), was the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Air Force
The Royal Air Force (RAF) is the United Kingdom's air and space force. It was formed towards the end of the First World War on 1 April 1918, becoming the first independent air force in the world, by regrouping the Royal Flying Corps (RFC) and the Royal Naval Air Service (RNAS). Following the Allied victory over the Central Powers in 1918, the RAF emerged as the largest air force in the world at the time. Since its formation, the RAF has taken a significant role in British military history. In particular, it played a large part in the Second World War where it fought its most famous campaign, the Battle of Britain. The RAF's mission is to support the objectives of the British Ministry of Defence (MOD), which are to "provide the capabilities needed to ensure the security and defence of the United Kingdom and overseas territories, including against terrorism; to support the Government's foreign policy objectives particularly in promoting international peace and security". ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against France. The modern Royal Navy traces its origins to the early 16th century; the oldest of the UK's armed services, it is consequently known as the Senior Service. From the middle decades of the 17th century, and through the 18th century, the Royal Navy vied with the Dutch Navy and later with the French Navy for maritime supremacy. From the mid 18th century, it was the world's most powerful navy until the Second World War. The Royal Navy played a key part in establishing and defending the British Empire, and four Imperial fortress colonies and a string of imperial bases and coaling stations secured the Royal Navy's ability to assert naval superiority globally. Owing to this historical prominence, it is common, even among non-Britons, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proportional Navigation
For example, if the line of sight rotates slowly from north to east, the missile should turn to the right by a certain factor faster than the LOS-rate. This factor is ''N''. Proportional navigation (also known as PN or Pro-Nav) is a guidance law (analogous to proportional control) used in some form or another by most homing air target missiles.Yanushevsky, page 3. It is based on the fact that two vehicles are on a collision course when their direct line-of-sight does not change direction as the range closes. PN dictates that the missile velocity vector should rotate at a rate proportional to the rotation rate of the line of sight (Line-Of-Sight rate or LOS-rate), and in the same direction. : a_n = N\dot \lambda V Where a_n is the acceleration perpendicular to the missile's instantaneous velocity vector, N is the proportionality constant generally having an integer value 3-5 (dimensionless), \dot \lambda is the line of sight rate, and V is the closing velocity. Since the line ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
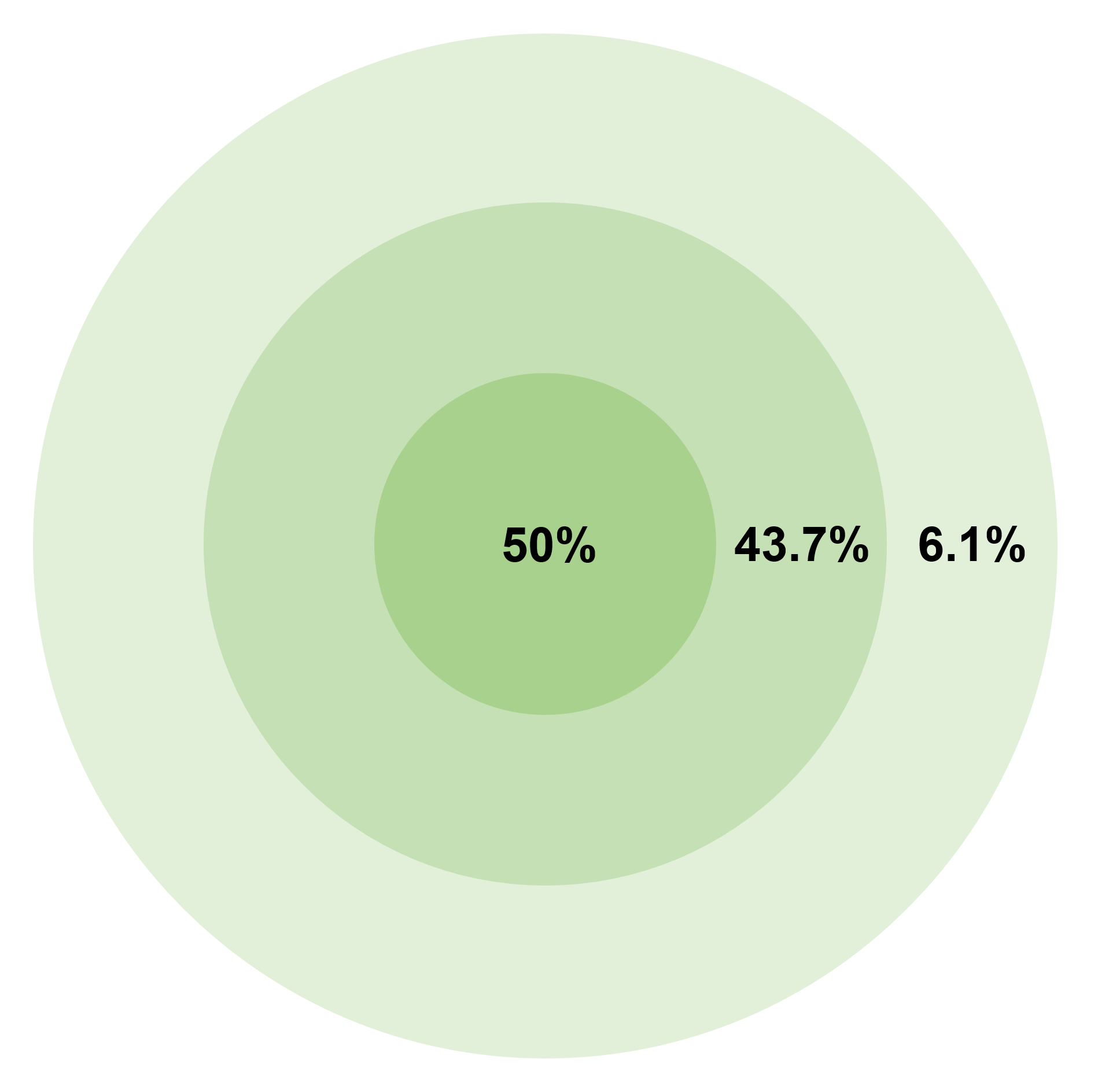
Circular Error Probable
In the military science of ballistics, circular error probable (CEP) (also circular error probability or circle of equal probability) is a measure of a weapon system's precision. It is defined as the radius of a circle, centered on the mean, whose perimeter is expected to include the landing points of 50% of the rounds; said otherwise, it is the median error radius. That is, if a given munitions design has a CEP of 100 m, when 100 munitions are targeted at the same point, 50 will fall within a circle with a radius of 100 m around their average impact point. (The distance between the target point and the average impact point is referred to as bias.) There are associated concepts, such as the DRMS (distance root mean square), which is the square root of the average squared distance error, and R95, which is the radius of the circle where 95% of the values would fall in. The concept of CEP also plays a role when measuring the accuracy of a position obtained by a navig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angle Of Attack
In fluid dynamics, angle of attack (AOA, α, or \alpha) is the angle between a reference line on a body (often the chord line of an airfoil) and the vector representing the relative motion between the body and the fluid through which it is moving. Angle of attack is the angle between the body's reference line and the oncoming flow. This article focuses on the most common application, the angle of attack of a wing or airfoil moving through air. In aerodynamics, angle of attack specifies the angle between the chord line of the wing of a fixed-wing aircraft and the vector representing the relative motion between the aircraft and the atmosphere. Since a wing can have twist, a chord line of the whole wing may not be definable, so an alternate reference line is simply defined. Often, the chord line of the root of the wing is chosen as the reference line. Another choice is to use a horizontal line on the fuselage as the reference line (and also as the longitudinal axis). Some aut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deutsche Forschungsanstalt Für Segelflug
The ''Deutsche Forschungsanstalt für Segelflug'' (), or DFS , was formed in 1933 to centralise all gliding activity in Germany, under the directorship of Professor Walter Georgii. It was formed by the nationalisation of the Rhön-Rossitten Gesellschaft (RRG) at Darmstadt.Reitsch, H., 1955, The Sky My Kingdom, London: Biddles Limited, Guildford and King's Lynn, The DFS was involved in producing training sailplanes for the Hitler Youth and Luftwaffe, as well as conducting research into advanced technologies such as flying wings and rocket propulsion. Notable DFS-produced aircraft include the DFS 230 transport glider (1600+ produced), the German counterpart to the British Airspeed Horsa glider, and the DFS 194, similar to the famous Messerschmitt Me 163 rocket fighter. In 1938, following a fatal accident at the Wasserkuppe, DFS held a competition to design a more effective speed brake for gliders. The final design, produced by Wolfgang and Ulrich Hütter of Schempp-Hirth, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cathode Ray Tube
A cathode-ray tube (CRT) is a vacuum tube containing one or more electron guns, which emit electron beams that are manipulated to display images on a phosphorescent screen. The images may represent electrical waveforms ( oscilloscope), pictures ( television set, computer monitor), radar targets, or other phenomena. A CRT on a television set is commonly called a picture tube. CRTs have also been used as memory devices, in which case the screen is not intended to be visible to an observer. The term '' cathode ray'' was used to describe electron beams when they were first discovered, before it was understood that what was emitted from the cathode was a beam of electrons. In CRT television sets and computer monitors, the entire front area of the tube is scanned repeatedly and systematically in a fixed pattern called a raster. In color devices, an image is produced by controlling the intensity of each of three electron beams, one for each additive primary color (red, gre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)