|
Tau't Batu Language
Taaw't Bato (Tau't Batu) is one of several closely related languages spoken on Palawan Island in the Philippines. References Palawanic languages Languages of Palawan {{GCPhilippine-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no), * bik, Republika kan Filipinas * ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas * cbk, República de Filipinas * hil, Republika sang Filipinas * ibg, Republika nat Filipinas * ilo, Republika ti Filipinas * ivv, Republika nu Filipinas * pam, Republika ning Filipinas * krj, Republika kang Pilipinas * mdh, Republika nu Pilipinas * mrw, Republika a Pilipinas * pag, Republika na Filipinas * xsb, Republika nin Pilipinas * sgd, Republika nan Pilipinas * tgl, Republika ng Pilipinas * tsg, Republika sin Pilipinas * war, Republika han Pilipinas * yka, Republika si Pilipinas In the recognized optional languages of the Philippines: * es, República de las Filipinas * ar, جمهورية الفلبين, Jumhūriyyat al-Filibbīn is an archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. It is situated in the western Pacific Ocean and consists of around 7,641 islands t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palawan
Palawan (), officially the Province of Palawan ( cyo, Probinsya i'ang Palawan; tl, Lalawigan ng Palawan), is an archipelagic province of the Philippines that is located in the region of Mimaropa. It is the largest province in the country in terms of total area of . The capital city is Puerto Princesa. Palawan is known as the Philippines' ''Last Frontier'' and as the Philippines' ''Best Island''. The islands of Palawan stretch between Mindoro island in the northeast and Borneo in the southwest. It lies between the South China Sea and the Sulu Sea. The province is named after its largest island, Palawan Island (), measuring long, and wide."Palawan – the Philippines' Last Frontier" ''WowPhilippines''. Accessed August 27, 2008. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
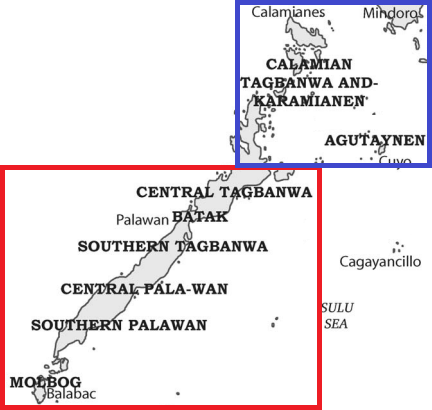
Peoples Of Palawan
A person ( : people) is a being that has certain capacities or attributes such as reason, morality, consciousness or self-consciousness, and being a part of a culturally established form of social relations such as kinship, ownership of property, or legal responsibility. The defining features of personhood and, consequently, what makes a person count as a person, differ widely among cultures and contexts. In addition to the question of personhood, of what makes a being count as a person to begin with, there are further questions about personal identity and self: both about what makes any particular person that particular person instead of another, and about what makes a person at one time the same person as they were or will be at another time despite any intervening changes. The plural form "people" is often used to refer to an entire nation or ethnic group (as in "a people"), and this was the original meaning of the word; it subsequently acquired its use as a plural form of per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malayo-Polynesian Languages
The Malayo-Polynesian languages are a subgroup of the Austronesian languages, with approximately 385.5 million speakers. The Malayo-Polynesian languages are spoken by the Austronesian peoples outside of Taiwan, in the island nations of Southeast Asia (Indonesian and Philippine Archipelago) and the Pacific Ocean, with a smaller number in continental Asia in the areas near the Malay Peninsula. Cambodia, Vietnam and the Chinese island Hainan serve as the northwest geographic outlier. Malagasy, spoken in the island of Madagascar off the eastern coast of Africa in the Indian Ocean, is the furthest western outlier. The languages spoken south-westward from central Micronesia until Easter Island are sometimes referred to as the Polynesian languages. Many languages of the Malayo-Polynesian family show the strong influence of Sanskrit and Arabic, as the western part of the region has been a stronghold of Hinduism, Buddhism, and, later, Islam. Two morphological characteristics of the M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philippine Languages
The Philippine languages or Philippinic are a proposed group by R. David Paul Zorc (1986) and Robert Blust (1991; 2005; 2019) that include all the languages of the Philippines and northern Sulawesi, Indonesia—except Sama–Bajaw (languages of the "Sea Gypsies") and a few languages of Palawan—and form a subfamily of Austronesian languages. Although the Philippines is near the center of Austronesian expansion from Formosa, there is little linguistic diversity among the approximately 150 Philippine languages, suggesting that earlier diversity has been erased by the spread of the ancestor of the modern Philippine languages. Classification History and criticism One of the first explicit classifications of a "Philippine" grouping based on genetic affiliation was in 1906 by Frank Blake, who placed them as a subdivision of the "Malay branch" within Malayo-Polynesian (MP), which at that time was considered as a family. Blake however encompasses every language within the geogr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greater Central Philippine Languages
The Greater Central Philippine languages are a proposed subgroup of the Austronesian language family, defined by the change of Proto-Malayo-Polynesian ''*R'' to ''*g''. They are spoken in the central and southern parts of the Philippines, and in northern Sulawesi, Indonesia. This subgroup was first proposed by Robert Blust (1991) based on lexical and phonological evidence, and is accepted by most specialists in the field. Most of the major languages of the Philippines belong to the Greater Central Philippine subgroup: Tagalog, the Visayan languages Cebuano, Hiligaynon, Waray; Central Bikol, the Danao languages Maranao and Magindanaon. On the island of Sulawesi, Indonesia, Gorontalo is the third-largest language by number of speakers. History According to Blust, the current distribution of the Greater Central Philippine languages is the result of an expansion that occurred around 500 B.C. and which led to levelling of much of the linguistic diversity in the central and sout ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palawanic Languages
The Palawanic languages are a subgroup in the Greater Central Philippine-family spoken on the island of Palawan and nearby islets. Languages The Palawanic languages are: * Palawano (a dialect cluster) * Aborlan Tagbanwa * Central Tagbanwa (not to be confused with Kalamian Tagbanwa) *Batak Batak is a collective term used to identify a number of closely related Austronesian ethnic groups predominantly found in North Sumatra, Indonesia, who speak Batak languages. The term is used to include the Karo, Pakpak, Simalungun, Toba, ... (not to be confused with the Batak languages) * Tau't Batu Molbog may also be in this group, closest to Palawano. Reconstruction Proto-Palawanic has been reconstructed by Thiessen (1980). References Further reading *Zorc, R. David. (1972a). Palawano Notes'. *Zorc, R. David. (1972b). Tagbanwa (Northern) Notes'. Greater Central Philippine languages Languages of Palawan {{GCPhilippine-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palawan Island
Palawan is the largest island of the province of Palawan in the Philippines and fifth-largest by area and tenth-most populous island of the country, with a total population of 994,101 as of 2020 census. The north west coast of the island is along the South China Sea, while the south east coast forms part of the northern limit of the Sulu Sea. Much of the island remains traditional and is considered by some as under-developed. Abundant wildlife, jungle mountains, and some white sandy beaches attract many tourists, as well as international companies looking for development opportunities. As of 2016, the main island of Palawan was rated the "Most Beautiful Island in the World" as voted by respective readers of rival travel publications Conde Nast Traveller and Travel + Leisure. It is the second year running that Palawan has won the Conde Nast Traveller award, as well as the second time in four years that it has occupied Travel + Leisure's top spot (2013). El Nido, Palawan, El Nido, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_1938.jpg)