|
Taxation In Premodern China
__NOTOC__ Taxation in premodern China varied greatly over time. The most important source of state revenue was the tax on agriculture, or land tax. During some dynasties, the government also imposed monopolies that became important sources of revenue. The monopoly on salt was especially lucrative and stable. Commercial taxes were generally quite low, except in times of war. Other means of state revenues were inflation, forced labor (the corvee), and expropriation of rich merchants and landowners. Below is a chart of the sources of state revenue in Imperial China. See also * History of canals in China The history of canals in China connecting its major rivers and centers of agriculture and population extends from the legendary exploits of Yu the Great in his attempts control the flooding of the Yellow River to the present infrastructure project ..., for their use in conveying the grain taxes References Citations General sources * * * * * * * * {{China top ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poll Tax Receipts - 7
Poll, polled, or polling may refer to: Figurative head counts * Poll, a formal election ** Election verification exit poll, a survey taken to verify election counts ** Polling, voting to make decisions or determine opinions ** Polling places or polling station, a.k.a. the polls, where voters cast their ballots in elections * Poll, a non-formal election: ** Opinion poll, a survey of public opinion ** Exit poll, a survey of voters taken immediately after they have exited the polling stations ** Straw poll, an ad-hoc or unofficial vote ** Survey (human research) Agriculture * Poll (livestock), the top of an animal's head * Polled livestock, hornless livestock of normally horned species * Polling, livestock dehorning Arts, entertainment, and media * Poll (band), a Greek pop group of the 1970s * ''Poll'', the German title for the 2010 film ''The Poll Diaries'' Mathematics, science, and technology * poll (Unix), a Unix system call *POLL, DNA polymerase lambda * Polling (comput ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wang Anshi
Wang Anshi ; ; December 8, 1021 – May 21, 1086), courtesy name Jiefu (), was a Chinese economist, philosopher, poet, and politician during the Song dynasty. He served as chancellor and attempted major and controversial socioeconomic reforms known as the New Policies. These reforms constituted the core concepts of the Song-Dynasty Reformists, in contrast to their rivals, the Conservatives, led by the Chancellor Sima Guang. Wang Anshi's ideas are usually analyzed in terms of the influence the '' Rites of Zhou'' or Legalism had on him. His economic reforms included increased currency circulation, breaking up of private monopolies, and early forms of government regulation and social welfare. His military reforms expanded the use of local militias, and his government reforms expanded the civil service examination system and attempted to suppress nepotism in government. Although successful for a while, he eventually fell out of favor with the emperor. Early career Wang Anshi was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Imperial China
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as well as the memory, discovery, collection, organization, presentation, and interpretation of these events. Historians seek knowledge of the past using historical sources such as written documents, oral accounts, art and material artifacts, and ecological markers. History is not complete and still has debatable mysteries. History is also an academic discipline which uses narrative to describe, examine, question, and analyze past events, and investigate their patterns of cause and effect. Historians often debate which narrative best explains an event, as well as the significance of different causes and effects. Historians also debate the nature of history as an end in itself, as well as its usefulness to give perspective on the problems of the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economic History Of China
The economic history of China is covered in the following articles: * Economic history of China before 1912, the economic history of China during the ancient China and imperial China, before the establishment of the Republic of China in 1912. ** Economy of the Han dynasty (202 BC – AD 220) ** Economy of the Song dynasty (960–1279) ** Economy of the Ming dynasty (1368–1644) * Economic history of China (1912–1949), the economic history of the Republic of China during the period when it controlled Chinese mainland from 1912 to 1949.For the economic history of the Republic of China during the period when it only controls Taiwan area after 1949, see Economic history of Taiwan#Modern history. * Economic history of China (1949–present), the economic history of the People's Republic of China. See also *Economy of China *Economic history of the Republic of China Economic history of the Republic of China is covered in the following articles: * Economic history of China (1912–4 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Cambridge History Of China
''The Cambridge History of China'' is a series of books published by the Cambridge University Press (CUP) covering the history of China from the founding of the Qin dynasty in 221 BC to 1982 AD. The series was conceived by British historian Denis C. Twitchett and American historian John K. Fairbank in the late 1960s, and publication began in 1978. The complete ''History'' will contain 15 volumes made up of 17 books (not including the ''Cambridge History of Ancient China'') with volumes 5 and 9 consisting of two books each. Chinese history before the Qin dynasty is covered in an independent volume, ''The Cambridge History of Ancient China'' (1999) which follows the Pinyin romanization system; the other volumes except vol. 2 use Wade–Giles romanization. The final volume, Volume 4, was to be published in 2020, but is indefinitely delayed. An unauthorized Chinese translation of volume 7 (''The Ming Dynasty, 1368–1644, Part 1'') was made in 1992 by the Chinese Academy of Social ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Canals In China
The history of canals in China connecting its major rivers and centers of agriculture and population extends from the legendary exploits of Yu the Great in his attempts control the flooding of the Yellow River to the present infrastructure projects of the People's Republic of China. From the Spring and Autumn period (8th–5th centuriesBCE) onward, the canals of China were used for army transportation and supply, as well as colonization of new territories. From the Qin (3rd century BCE) to the Qing (17th–20th centuriesCE), China's canal network was also essential to imperial taxation-in-kind. Control of shipbuilding and internal tariffs were also administered along the canals. History Spring and Autumn and Warring States periods In 647BCE, the State of Jin suffered major crop failure. Duke Mu of Qin despatched a large fleet of ships manned by Corvée labour from his capital at Yong (雍) in modern-day Fengxiang County, Shaanxi Province. The ships carried several thousands ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Likin (taxation)
The likin or lijin was a form of internal tariff in the Chinese Empire and Republic, which was first introduced as a means of financing the largely locally recruited armies to suppress the Taiping Rebellion. History The lijin tax was first introduced in 1853 by censor Lei Yixian in the area around Yangzhou as a way of raising funds in the campaigns against local rebels. As the central government was short of revenue, the imperial court sanctioned the tax and it quickly became an important source of funds for the campaign against the Taiping and Nian rebellions. The tax was levied on an ad valorem basis on goods in transit between provinces and on shops, with rates ranging from 2 to 10 per cent.Philip A. Kuhn. The creation of the treaty system in TWITCHETT / FAIRBANK The Cambridge History of China, Vol. 10 , Cambridge, 1978. Cf. Pg 289 After the Taipings were suppressed in 1864, the likin became a permanent feature of the Chinese tax system and it became an important source of revenu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Confucian
Confucianism, also known as Ruism or Ru classicism, is a system of thought and behavior originating in ancient China. Variously described as tradition, a philosophy, a Religious Confucianism, religion, a humanistic or rationalistic religion, a way of governing, or a way of life, Confucianism developed from what was later called the Hundred Schools of Thought from the teachings of the Chinese philosophy, Chinese philosopher Confucius (551–479 BCE). Confucius considered himself a transmitter of cultural values inherited from the Xia dynasty, Xia (c. 2070–1600 BCE), Shang dynasty, Shang (c. 1600–1046 BCE) and Western Zhou, Western Zhou dynasties (c. 1046–771 BCE). Confucianism was suppressed during the Legalism (Chinese philosophy), Legalist and autocratic Qin dynasty (221–206 BCE), but survived. During the Han dynasty (206 BCE–220 CE), Confucian approaches edged out the "proto-Taoist" Huang–Lao as the official ideology, while the emperors mixed both with the real ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
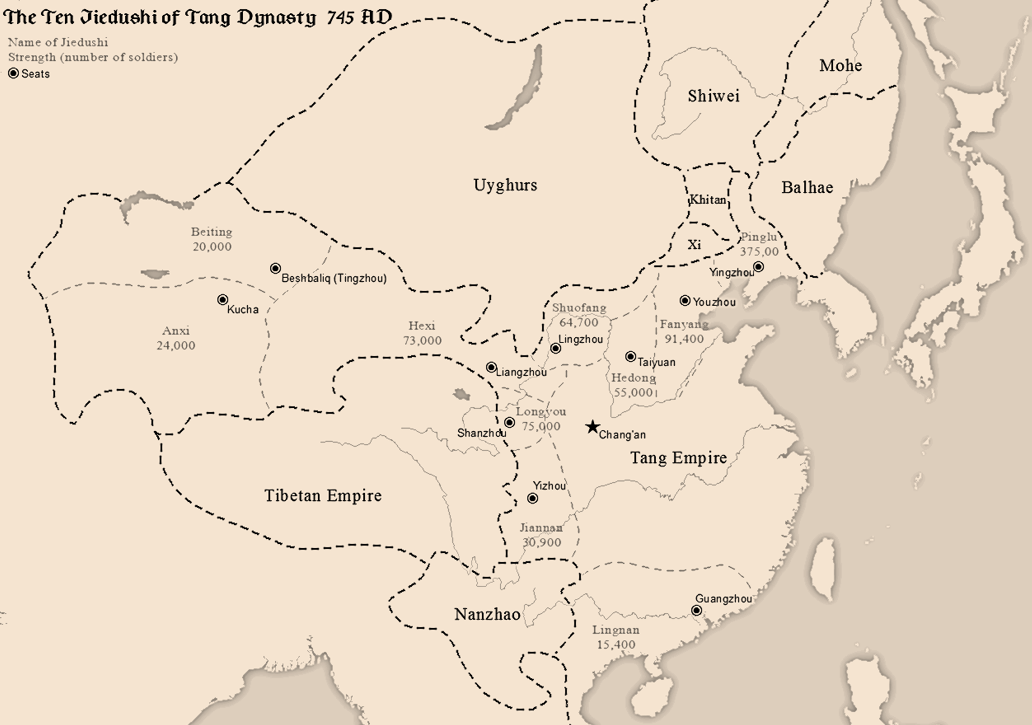
Anshi Rebellion
The An Lushan Rebellion was an uprising against the Tang dynasty of China towards the mid-point of the dynasty (from 755 to 763), with an attempt to replace it with the Yan dynasty. The rebellion was originally led by An Lushan, a general officer of the Tang military system. The event involved military activity and direct deaths from battle, but also significant associated population loss from famine, and population dislocations. The event is also known, especially in Chinese historiography, either as the An–Shi Rebellion or as the An–Shi Disturbances (). The use of the term ''luàn'' ("chaos") indicates the extreme social instability and population loss which eventually resulted, far beyond the initial consequences of the rebellion. Traditionally, Chinese family names have begun with the family name first. In this case the family name of the initial rebel leader is An. The term ''Ān-Shǐ'' is used to recognize that the rebellion continued after An Lushan's death, with t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salt In Chinese History
Salt, salt production, and salt taxes played key roles in Chinese history, economic development, and relations between state and society. The lure of salt profits led to technological innovation and new ways to organize capital. Debate over government salt policies brought forth conflicting attitudes toward the nature of government, private wealth, the relation between the rich and the poor, while the administration of these salt policies was a practical test of a government's competence. Because salt is a necessity of life, the salt tax (sometimes called the salt gabelle, after the French term for a salt tax) had a broad base and could be set at a low rate and still be one of the most important sources of government revenue. In early times, governments gathered salt revenues by managing production and sales directly. After innovations in the mid-8th century, imperial bureaucracies reaped these revenues safely and indirectly by selling salt rights to merchants who then sold t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wu Hu Uprising
The Upheaval of the Five Barbarians also translated as the Rebellion, the Revolt, or the Invasion of the Five Barbarians () is a Chinese expression which refers to a series of rebellions and invasions between 304 and 316 by non-Han Chinese, Han peoples, commonly called the Five Barbarians, living in North China against the Jin dynasty (266–420), Jin Empire, which had recently been weakened by War of the Eight Princes, a series of civil wars. The uprisings helped topple Emperor Huai of Jin in Luoyang and they ended the Western Jin dynasty in northern China. Rulers from four ethnic groups, the Xiongnu, Jie people, Jie, Qiang people, Qiang and Di (Five Barbarians), Di, then established a series of independent dynastic realms in northern China. The fifth group, the Xianbei in the north, were allied to the Western Jin and later Eastern Jin against the other four barbarians until turning on the Jin much later. A series of revolts in southern China occurred at the same time by souther ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Discourses On Salt And Iron
The Discourses on Salt and Iron () was a debate held at the imperial court in 81 BCE on state policy during the Han dynasty in China. The previous emperor, Emperor Wu of Han, Emperor Wu, had reversed the laissez-faire policies of his predecessors and imposed a wide variety of state interventions, such as creating Salt in Chinese History#Ancient China and the early empire, monopolies on China's salt and iron enterprises, price stabilization schemes, and taxes on capital. These actions sparked a fierce debate as to the policies of the Emperor. After his death, during the reign of Emperor Zhao of Han, the regent Huo Guang called on all the scholars of the empire to come to the capital, Chang'an, to debate the government's economic policies. The debate was characterized by two opposing factions, the reformists and the modernists. The reformists were largely Confucian scholars who opposed the policies of Emperor Wu and demanded the abolition of the monopolies on salt and iron, an end to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_and_8-Candareens%2C_Year_25_(1899).jpg)

.jpg)

.jpg)