Syncline on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In
File:Sideling Hill cut MD1.jpg, Syncline exposed in Sideling Hill roadcut
File:Provo Canyon syncline.jpg, Snow-dusted syncline in
 In
In structural geology
Structural geology is the study of the three-dimensional distribution of rock units with respect to their deformational histories. The primary goal of structural geology is to use measurements of present-day rock geometries to uncover informati ...
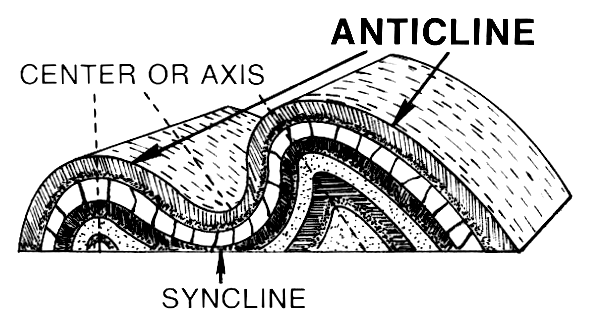
, a syncline is a fold
Fold, folding or foldable may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
* ''Fold'' (album), the debut release by Australian rock band Epicure
*Fold (poker), in the game of poker, to discard one's hand and forfeit interest in the current pot
*Above ...
with younger layers closer to the center of the structure, whereas an anticline
In structural geology, an anticline is a type of fold that is an arch-like shape and has its oldest beds at its core, whereas a syncline is the inverse of an anticline. A typical anticline is convex up in which the hinge or crest is the ...
is the inverse of a syncline. A synclinorium (plural synclinoriums or synclinoria) is a large syncline with superimposed smaller folds. Synclines are typically a downward fold (synform), termed a synformal syncline (i.e. a trough), but synclines that point upwards can be found when strata have been overturned and folded (an antiformal syncline).
Characteristics
On a geologic map, synclines are recognized as a sequence of rock layers, with the youngest at the fold's center or ''hinge'' and with a reverse sequence of the same rock layers on the opposite side of the hinge. If the fold pattern is circular or elongate, the structure is a basin. Folds typically form duringcrustal deformation
Orogeny is a mountain building process. An orogeny is an event that takes place at a convergent plate margin when plate motion compresses the margin. An '' orogenic belt'' or ''orogen'' develops as the compressed plate crumples and is uplifted ...
as the result of compression that accompanies orogenic mountain building.
Notable examples
*Powder River Basin
The Powder River Basin is a geologic structural basin in southeast Montana and northeast Wyoming, about east to west and north to south, known for its extensive coal reserves. The former hunting grounds of the Oglala Lakota, the area is very ...
, Wyoming
Wyoming () is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It is bordered by Montana to the north and northwest, South Dakota and Nebraska to the east, Idaho to the west, Utah to the southwest, and Colorado to the sou ...
, US
* Sideling Hill roadcut along Interstate 68 in western Maryland
Maryland ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It shares borders with Virginia, West Virginia, and the District of Columbia to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; ...
, US, where the Rockwell Formation and overlying Purslane Sandstone are exposed
* Forêt de Saou syncline in Saou, France
* The Southland Syncline in the southeastern corner of the South Island
The South Island, also officially named , is the larger of the two major islands of New Zealand in surface area, the other being the smaller but more populous North Island. It is bordered to the north by Cook Strait, to the west by the Tasma ...
of New Zealand, including The Catlins
The Catlins (sometimes referred to as The Catlins Coast) comprises an area in the southeastern corner of the South Island of New Zealand. The area lies between Balclutha and Invercargill, straddling the boundary between the Otago and Southl ...
and the Hokonui Hills
* Strathmore Syncline, Scotland
* Wilpena Pound, Flinders Ranges
The Flinders Ranges are the largest mountain range in South Australia, which starts about north of Adelaide. The ranges stretch for over from Port Pirie to Lake Callabonna.
The Adnyamathanha people are the Aboriginal group who have inhabit ...
, South Australia
South Australia (commonly abbreviated as SA) is a state in the southern central part of Australia. It covers some of the most arid parts of the country. With a total land area of , it is the fourth-largest of Australia's states and territories ...
* Fort Valley, Shenandoah County, Virginia
* The Picuris Mountains
The Picuris Mountains are a mountain range in northern New Mexico. They are considered a subrange of the Sangre de Cristo Mountains.
Geography
The mountains are located to the east of Dixon and surround Picuris Pueblo to the west, north, and e ...
of New Mexico
)
, population_demonym = New Mexican ( es, Neomexicano, Neomejicano, Nuevo Mexicano)
, seat = Santa Fe, New Mexico, Santa Fe
, LargestCity = Albuquerque, New Mexico, Albuquerque
, LargestMetro = Albuquerque metropolitan area, Tiguex
, Offi ...
, US, contain an example of an overturned syncline, the Hondo Syncline.
Gallery
Provo Canyon
Provo Canyon is located in unincorporated Utah County and Wasatch County, Utah. Provo Canyon runs between Mount Timpanogos on the north and Mount Cascade on the south. The canyon extends from Orem on the west end to Heber City on the east. Pro ...
, Utah
Utah ( , ) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. Utah is a landlocked U.S. state bordered to its east by Colorado, to its northeast by Wyoming, to its north by Idaho, to its south by Arizona, and to its ...
File:Syncline.JPG, Road cut near Fort Davis, Texas
Fort Davis is an unincorporated community and census-designated place (CDP) in Jeff Davis County, Texas, United States. The population was 1,201 at the 2010 census, up from 1,050 at the 2000 census. It is the county seat of Jeff Davis County.
Hist ...
showing a syncline
File:Rainbow Basin.JPG, Rainbow Basin Syncline in the Barstow Formation
The Barstow Formation is a series of limestones, conglomerates, sandstones, siltstones and shales exposed in the Mojave Desert near Barstow in San Bernardino County, California.Dibblee, T.W., Jr. (1967). Areal Geology of the Western Mojave ...
near Barstow, California
Barstow is a city in San Bernardino County, California, in the Mojave Desert of Southern California. Located in the Inland Empire region of California, the population was 25,415 at the 2020 census. Barstow is an important crossroads for the In ...
File:SynclineCalico.JPG, Syncline in the lower parking lot of Calico Ghost Town
Calico is a ghost town and former mining town in San Bernardino County, California, United States. Located in the Calico Mountains (California), Calico Mountains of the Mojave Desert region of Southern California, it was founded in 1881 as a silve ...
; the ductile folding is at the base and the brittle is above.
File:Roundtop Hill outcrop1.jpg, Synclinal fold in Silurian
The Silurian ( ) is a geologic period and system spanning 24.6 million years from the end of the Ordovician Period, at million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Devonian Period, Mya. The Silurian is the shortest period of the Paleozoi ...
Wills Creek Formation or Bloomsburg Formation
The Silurian Bloomsburg Formation is a mapped bedrock unit in Pennsylvania, New Jersey, New York and Maryland. It is named for the town of Bloomsburg, Pennsylvania in which it was first described. The Bloomsburg marked the first occurrence of red s ...
at Roundtop Hill (Maryland)
File:Bear Valley east wall.jpg, East wall of Bear Valley Strip Mine, near Shamokin, Pennsylvania
File:Upheaval Syncline campsite.jpg, Syncline in Navajo Sandstone
The Navajo Sandstone is a geological formation in the Glen Canyon Group that is spread across the U.S. states of southern Nevada, northern Arizona, northwest Colorado, and Utah as part of the Colorado Plateau province of the United States.Anonym ...
, Upheaval Dome, Canyonlands National Park
Canyonlands National Park is an American national park located in southeastern Utah near the town of Moab. The park preserves a colorful landscape eroded into numerous canyons, mesas, and buttes by the Colorado River, the Green River, and their ...
, Utah
File:The Catlins.jpg, Satellite view of part of New Zealand's Southland Syncline, showing parallel folds running northwest–southeast
File:Wilpena Pound - Aerial View.jpg, Wilpena Pound, a synclinal basin in the Flinders Ranges
The Flinders Ranges are the largest mountain range in South Australia, which starts about north of Adelaide. The ranges stretch for over from Port Pirie to Lake Callabonna.
The Adnyamathanha people are the Aboriginal group who have inhabit ...
of South Australia
See also
*Anticline
In structural geology, an anticline is a type of fold that is an arch-like shape and has its oldest beds at its core, whereas a syncline is the inverse of an anticline. A typical anticline is convex up in which the hinge or crest is the ...
* Homocline
* Monocline
A monocline (or, rarely, a monoform) is a step-like fold in rock strata consisting of a zone of steeper dip within an otherwise horizontal or gently-dipping sequence.
Formation
Monoclines may be formed in several different ways (see diagram)
* ...
* Ridge-and-Valley Appalachians
The Ridge-and-Valley Appalachians, also called the Ridge and Valley Province or the Valley and Ridge Appalachians, are a physiographic province of the larger Appalachian division and are also a belt within the Appalachian Mountains extendin ...
References
Structural geology {{Geology-stub