|
Takamatsuzuka Kofun
The or "Tall Pine Tree Ancient Burial Mound" in Japanese language, Japanese is an ancient circular tomb in Asuka, Nara, Asuka village, Nara Prefecture, Japan. History The tomb is thought to have been built at some time between the end of the 7th century and the beginning of the 8th century. It was accidentally discovered by a local farmer in the 1960s. Description The mound of the tomb was built of alternating layers of clay and sand. It is about in diameter and high. Excavation yielded a burial chamber with painted fresco wall paintings of courtiers in Goguryeo-style garb. The paintings are in full color with red, blue, gold, and silver foil representing four male followers and four serving maidens together with the Azure Dragon (Chinese constellation), Azure Dragon, Black Tortoise (Chinese constellation), Black Tortoise, White Tiger (Chinese constellation), White Tiger, and Vermilion Bird (Chinese constellation), Vermilion Bird groups of stars. The paintings are Cultural Prope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prince Osakabe
Prince Osakabe (刑部(忍壁)親王, ''Osakabe Shinnō'') (died June 2, 705) was a Japanese imperial prince who helped write the Taihō Code (681 A.D.), alongside Fujiwara no Fuhito. The Code was essentially an administrative reorganization, which would serve as the basis for Japan's governmental structure for centuries afterwards. Background Prince Osakabe was born to Emperor Tenmu and Kajihime no Iratsume in approximately 663 A.D. According to the Nihon Shoki in the fifth month, on the fifth day of 679 A.D. Prince Osakabe, Prince Kusakabe, Prince Otsu, Prince Takechi, Prince Kawashima, and Prince Shiki, all swore to Emperor Tenmu that they wouldn't engage in future succession disputes. This occurred after Emperor Tenmu ascended the throne after the Jinshin War. In the first months of 704 A.D. he, Prince Naga, Prince Toneri, and Prince Hozumi were collectively awarded two hundred households by Emperor Monmu and Empress Genmei. Along with Prince Kawashima, Osakabe was appo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mural
A mural is any piece of graphic artwork that is painted or applied directly to a wall, ceiling or other permanent substrate. Mural techniques include fresco, mosaic, graffiti and marouflage. Word mural in art The word ''mural'' is a Spanish adjective that is used to refer to what is attached to a wall. The term ''mural'' later became a noun. In art, the word mural began to be used at the beginning of the 20th century. In 1906, Dr. Atl issued a manifesto calling for the development of a monumental public art movement in Mexico; he named it in Spanish ''pintura mural'' (English: ''wall painting''). In ancient Roman times, a mural crown was given to the fighter who was first to scale the wall of a besieged town. "Mural" comes from the Latin ''muralis'', meaning "wall painting". History Antique art Murals of sorts date to Upper Paleolithic times such as the cave paintings in the Lubang Jeriji Saléh cave in Borneo (40,000-52,000 BP), Chauvet Cave in Ardèche departmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cultural Affairs Agency
The is a special body of the Japanese Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT). It was set up in 1968 to promote Japanese arts and culture. The agency's budget for FY 2018 rose to ¥107.7 billion. Overview The agency's Cultural Affairs Division disseminates information about the arts within Japan and internationally, and the Cultural Properties Protection Division protects the nation's cultural heritage. The Cultural Affairs Division is concerned with such areas as art and culture promotion, art copyrights, and improvements in the national language. It also supports both national and local arts and cultural festivals, and it funds traveling cultural events in music, theater, dance, art exhibitions, and film-making. Special prizes are offered to encourage young artists and established practitioners, and some grants are given each year to enable them to train abroad. The agency funds national museums of modern art in Kyoto and Tokyo and The National ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Three Kingdoms Of Korea
Samhan or the Three Kingdoms of Korea () refers to the three kingdoms of Goguryeo (고구려, 高句麗), Baekje (백제, 百濟), and Silla (신라, 新羅). Goguryeo was later known as Goryeo (고려, 高麗), from which the modern name ''Korea'' is derived. The Three Kingdoms period is defined as being from 57 BC to 668 AD (but there existed Gaya confederacy in the southern region of the Korean Peninsula and relatively large states like Okjeo, Buyeo, and Dongye in its northern part and Manchuria of modern China). The "Korean Three Kingdoms" (Goguryeo, Baekje and Silla) contributed to what would become Korea; and the Goguryeo, Baekje and Silla peoples became what we know as the Korean people. The Book of Sui (Volume 81) recorded: "The customs, laws and clothes of Goguryeo, Baekje and Silla are generally identical." The three kingdoms occupied the entire peninsula of Korea and roughly half of Manchuria, located mostly in present-day China, along with smaller parts from present- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baekje
Baekje or Paekche (, ) was a Korean kingdom located in southwestern Korea from 18 BC to 660 AD. It was one of the Three Kingdoms of Korea, together with Goguryeo and Silla. Baekje was founded by Onjo, the third son of Goguryeo's founder Jumong and So Seo-no, at Wiryeseong (present-day southern Seoul). Baekje, like Goguryeo, claimed to succeed Buyeo, a state established in present-day Manchuria around the time of Gojoseon's fall. Baekje alternately battled and allied with Goguryeo and Silla as the three kingdoms expanded control over the peninsula. At its peak in the 4th century, Baekje controlled most of the western Korean peninsula, as far north as Pyongyang, and may have even held territories in China, such as in Liaoxi, though this view is controversial. It became a significant regional sea power, with political and trade relations with China and Japan. Baekje was a great maritime power; its nautical skill, which made it the Phoenicia of East Asia, was instrumental i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kudara No Konikishi
The Kudara no Konikishi ( ja, 百済王) was a Japanese clan whose founder, Zenkō ( or ), was a son of King Uija, the last king of Baekje, in southwestern Korea. ''Kudara'' was an ''uji'', or clan name, and represented its country of origin, Baekje. ''Konikishi'' or ''Kokishi'', which literally means "king", was a special ''kabane'' that was given only to the former royal families of Baekje and Goguryeo: the Kudara, Shōna (肖奈) and Koma (高麗) clans. The founder Zenkō came from Baekje to Japan as a hostage along with his brother Hōshō in 643. Even though Japan sent Hōshō back to Korea for a failed campaign to revive Baekje, Zenkō remained in Japan. The former royal family members were treated as "barbarian guests" (蕃客) and were not incorporated into the domestic political system of Japan for some time. They enjoyed privileged treatment although they were obliged to serve to the emperor in a symbolic fashion. They were finally assimilated into Japanese bureaucrac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heijō-kyō
was the Capital of Japan during most of the Nara period, from 710 to 740 and again from 745 to 784. The imperial palace is a listed UNESCO World Heritage together with other places in the city of Nara (cf. Historic Monuments of Ancient Nara). Empress Genmei ordered the Imperial capital moved from Fujiwara-kyō to Heijō-kyō in 708, and the move to Heijō-kyō was complete in 710. Heijō-kyō was modeled after Chang'an, the capital of Tang-dynasty China, although Heijō-kyō lacked walls. In the city, merchants and traders from China, Korea and India introduced various foreign cultures to Heijō-kyō through the Silk Road. As a result, Heijō-kyō flourished as Japan's first international and political capital, with a peak population of between 50,000 and 100,000. The overall form of the city was an irregular rectangle, and the area of city is more than 25 km2. Architecture In the area of Heijō-kyō, there are ancient Buddhist temples, and some temples are also l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
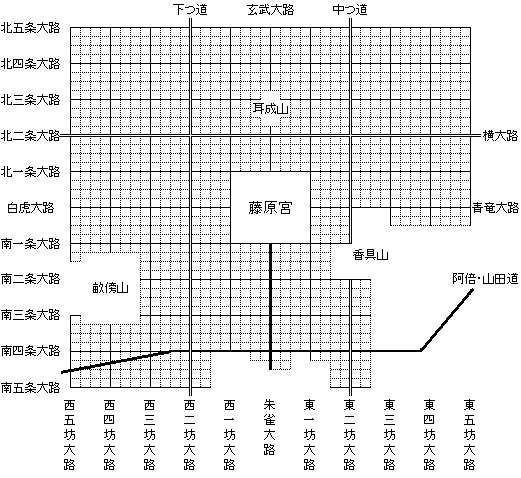
Fujiwara-kyō
was the Imperial capital of Japan for sixteen years, between 694 and 710. It was located in Yamato Province (present-day Kashihara, Nara, Kashihara in Nara Prefecture), having been moved from nearby Asuka, Yamato, Asuka. However, the name Fujiwara-kyō was never used in the ''Nihon Shoki''. During those times it was recorded as Aramashi-kyō (新益京). As of 2006, ongoing excavations have revealed construction on the site of Fujiwara-kyō as early as 682, near the end of the reign of Emperor Tenmu. With a brief halt upon Emperor Tenmu's death, construction resumed under Empress Jitō, who officially moved the capital in 694. Fujiwara-kyō remained the capital for the reigns of Emperor Monmu and Empress Genmei, but in 710 the Imperial court moved to the Heijō Palace in Nara, Nara, Nara, beginning the Nara period. History Fujiwara was Japan's first capital built in a grid pattern on the Chinese model (条坊制 ''jōbō-sei''); recent investigation has revealed that the city c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mononobe Clan
The was a Japan, Japanese aristocratic kin group Uji (clan), (''uji'') of the Kofun period, known for its military opposition to the Soga clan. The Mononobe were opposed to the spread of Buddhism, partly on religious grounds, claiming that the local deities would be offended by the worshiping of foreign deities, but also as the result of feelings of conservatism and a degree of xenophobia. The Nakatomi clan, ancestors of the Fujiwara clan, Fujiwara, were also Shinto ritualists allied with the Mononobe in opposition to Buddhism. The Mononobe, like many other major families of the time, were something of a corporation or guild in addition to being a proper family by blood-relation. While the only members of the clan to appear in any significant way in the historical record were statesmen, the clan as a whole was known as the Corporation of Arms or Armorers. History The Mononobe were said to have been descended from List of Japanese deities#Nigihayahi, Nigihayahi no Mikoto, (饒 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jinshin War
The was a war of succession in Japan during the Asuka period of the Yamato state. It broke out in 672 following the death of Emperor Tenji. The name refers to the ''jinshin'' (壬申) or ninth year of the sixty-year Jikkan Jūnishi calendrical cycle, corresponding to the Western year 672. Tenji had originally designated his brother, Prince Ōama, as his successor, but later changed his mind in favor of his son, Prince Ōtomo. In the course of the violence that erupted as a result of factional rivalries, Ōtomo, having taken the throne as Emperor, took his own life after reigning for less than a year. His uncle Ōama then succeeded to the throne as the Emperor Tenmu. Background Emperor Tenji ascended to the throne and set up a capital at Ōmi-Ōtsu (currently Ōtsu city, Shiga Prefecture). He made his best efforts for the foundation of a strong country, mimicking the Tang Dynasty's bureaucracy fron China, importing the Tangs' political systems and consequently affecting Japane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |