|
Taifa Of Algeciras
The Taifa of Algeciras () was a medieval Muslim taifa kingdom in what is now southern Spain and Gibraltar, that existed from 1035 to 1058. History The ''taifa'' was created in 1013, in the wake of the disintegration of the caliphate of Córdoba which began after 1009. When Sulayman ibn al-Hakam took control of the caliphate, he gave Algeciras to the Hammudids, a dynasty who had helped him in gaining the power. The first king of Algeciras was al-Qasim al-Ma'mun, who later was also caliph. His cousin Yahya al-Mu'tali annexed Algeciras to the taifa of Málaga in 1035. In 1039 Muhammad ibn al-Qasim, son of al-Qasim, was proclaimed emir of Algeciras. In 1055 al-Mu'tamid ibn Abbad, lord of Seville, appeared under Algeciras' walls, forcing Muhammad to leave the taifa, which was annexed to that of Seville. Following its conquest, the kings of Spain (such as Philip IV) sometimes included the kingdom of Algeciras among their titles. List of Emirs *Muhammad ibn al-Qasim: 1035–10 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taifa Of Seville
The Taifa of Seville ( ''Ta'ifat-u Ishbiliyyah'') was an Arab kingdom which was ruled by the Abbadid dynasty. It was established in 1023 and lasted until 1091, in what is today southern Spain and Portugal. It gained independence from the Caliphate of Cordoba and it expanded the territory it ruled in the mid-11th century. The emerging power of Castile led Seville to ask military assistance from the Almoravids, who then occupied Seville. History The ''taifa'' (principality) began as a small, weakly-defended territory comprising parts of the modern Spanish provinces of Seville, Huelva, and Cádiz, but quickly emerged as the most powerful taifa of the time, after its rulers began a policy of expansion. The first emir of Seville was Abu al-Qasim (1023–1042). He was qadi of Seville and declared independence from the Caliphate of Córdoba after its downfall in 1031, becoming Abbad I, emir of Seville. His son, Abbad II al-Mu'tadid (1042–1069) who succeeded him, expanded the taifa b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hammudid
The Hammudid dynasty () was a Berberized Arab Muslim family that briefly ruled the Caliphate of CórdobaLane-Poole (1894), p.21 and the taifas of Málaga and Algeciras and nominal control in Ceuta. The dynasty The dynasty is named after their ancestor, Hammud, a descendant of Idris ibn Abdallah, founder of the Idrisid dynasty and great-grandchild of Hasan, son of Fatimah and Ali and grandson of the Islamic prophet, Muhammad.''Hammudids'', A. Huici Miranda, ''The Encyclopaedia of Islam'', Vol. III, ed. B. Lewis, V.L. Menage, C. Pellat and J. Schacht, (Brill, 1986), 147;"''HAMMUDIDS, dynasty which reigned over various towns in Muslim Spain from 407/1016 till 450/1058. Sulayman al-Musta'm .v. on his second succession to the caliphal throne in Shawwal 4O3/ May 1013, had to distribute large fiefs among the Berbers who had raised him to power. He allotted to 'Ali b. Hammud the governorship of Ceuta and to his brother al-Kasim that of Algeciras, Tangier, and Arzila. The two were genu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
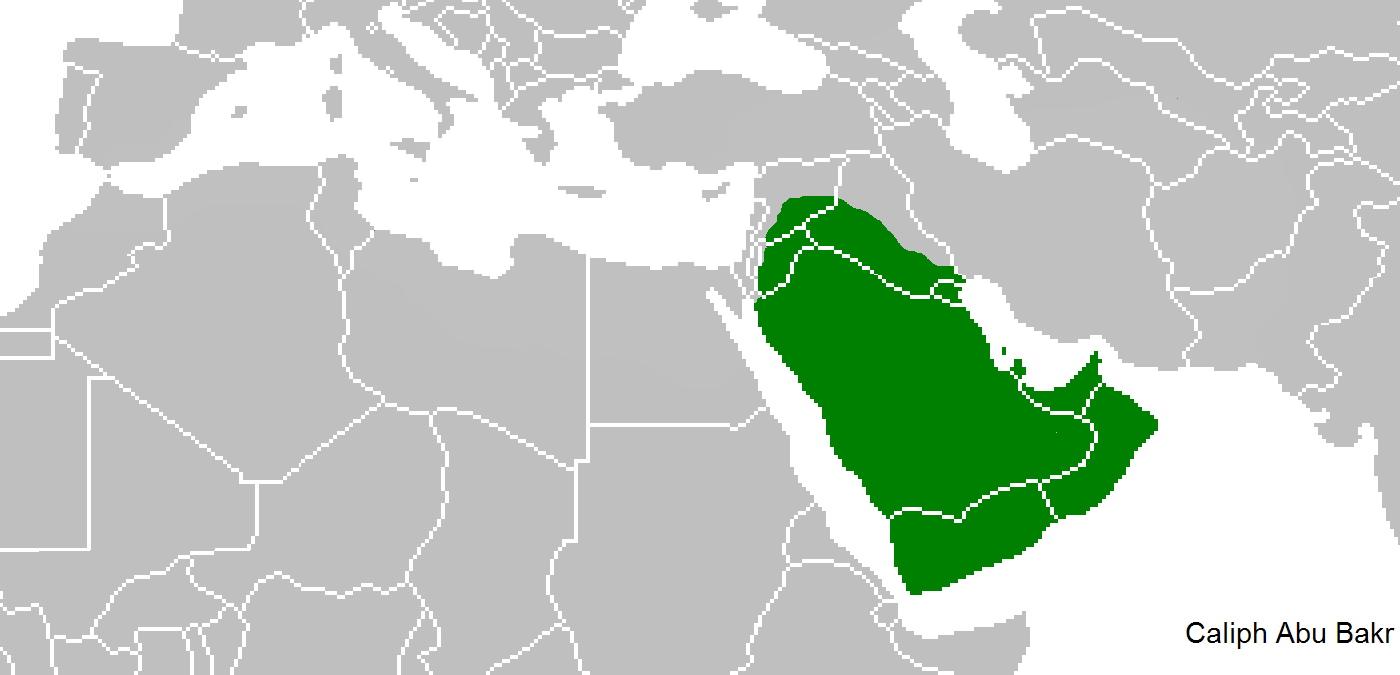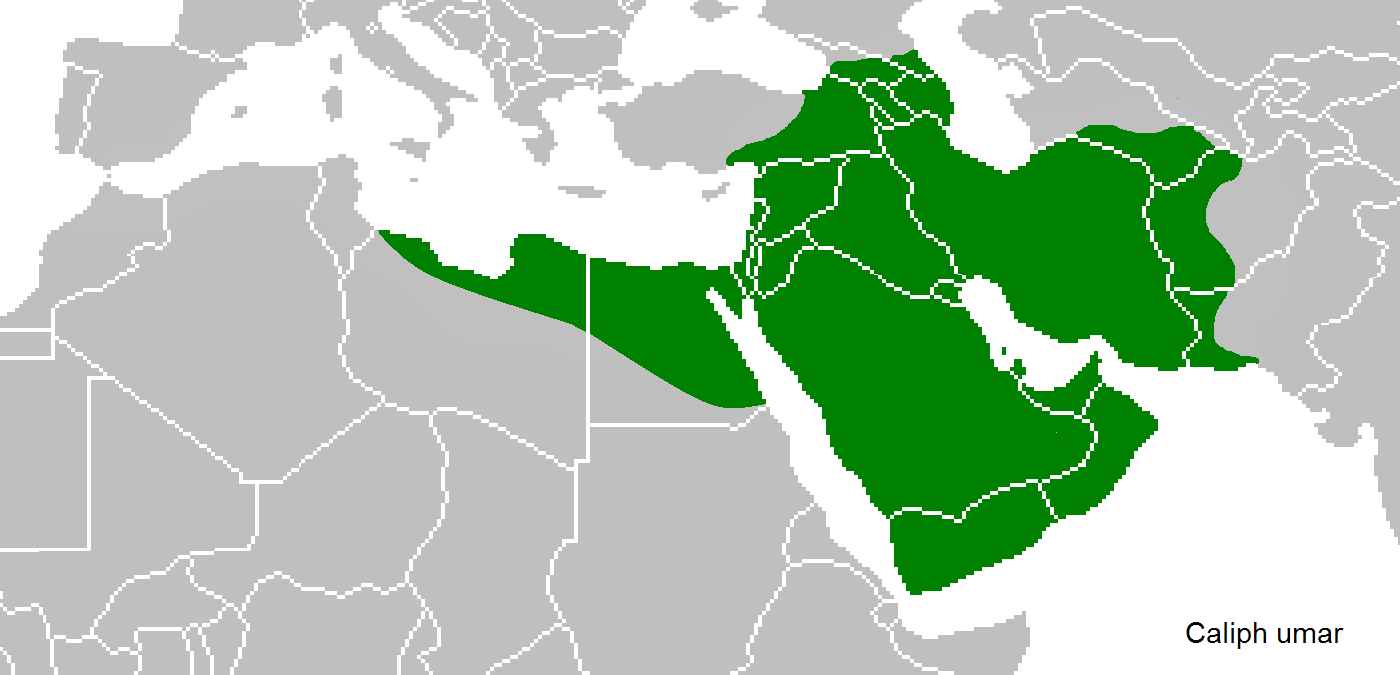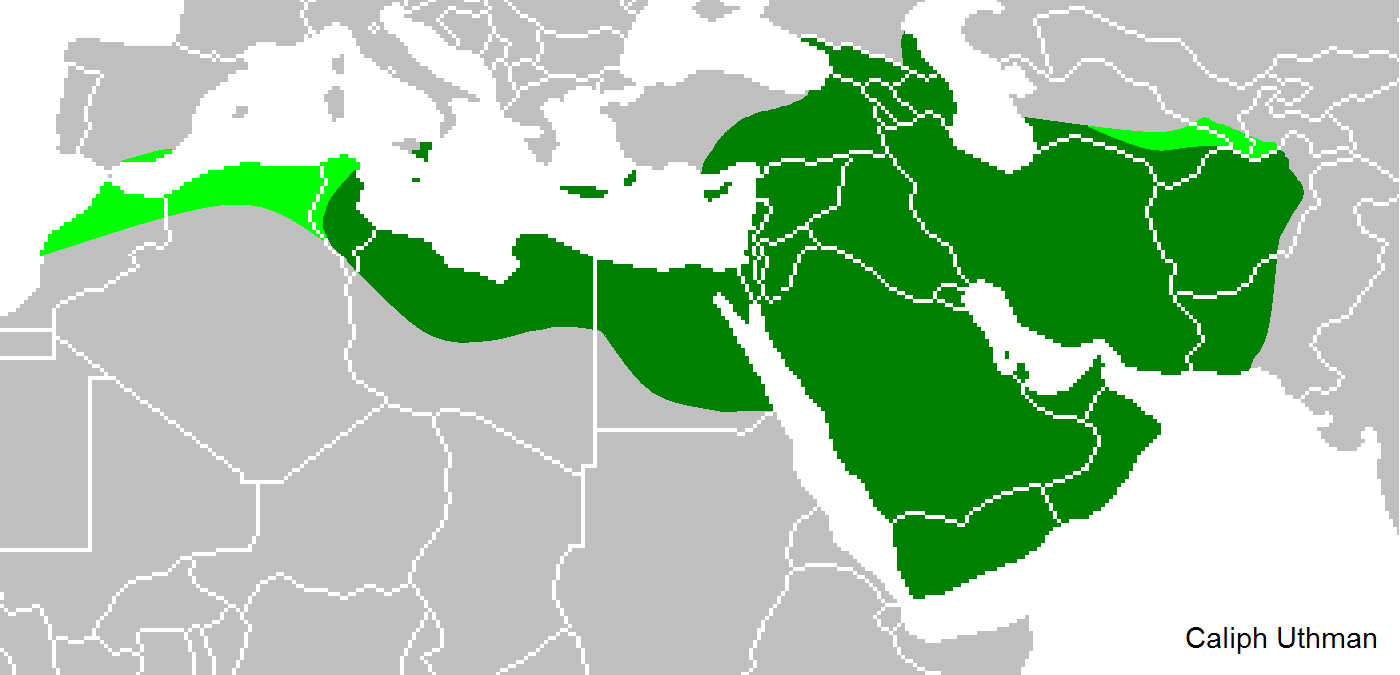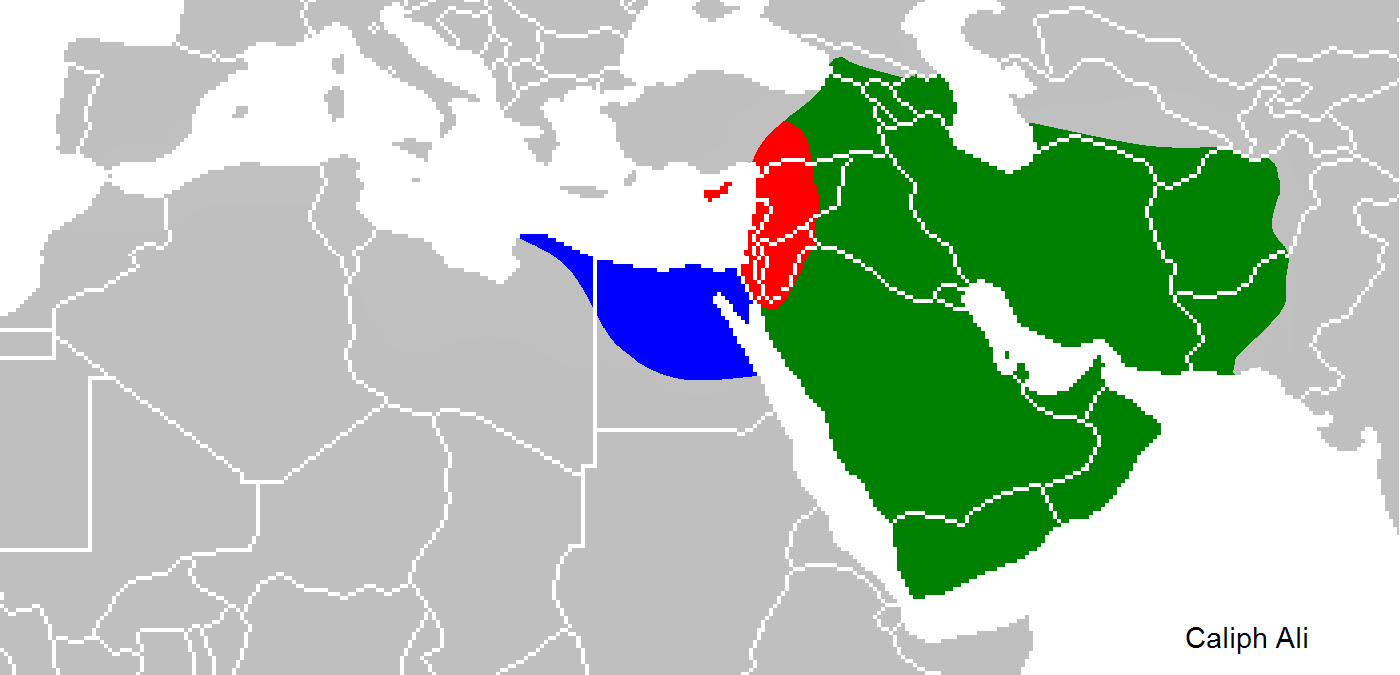
Taifas
The ''taifas'' (singular ''taifa'', from ar, طائفة ''ṭā'ifa'', plural طوائف ''ṭawā'if'', a party, band or faction) were the independent Muslim principalities and kingdoms of the Iberian Peninsula (modern Portugal and Spain), referred to by Muslims as al-Andalus, that emerged from the decline and fall of the Umayyad Caliphate of Córdoba between 1009 and 1031. They were a recurring feature of al-Andalus history. The ''taifas'' were eventually incorporated by the Almoravid dynasty in the late 11th century and, on its collapse, many ''taifas'' re-appeared only to be incorporated by the Almohad Caliphate. The fall of the Almohads resulted in a flourishing of the ''taifas'', and this was the case despite constant warfare with Christian kingdoms. Taifa kings were wary of calling themselves “kings,” so they took the title of ''hajib'', presenting themselves as representatives for a temporarily absent caliph. The ''taifa'' courts were renowned centres of cultural ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Sunni Muslim Dynasties
The following is a list of Sunni Muslim dynasties. Asia Middle East Arabian Peninsula * Banu Wajih (926–965) *Sharif of Mecca (967–1925) * Al Uyuniyun (1076–1253) *Sulaymanids (1063–1174) *Mahdids (1159–1174) *Kathiri (Hadhramaut) (1395–1967) * Al-Jabriyun (1417–1521) *Banu Khalid (1669–1796) *Al Qasimi (Ras al Khaymah) (1727–present) *House of Saud (Saudi Arabia) (1744–present) *House of Al-Sabah (Kuwait) (1752–present) *Al Nahyan family (Abu Dhabi) (1761–present) *Al Qasimi (Sharjah) (18th century–present) *Al Mualla (Umm al-Quwain) (1775–present) *Al Khalifa family (Bahrain) (1783–present) *Mahra Sultanate (18th century–1967) *Al Nuaimi (Ajman) (1816–present) *House of Thani (Qatar) (1825–present) *Al Maktoum (Dubai) (1833–present) * Al Rashid (1836–1921) *Al Sharqi (Fujairah) (1876–present) *Qu'aiti (1902–1967) *Emirate of Beihan (1903–1967) *Lower Yafa (19th century–1967) *Upper Yafa (19th century–1967) Iran and Caucasus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Qasim Al-Wathiq
The Qassim Province ( ar, منطقة القصيم ' , Najdi Arabic: ), also known as the Qassim Region, is one of the 13 provinces of Saudi Arabia. Located at the heart of the country near the geographic center of the Arabian Peninsula, it has a population of 1,370,727 and an area of 58,046 km². It is known to be the "alimental basket" of the country, for its agricultural assets. Al-Qassim has the lowest share of population living below local poverty line in Saudi Arabia. It is the seventh most populated region in the country after Jizan and the fifth most densely populated. It has more than 400 cities, towns, villages, and Bedouin settlements, ten of which are recognized as governorates. Its capital city is Buraydah, which is inhabited by approximately 60% of the region's total population. The governor of the province from 1992 to 29 January 2015 was Prince Faisal bin Bandar, succeeded by Prince Faisal bin Mishaal. Etymology Al Qassim also "Al Gassim" "Gassim" derived ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muhammad Ibn Al-Qasim (Algeciras)
Muḥammad ibn al-Qāsim al-Thaqafī ( ar, محمد بن القاسم الثقفي; –) was an Arab military commander in service of the Umayyad Caliphate who led the Muslim conquest of Sindh (part of modern Pakistan), inaugurating the Umayyad campaigns in India. His military exploits led to the establishment of the Islamic province of Sindh, and the takeover of the region from the Sindhi Brahman dynasty and its ruler, Raja Dahir, who was subsequently decapitated with his head sent to al-Hajjaj ibn Yusuf in Basra. With the capture of the then-capital of Aror by Arab forces, Muhammad ibn al-Qasim became the first Muslim to have successfully captured Hindu land, which marked the beginning of Muslim rule in South Asia. Muhammad ibn al-Qasim belonged to the Banu Thaqif, an Arab tribe that is concentrated around the city of Taif in western Arabia. After the Muslim conquest of Persia, he was assigned as the governor of Fars, likely succeeding his uncle Muhammad ibn Yusuf al- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philip IV Of Spain
Philip IV ( es, Felipe, pt, Filipe; 8 April 160517 September 1665), also called the Planet King (Spanish: ''Rey Planeta''), was King of Spain from 1621 to his death and (as Philip III) King of Portugal from 1621 to 1640. Philip is remembered for his patronage of the arts, including such artists as Diego Velázquez, and his rule over Spain during the Thirty Years' War. By the time of his death, the Spanish Empire had reached approximately 12.2 million square kilometers (4.7 million square miles) in area but in other aspects was in decline, a process to which Philip contributed with his inability to achieve successful domestic and military reform. Personal life Philip IV was born in the Royal Palace of Valladolid, and was the eldest son of Philip III of Spain, Philip III and his wife, Margaret of Austria (1584–1611), Margaret of Austria. In 1615, at the age of 10, Philip was married to 13-year-old Elisabeth of France (1602–1644), Elisabeth of France. Although the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Spanish Kings
This is a list of Spanish monarchs, that is, rulers of the country of Spain. The forerunners of the monarchs of the Spanish throne were the following: *Kings of the Visigoths * Kings of Asturias * Kings of Navarre *Kings of León *Kings of Galicia *Kings of Aragon *Kings of Castile These seven lineages were eventually united by the marriage of the Catholic Monarchs, Ferdinand II of Aragon (king of the Crown of Aragon) and Isabella I of Castile (queen of the Crown of Castile). Although their kingdoms continued to be separate, with their personal union they ruled them together as one dominion. The regnal numbers follow those of the rulers of Asturias, León, and Castile; thus, Alfonso XII is numbered in succession to Alfonso XI of Castile. House of Trastámara (1479–1555) Under Isabella and Ferdinand, the royal dynasties of Castile and Aragon, their respective kingdoms, were united into a single line. Historiography of Spain generally treats this as the formation of the Ki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seville
Seville (; es, Sevilla, ) is the capital and largest city of the Spanish autonomous community of Andalusia and the province of Seville. It is situated on the lower reaches of the River Guadalquivir, in the southwest of the Iberian Peninsula. Seville has a municipal population of about 685,000 , and a metropolitan population of about 1.5 million, making it the largest city in Andalusia, the fourth-largest city in Spain and the 26th most populous municipality in the European Union. Its old town, with an area of , contains three UNESCO World Heritage Sites: the Alcázar palace complex, the Cathedral and the General Archive of the Indies. The Seville harbour, located about from the Atlantic Ocean, is the only river port in Spain. The capital of Andalusia features hot temperatures in the summer, with daily maximums routinely above in July and August. Seville was founded as the Roman city of . Known as ''Ishbiliyah'' after the Islamic conquest in 711, Seville became ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taifa Of Seville
The Taifa of Seville ( ''Ta'ifat-u Ishbiliyyah'') was an Arab kingdom which was ruled by the Abbadid dynasty. It was established in 1023 and lasted until 1091, in what is today southern Spain and Portugal. It gained independence from the Caliphate of Cordoba and it expanded the territory it ruled in the mid-11th century. The emerging power of Castile led Seville to ask military assistance from the Almoravids, who then occupied Seville. History The ''taifa'' (principality) began as a small, weakly-defended territory comprising parts of the modern Spanish provinces of Seville, Huelva, and Cádiz, but quickly emerged as the most powerful taifa of the time, after its rulers began a policy of expansion. The first emir of Seville was Abu al-Qasim (1023–1042). He was qadi of Seville and declared independence from the Caliphate of Córdoba after its downfall in 1031, becoming Abbad I, emir of Seville. His son, Abbad II al-Mu'tadid (1042–1069) who succeeded him, expanded the taifa b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Mu'tamid Ibn Abbad
Al-Mu'tamid Muhammad ibn Abbad al-Lakhmi ( ar, المعتمد محمد ابن عباد بن اسماعيل اللخمي; reigned c. 1069–1091, lived 1040–1095), also known as Abbad III, was the third and last ruler of the Taifa of Seville in Al-Andalus, as well as a renowned poet. He was the final ruler of the Abbadid dynasty of Seville, being overthrown by the Almoravids in 1091. Early life When he was 13 years old, Al-Mu'tamid's father bestowed on him the title of Emir and appointed the Andalusi Arabic poet Ibn Ammar as his vizier. However, Al-Mu'tamid fell strongly under the influence of Ibn Ammar. Al-Mu’tamid's father was wary of Ibn Ammar and the influence he had, ultimately sending him into exile. Reign After the death of his father Abbad II al-Mu'tadid in 1069, Al-Mu'tamid inherited Seville as caliph. One of his first acts was to recall Ibn Ammar and to bestow military honours and high political offices on him, including as Governor of Silves and Prime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muhammad Ibn Al-Qasim (emir Of Algeciras)
Muḥammad ibn al-Qāsim al-Thaqafī ( ar, محمد بن القاسم الثقفي; –) was an Arab military commander in service of the Umayyad Caliphate who led the Muslim conquest of Sindh (part of modern Pakistan), inaugurating the Umayyad campaigns in India. His military exploits led to the establishment of the Islamic province of Sindh, and the takeover of the region from the Sindhi Brahman dynasty and its ruler, Raja Dahir, who was subsequently decapitated with his head sent to al-Hajjaj ibn Yusuf in Basra. With the capture of the then-capital of Aror by Arab forces, Muhammad ibn al-Qasim became the first Muslim to have successfully captured Hindu land, which marked the beginning of Muslim rule in South Asia. Muhammad ibn al-Qasim belonged to the Banu Thaqif, an Arab tribe that is concentrated around the city of Taif in western Arabia. After the Muslim conquest of Persia, he was assigned as the governor of Fars, likely succeeding his uncle Muhammad ibn Yusuf al- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |