|
Tōdōza
The was a Japanese guild for Visual impairment, blind men, established in the 14th century by the biwa hōshi . Members performed a variety of roles, as itinerant musicians, massage, masseurs, and acupuncture, acupuncturists. It received the patronage of the Muromachi period, Muromachi and Edo period, Edo shogunates, and remained active until the Meiji restoration, being eventually disbanded in 1871. The organization was hierarchically structured. The primary ranks, known as , were (the highest), then , , and ; these were further subdivided into a total of 73 distinct grades. Total membership was usually around 3,000; it is not known what proportion of the total blind population this represents. The Tōdōza accepted only male members; a separate organization, the , existed for blind women. There was additionally a further guild, the , similar to the Tōdōza but active mostly in the western regions of Japan. References Further reading *Achttiende-eeuwse verhandelin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akashi Kakuichi
also known as was a Japanese Buddhist monk of the early Muromachi period of Japanese history, noted as the blind itinerant lute player (''biwa hōshi'') who gave the epic ''Heike Monogatari'' its present form. Life Little is known about his early life, but Kakuichi may have originally been a monk of Enkyō-ji near Himeji in Harima Province and may have been a nephew of Ashikaga Takauji. After losing his sight in his 30s, he is said to have come to Kyoto and joined the Tōdōza, a ''biwa hōshi'' guild, performing versions of the ''Heike Monogatari'' as entertainment for members of the aristocracy. Kakuichi was a student of Jōichi (城一), the most famous Heike reciter in Kyoto, but soon surpassed his master and 1363 had the attained the highest rank (検校, ''Kengyō'') within the guild. On his death, he was posthumous awarded the rank of Grand Master (総検校, ''Sōkengyō''). Work Kakuichi's version of the ''Heike Monogatari'', known as the Kakuichi-bon, was developed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visual Impairment
Visual or vision impairment (VI or VIP) is the partial or total inability of visual perception. In the absence of treatment such as corrective eyewear, assistive devices, and medical treatment, visual impairment may cause the individual difficulties with normal daily tasks, including reading and walking. The terms ''low vision'' and ''blindness'' are often used for levels of impairment which are difficult or impossible to correct and significantly impact daily life. In addition to the various permanent conditions, fleeting temporary vision impairment, amaurosis fugax, may occur, and may indicate serious medical problems. The most common causes of visual impairment globally are uncorrected refractive errors (43%), cataracts (33%), and glaucoma (2%). Refractive errors include near-sightedness, far-sightedness, presbyopia, and astigmatism (eye), astigmatism. Cataracts are the most common cause of blindness. Other disorders that may cause visual problems include age-related macular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biwa Hōshi
, also known as "lute priests", were travelling performers in the era of Japanese history preceding the Meiji period. They earned their income by reciting vocal literature to the accompaniment of music. were mostly blind, and adopted the shaved heads and robes common to Buddhist monks. The occupation likely had its origin in China and India, where blind Buddhist lay-priest performers were once common. The musical style of the is referred to as , which literally means " music". Although these performers existed well before the events of the Genpei War, they eventually became famous for narrating tales about this war. Before sang , they were entertainers and ritual performers. They took on a broad range of roles, including poetry and song, plague prevention, and spiritual purification; it was probably because of their ritualistic duties that they became the caretakers of . The are considered the first performers of the ''Tale of the Heike'', which is one of Japan's most famous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zatoichi
is a fictional character created by Japanese novelist Kan Shimozawa. He is an itinerant blind masseur and swordsman of Japan's late Edo period (1830s and 1840s). He first appeared in the 1948 essay ''Zatoichi Monogatari'', part of Shimozawa's ''Futokoro Techō'' series that was serialized in the magazine ''Shōsetsu to Yomimono''. This originally minor character was drastically altered and developed for the screen by Daiei Film and actor Shintaro Katsu, becoming the subject of one of Japan's longest-running film series. A total of 26 films were made between 1962 and 1989. From 1974 to 1979, a television series was produced, starring Katsu and some of the same actors that appear in the films. Produced by Katsu Productions, 100 episodes were aired before the ''Zatoichi'' television series was cancelled. The seventeenth film of the ''Zatoichi'' series was remade in the US in 1989 by TriStar Pictures as '' Blind Fury'', starring Rutger Hauer. A 2003 film was directed by Takeshi K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Massage
Massage is the rubbing or kneading of the body's soft tissues. Massage techniques are commonly applied with hands, fingers, elbows, knees, forearms, feet, or a device. The purpose of massage is generally for the treatment of body stress or pain. In English-speaking European countries, traditionally a person professionally trained to give massages is known by the gendered French loanwords ''masseur'' (male) or ''masseuse'' (female). In the United States, these individuals are often referred to as "massage therapists". In some provinces of Canada, they are called "registered massage therapists." In professional settings, clients are treated while lying on a massage table, sitting in a massage chair, or lying on a mat on the floor. There are many different modalities in the massage industry, including (but not limited to): deep tissue, manual lymphatic drainage, Medical massage, medical, sports, Structural Integration, structural integration, #Swedish massage, Swedish, Thai massa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
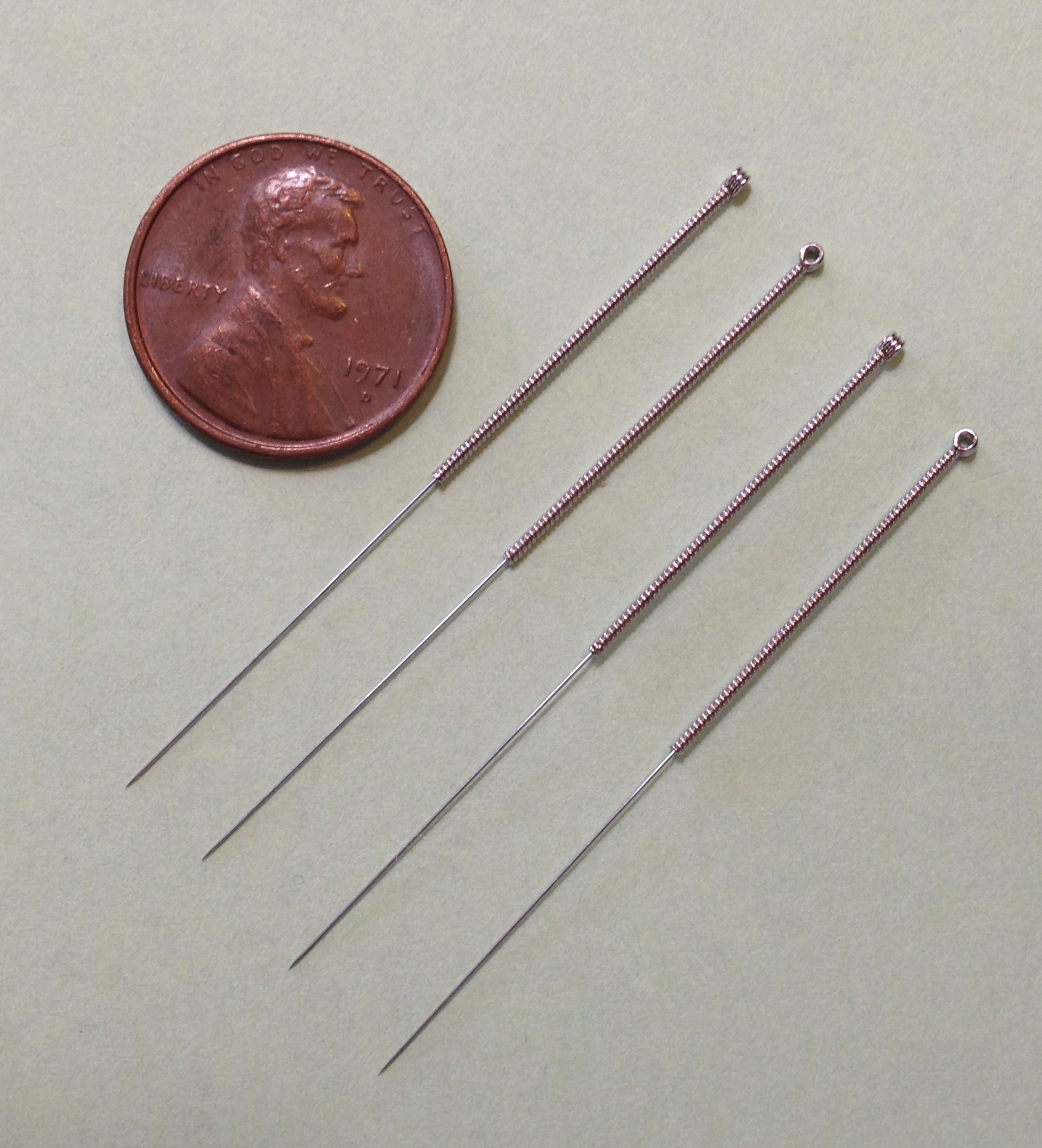
Acupuncture
Acupuncture is a form of alternative medicine and a component of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) in which thin needles are inserted into the body. Acupuncture is a pseudoscience; the theories and practices of TCM are not based on scientific knowledge, and it has been characterized as quackery. There is a range of acupuncture technological variants that originated in different philosophies, and techniques vary depending on the country in which it is performed. However, it can be divided into two main foundational philosophical applications and approaches; the first being the modern standardized form called eight principles TCM and the second being an older system that is based on the ancient Daoist '' wuxing'', better known as the five elements or phases in the West. Acupuncture is most often used to attempt pain relief, though acupuncturists say that it can also be used for a wide range of other conditions. Acupuncture is typically used in combination with other forms o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muromachi Period
The , also known as the , is a division of Japanese history running from approximately 1336 to 1573. The period marks the governance of the Muromachi or Ashikaga shogunate ( or ), which was officially established in 1338 by the first Muromachi ''shōgun'', Ashikaga Takauji, two years after the brief Kenmu Restoration (1333–1336) of imperial rule was brought to a close. The period ended in 1573 when the 15th and last shogun of this line, Ashikaga Yoshiaki, was driven out of the capital in Kyoto by Oda Nobunaga. From a cultural perspective, the period can be divided into the Kitayama and Higashiyama cultures (later 15th – early 16th centuries). The early years from 1336 to 1392 of the Muromachi period are known as the or Northern and Southern Court period. This period is marked by the continued resistance of the supporters of Emperor Go-Daigo, the emperor behind the Kenmu Restoration. The Sengoku period or Warring States period, which begins in 1465, largely overlaps ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edo Period
The , also known as the , is the period between 1600 or 1603 and 1868 in the history of Japan, when the country was under the rule of the Tokugawa shogunate and some 300 regional ''daimyo'', or feudal lords. Emerging from the chaos of the Sengoku period, the Edo period was characterized by prolonged peace and stability, urbanization and economic growth, strict social order, Isolationism, isolationist foreign policies, and popular enjoyment of Japanese art, arts and Culture of Japan, culture. In 1600, Tokugawa Ieyasu prevailed at the Battle of Sekigahara and established hegemony over most of Japan, and in 1603 was given the title ''shogun'' by Emperor Go-Yōzei. Ieyasu resigned two years later in favor of his son Tokugawa Hidetada, Hidetada, but maintained power, and defeated the primary rival to his authority, Toyotomi Hideyori, at the Siege of Osaka in 1615 before his death the next year. Peace generally prevailed from this point on, making samurai largely redundant. Tokugawa sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meiji Restoration
The , referred to at the time as the , and also known as the Meiji Renovation, Revolution, Regeneration, Reform, or Renewal, was a political event that restored Imperial House of Japan, imperial rule to Japan in 1868 under Emperor Meiji. Although there were ruling emperors before the Meiji Restoration, the events restored practical power to, and consolidated the political system under, the Emperor of Japan. The Restoration led to enormous changes in Japan's political and social structure and spanned both the late Edo period (often called the Bakumatsu) and the beginning of the Meiji era, during which time Japan rapidly Industrialization, industrialised and adopted Western culture, Western ideas and production methods. The origins of the Restoration lay in economic and political difficulties faced by the Tokugawa shogunate. These problems were compounded by the encroachment of foreign powers in the region which challenged the Tokugawa policy of , specifically the arrival of the Pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goze
is a Japanese historic term referring to visually-impaired Japanese women, most of whom worked as musicians. Etymology The kanji for mean "blind" and "woman." is most likely derived from , which also means "blind person" ( is a formal second-person pronoun). Although the term can be found in medieval records, other terms such as , were also in use (especially in written records) until the modern era. In spoken language, the term is usually suffixed by an honorific: , , , etc. Organizations From the Edo period (1600–1868), organized themselves in a number of ways. Some large-scale organizations could be found in urban areas, though during the nineteenth century, some documents mention associations in the city of Edo. In Osaka and some regional towns, were sometimes informally linked to pleasure quarters, where they were called to perform their songs at parties. ''Goze'' organizations developed most in rural areas and continued to exist in Niigata (once known a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Za (guilds)
The were one of the primary types of trade guilds in feudalism, feudal Japan. The za grew out of protective cooperation between merchants and religious authorities. They became more prominent during the Muromachi period where they would ally themselves with noble patrons, before they became more independent later in the period. The za commonly organized by locality, and not by trade in the rural areas; but grouped by trade in the larger cities, more familiar to their European counterparts. The monopoly of the za was challenged during the reign of Oda Nobunaga. Later in the early 18th century, the za gained in influence by working more closely with the Tokugawa shogunate, Tokugawa government; this brought more centralization and a return to their monopoly power. After the Meiji Restoration, Meiji restoration, the za was either replaced, eclipsed or gradually adopted more modern forms of business, eventually giving rise to the modern ''zaibatsu'' and ''keiretsu'' monopolies of the 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |