|
Table Mountain Sandstone
The Table Mountain Sandstone (TMS) is a group of rock formations within the Cape Supergroup sequence of rocks. Although the term "Table Mountain Sandstone" is still widely used in common parlance, the term TMS is no longer formally recognized; the correct name is the " Peninsula Formation Sandstone", which is part of the Table Mountain Group. The designation "Table Mountain Sandstone" will, however, in deference to the title, continue to be used in the rest of this article. The name is derived from the famous landmark in Cape Town, Table Mountain. Table Mountain Sandstone is made up predominantly of quartzitic sandstone laid down between 510 (Cambrian Period) and 400 (Silurian Period) million years ago. It is the hardest, and most erosion resistant layer of the Cape Supergroup. It therefore forms most of the highest and most conspicuous peaks in the Western Cape, as well as the steepest cliffs of the Cape Fold Mountains, despite being the oldest, and, therefore, low ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Table Mountain Geology
Table may refer to: * Table (furniture), a piece of furniture with a flat surface and one or more legs * Table (landform), a flat area of land * Table (information), a data arrangement with rows and columns * Table (database), how the table data arrangement is used within databases * Calligra Tables, a spreadsheet application * Mathematical table * Table (parliamentary procedure) * Tables (board game) * Table, surface of the sound board (music) of a string instrument * ''Al-Ma'ida'', the fifth ''surah'' of the Qur'an, usually translated as “The Table” * Water table See also * Spreadsheet, a computer application * Table cut, a type of diamond cut * The Table (other) * Table Mountain (other) * Table Rock (other) * Tabler (other) Tabler may refer to: People * P. Dempsey Tabler (1876–1956), an American singer, athlete, businessman, and actor *William B. Tabler (1914–2004), an American architect, and his son, William B. Tabler, J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gondwana
Gondwana () was a large landmass, often referred to as a supercontinent, that formed during the late Neoproterozoic (about 550 million years ago) and began to break up during the Jurassic period (about 180 million years ago). The final stages of break-up, involving the separation of Antarctica from South America (forming the Drake Passage) and Australia, occurred during the Paleogene. Gondwana was not considered a supercontinent by the earliest definition, since the landmasses of Baltica, Laurentia, and Siberia were separated from it. To differentiate it from the Indian region of the same name (see ), it is also commonly called Gondwanaland. Gondwana was formed by the accretion of several cratons. Eventually, Gondwana became the largest piece of continental crust of the Palaeozoic Era, covering an area of about , about one-fifth of the Earth's surface. During the Carboniferous Period, it merged with Laurasia to form a larger supercontinent called Pangaea. Gondwana (and Pan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
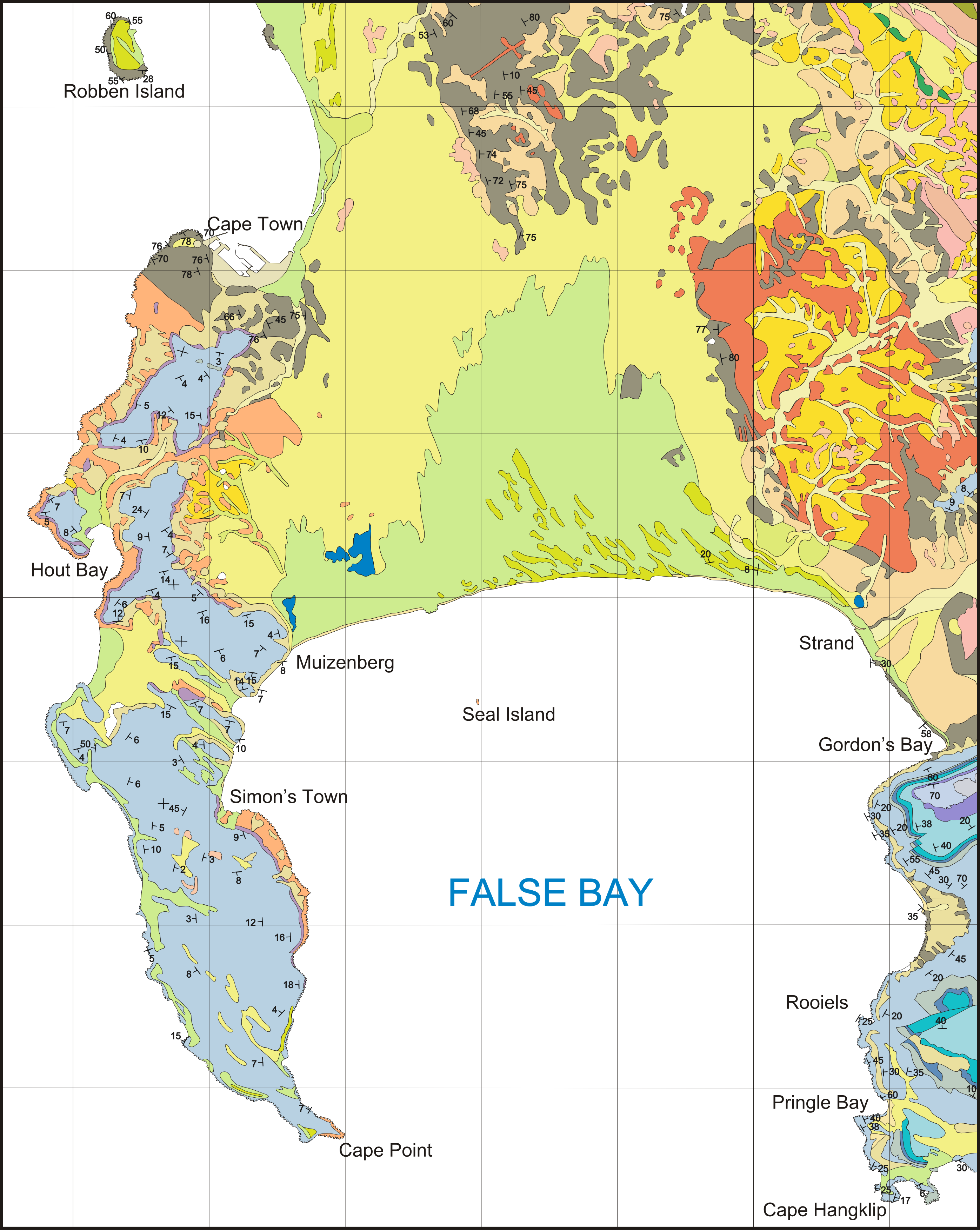
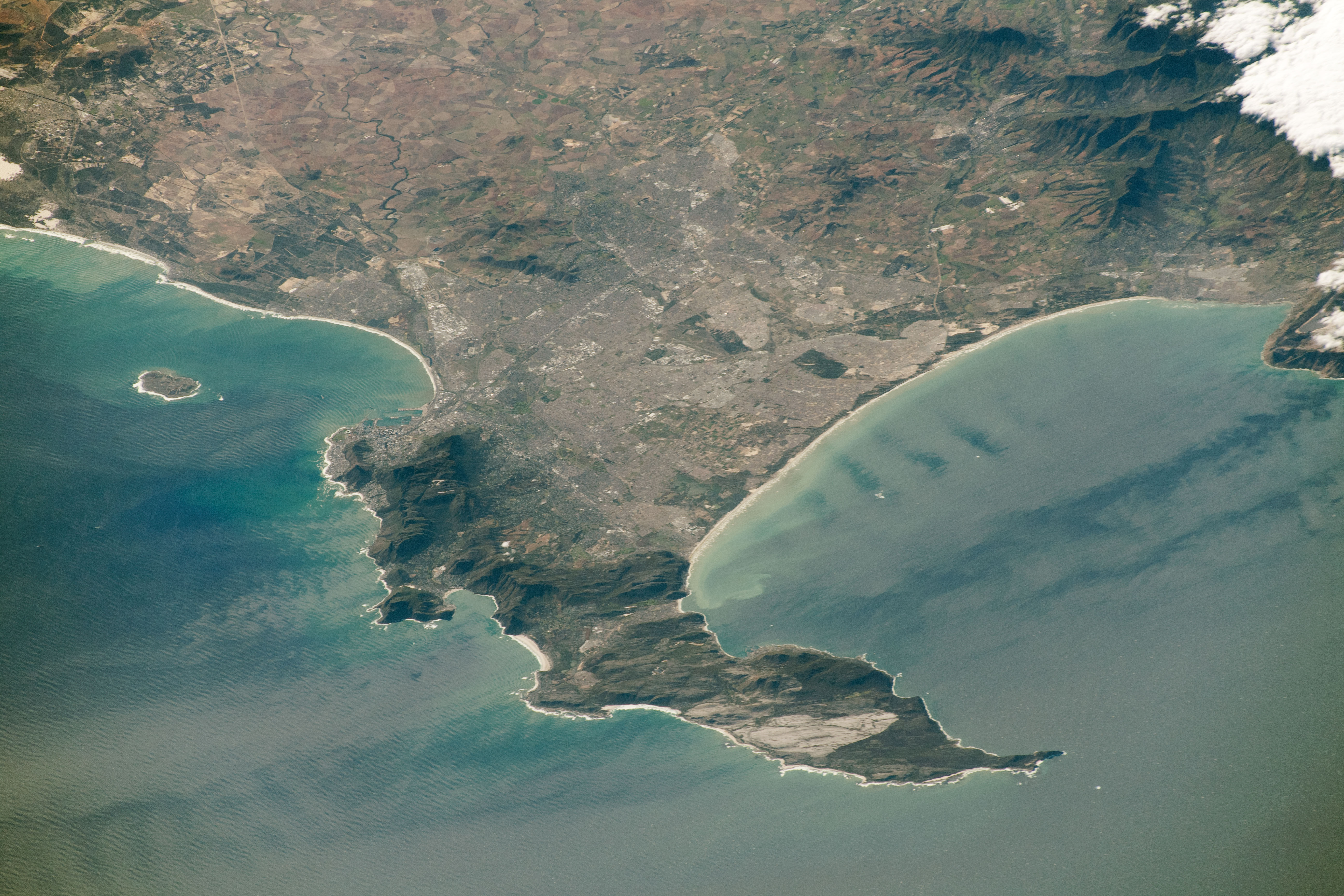
Marine Geology Of The Cape Peninsula And False Bay
Cape Town lies at the south-western corner of the continent of Africa. It is bounded to the south and west by the Atlantic Ocean, and to the north and east by various other municipalities in the Western Cape province of South Africa. The Cape Peninsula is a rocky and mountainous peninsula that juts out into the Atlantic Ocean at the south-western extremity of the continent. At its tip is Cape Point and the Cape of Good Hope. The peninsula forms the west side of False Bay and the Cape Flats. On the east side are the Helderberg and Hottentots Holland mountains. The three main rock formations are the late-Precambrian Malmesbury group (sedimentary and metamorphic rock), the Cape Granite suit, comprising the huge Peninsula, Kuilsriver-Helderberg, and Stellenbosch batholiths, that were intruded into the Malmesbury Group about 630 million years ago, and the Table Mountain group sandstones that were deposited on the eroded surface of the granite and Malmesbury series basement about 45 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hottentots-Holland
The Hottentots Holland Mountains are part of the Cape Fold Belt in the Western Cape, South Africa. The mountain range forms a barrier between the Cape Town metropolitan area and the southern Overberg coast. The range is primarily composed of Table Mountain Sandstone, and lies between the eastern Cape Town suburbs of Somerset West and Gordon's Bay to the west, and the Elgin valley to the east. Sir Lowry's Pass is the only crossing, in the form of the N2 motorway. The Steenbras Dam, one of Cape Town's main supply dams, is located in the Elgin valley south of the town of Grabouw due to the abundant rainfall normally experienced in the uplands of the catchment area. Pass The Gantouw (Eland Pass) ceased to be used by wagons on the 6th July 1830, when the new Sir Lowry's Pass road was opened. Wagons of the Great Trek beginning 1835 did not actually use the old pass, instead they used the new road. When previous migrants decided to leave the Cape Town area, or Cape Colony as it was th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anticline
In structural geology, an anticline is a type of fold that is an arch-like shape and has its oldest beds at its core, whereas a syncline is the inverse of an anticline. A typical anticline is convex up in which the hinge or crest is the location where the curvature is greatest, and the limbs are the sides of the fold that dip away from the hinge. Anticlines can be recognized and differentiated from antiforms by a sequence of rock layers that become progressively older toward the center of the fold. Therefore, if age relationships between various rock strata are unknown, the term antiform should be used. The progressing age of the rock strata towards the core and uplifted center, are the trademark indications for evidence of anticlines on a geologic map. These formations occur because anticlinal ridges typically develop above thrust faults during crustal deformations. The uplifted core of the fold causes compression of strata that preferentially erodes to a deeper st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syncline
In structural geology, a syncline is a fold with younger layers closer to the center of the structure, whereas an anticline is the inverse of a syncline. A synclinorium (plural synclinoriums or synclinoria) is a large syncline with superimposed smaller folds. Synclines are typically a downward fold (synform), termed a synformal syncline (i.e. a trough), but synclines that point upwards can be found when strata have been overturned and folded (an antiformal syncline). Characteristics On a geologic map, synclines are recognized as a sequence of rock layers, with the youngest at the fold's center or ''hinge'' and with a reverse sequence of the same rock layers on the opposite side of the hinge. If the fold pattern is circular or elongate, the structure is a basin. Folds typically form during crustal deformation as the result of compression that accompanies orogenic mountain building. Notable examples * Powder River Basin, Wyoming, US * Sideling Hill roadcut along Interstate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape Peninsula
The Cape Peninsula ( af, Kaapse Skiereiland) is a generally mountainous peninsula that juts out into the Atlantic Ocean at the south-western extremity of the African continent. At the southern end of the peninsula are Cape Point and the Cape of Good Hope. On the northern end is Table Mountain, overlooking Table Bay and the city bowl of Cape Town, South Africa. The peninsula is 52 km long from Mouille point in the north to Cape Point in the south. The Peninsula has been an island on and off for the past 5 million years, as sea levels fell and rose with the Glacial period, ice age and interglacial global warming cycles of, particularly, the Pleistocene. The last time that the Peninsula was an island was about 1.5 million years ago. Soon afterwards it was joined to the mainland by the Geology of Cape Town#Tertiary to Recent events, emergence from the sea of the sandy area now known as the Cape Flats. The towns and villages of the Cape Peninsula and Cape Flats, and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weathering
Weathering is the deterioration of rocks, soils and minerals as well as wood and artificial materials through contact with water, atmospheric gases, and biological organisms. Weathering occurs ''in situ'' (on site, with little or no movement), and so is distinct from erosion, which involves the transport of rocks and minerals by agents such as water, ice, snow, wind, waves and gravity. Weathering processes are divided into ''physical'' and ''chemical weathering''. Physical weathering involves the breakdown of rocks and soils through the mechanical effects of heat, water, ice, or other agents. Chemical weathering involves the chemical reaction of water, atmospheric gases, and biologically produced chemicals with rocks and soils. Water is the principal agent behind both physical and chemical weathering, though atmospheric oxygen and carbon dioxide and the activities of biological organisms are also important. Chemical weathering by biological action is also known as biological wea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geology
Geology () is a branch of natural science concerned with Earth and other astronomical objects, the features or rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Modern geology significantly overlaps all other Earth sciences, including hydrology, and so is treated as one major aspect of integrated Earth system science and planetary science. Geology describes the structure of the Earth on and beneath its surface, and the processes that have shaped that structure. It also provides tools to determine the relative and absolute ages of rocks found in a given location, and also to describe the histories of those rocks. By combining these tools, geologists are able to chronicle the geological history of the Earth as a whole, and also to demonstrate the age of the Earth. Geology provides the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and the Earth's past climates. Geologists broadly study the properties and processes of E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sandstone
Sandstone is a clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate grains. Sandstones comprise about 20–25% of all sedimentary rocks. Most sandstone is composed of quartz or feldspar (both silicates) because they are the most resistant minerals to weathering processes at the Earth's surface. Like uncemented sand, sandstone may be any color due to impurities within the minerals, but the most common colors are tan, brown, yellow, red, grey, pink, white, and black. Since sandstone beds often form highly visible cliffs and other topographic features, certain colors of sandstone have been strongly identified with certain regions. Rock formations that are primarily composed of sandstone usually allow the percolation of water and other fluids and are porous enough to store large quantities, making them valuable aquifers and petroleum reservoirs. Quartz-bearing sandstone can be changed into quartzite through metamorphism, usually related to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quartzite
Quartzite is a hard, non- foliated metamorphic rock which was originally pure quartz sandstone.Essentials of Geology, 3rd Edition, Stephen Marshak, p 182 Sandstone is converted into quartzite through heating and pressure usually related to tectonic compression within orogenic belts. Pure quartzite is usually white to grey, though quartzites often occur in various shades of pink and red due to varying amounts of hematite. Other colors, such as yellow, green, blue and orange, are due to other minerals. The term ''quartzite'' is also sometimes used for very hard but unmetamorphosed sandstones that are composed of quartz grains thoroughly cemented with additional quartz. Such sedimentary rock has come to be described as orthoquartzite to distinguish it from metamorphic quartzite, which is sometimes called metaquartzite to emphasize its metamorphic origins. Quartzite is very resistant to chemical weathering and often forms ridges and resistant hilltops. The nearly pure silica conte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karoo Supergroup
The Karoo Supergroup is the most widespread stratigraphic unit in Africa south of the Kalahari Desert. The supergroup consists of a sequence of units, mostly of nonmarine origin, deposited between the Late Carboniferous and Early Jurassic, a period of about 120 million years. In southern Africa, rocks of the Karoo Supergroup cover almost two thirds of the present land surface, including all of Lesotho, almost the whole of Free State, and large parts of the Eastern Cape, Northern Cape, Mpumalanga and KwaZulu-Natal Provinces of South Africa. Karoo supergroup outcrops are also found in Namibia, Eswatini, Zambia, Zimbabwe and Malawi, as well as on other continents that were part of Gondwana. The basins in which it was deposited formed during the formation and breakup of Pangea.McCarthy, T., Rubridge, B. (2005). ''The Story of Earth and Life.'' pp. 161, 187–241. Struik Publishers, Cape Town The type area of the Karoo Supergroup is the Great Karoo in South Africa, where the most exte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.png)



Saunders_Quarry-1.jpg)
