|
Tłı̨chǫ People
The Tłı̨chǫ (, ) people, sometimes spelled Tlicho and also known as the Dogrib, are a Dene First Nations people of the Athabaskan-speaking ethnolinguistic group living in the Northwest Territories of Canada. Name The name ''Dogrib'' is an English adaptation of their own name, (or ) – “Dog-Flank People”, referring to their fabled descent from a supernatural dog-man. Like their Dene neighbours they called themselves often simply ("person", "human") or ("People, i.e. Dene People"). The Tłı̨chǫ's land is known as (or , or ). On the 1682 Franquelin map, Dogrib was recorded as "Alimousp oiak" (from Cree , "Dog-Flanks"). Communities Tłı̨chǫ people have now six settlements or settlements with mostly of Tłı̨chǫ residents: Behchoko (formerly Rae-Edzo), Whatì (Lac la Martre), Gamèti (Rae Lakes), Wekweeti (Snare Lake), Dettah, and Ndilǫ (Rainbow Valley) (a subcommunity of Yellowknife, known by the Tłįchǫ as – "where the money is"). The or Do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dene
The Dene people () are an Aboriginal peoples in Canada, indigenous group of First Nations in Canada, First Nations who inhabit the northern Boreal forest of Canada, boreal and Arctic regions of Canada. The Dene speak Northern Athabaskan languages. ''Dene'' is the common Athabaskan word for "people". The term "Dene" has two usages. More commonly, it is used narrowly to refer to the Athabaskan speakers of the Northwest Territories and Nunavut in Canada, especially including the Chipewyan (Denesuline), Tlicho (''Dogrib''), Yellowknives (T'atsaot'ine), Slavey people, Slavey (Deh Gah Got'ine or Deh Cho), and Sahtu (the Eastern group in Jeff Leer's classification; part of the Northwestern Canada group in Keren Rice's classification). However, it is sometimes also used to refer to all Northern Athabaskan speakers, who are spread in a wide range all across Alaska and northern Canada. The Southern Athabaskan speakers, however, also refer to themselves by similar words: Navajo people, D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Resolution
Fort Resolution (''Denı́nu Kų́ę́'' (pronounced "deh-nih-noo-kwenh") "moose island place") is a hamlet in the South Slave Region of the Northwest Territories, Canada. The community is situated at the mouth of the Slave River, on the shores of Great Slave Lake, and at the end of the Fort Resolution Highway (Highway 6). It is the headquarters of the Deninu Kųę́ First Nation, whose Chief is Louis Balsillie. It is the oldest documented European community in the Northwest Territories, built in 1819, and was a key link in the fur trade's water route north. Fort Resolution is designated as a National Historic Site of Canada as the oldest continuously occupied place in the Northwest Territories with origins in the fur trade and the principal fur trade post on Great Slave Lake. Fort Resolution's Deninoo School offers K-12 schooling. The town also has a hockey arena, community hall, a nursing station, a youth centre, Royal Canadian Mounted Police, a bed and breakfast, a 'Northern' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty No
A treaty is a formal, legally binding written agreement between actors in international law. It is usually made by and between sovereign states, but can include international organizations, individuals, business entities, and other legal persons. A treaty may also be known as an international agreement, protocol, covenant, convention, pact, or exchange of letters, among other terms. However, only documents that are legally binding on the parties are considered treaties under international law. Treaties vary on the basis of obligations (the extent to which states are bound to the rules), precision (the extent to which the rules are unambiguous), and delegation (the extent to which third parties have authority to interpret, apply and make rules). Treaties are among the earliest manifestations of international relations, with the first known example being a border agreement between the Sumerian city-states of Lagash and Umma around 3100 BC. International agreements were used in so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Na-Dené Languages
Na-Dene (; also Nadene, Na-Dené, Athabaskan–Eyak–Tlingit, Tlina–Dene) is a family of Native American languages that includes at least the Athabaskan languages, Eyak, and Tlingit languages. Haida was formerly included, but is now considered doubtful. By far the most widely spoken Na-Dene language today is Navajo. In February 2008, a proposal connecting Na-Dene (excluding Haida) to the Yeniseian languages of central Siberia into a Dené–Yeniseian family was published and well-received by a number of linguists.Dene–Yeniseic Symposium , University of Alaska Fairbanks, February 2008, accessed 30 Mar 2010 It was proposed in a 2014 paper that the Na-Dene languages of North America and the Yeniseian languages of Siberia had a common origin in a language spoken in |
Dogrib Language
The Tlicho language, also known as Tłı̨chǫ Yatıì or the Dogrib language, is a Northern Athabaskan language spoken by the Tłı̨chǫ (Dogrib people) First Nations of the Canadian Northwest Territories. According to Statistics Canada in 2011, there were 2,080 people who speak Tłı̨chǫ Yatıì. As of 2016, 1,735 people speak the language. Tłıchǫ Yatıì is spoken by the Tłıchǫ, a Dene First Nations people that reside in the Northwest Territories of Canada. Tłı̨chǫ lands lie east of Mackenzie River (Deh Cho) between Great Slave Lake (Tıdeè) and Great Bear Lake (Sahtu) in the Northwest Territories. There are four primary communities that speak the language: Gamèti (formerly Rae Lakes), Behchokǫ̀ (formerly Rae-Edzo), Wekweètì (formerly Snare Lakes) and Whatì (formerly Lac La Martre). From a population number of about 800 during the mid-19th century to about 1,700 by the 1970s, the population has grown to about 2,080 as recorded by the 2011 Census. Howev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tłı̨chǫ Girls
The Tłı̨chǫ (, ) people, sometimes spelled Tlicho and also known as the Dogrib, are a Dene First Nations people of the Athabaskan-speaking ethnolinguistic group living in the Northwest Territories of Canada. Name The name ''Dogrib'' is an English adaptation of their own name, (or ) – “Dog-Flank People”, referring to their fabled descent from a supernatural dog-man. Like their Dene neighbours they called themselves often simply ("person", "human") or ("People, i.e. Dene People"). The Tłı̨chǫ's land is known as (or , or ). On the 1682 Franquelin map, Dogrib was recorded as "Alimousp oiak" (from Cree , "Dog-Flanks"). Communities Tłı̨chǫ people have now six settlements or settlements with mostly of Tłı̨chǫ residents: Behchoko (formerly Rae-Edzo), Whatì (Lac la Martre), Gamèti (Rae Lakes), Wekweeti (Snare Lake), Dettah, and Ndilǫ (Rainbow Valley) (a subcommunity of Yellowknife, known by the Tłįchǫ as – "where the money is"). The or Do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yellowknife
Yellowknife (; Dogrib: ) is the capital, largest community, and only city in the Northwest Territories, Canada. It is on the northern shore of Great Slave Lake, about south of the Arctic Circle, on the west side of Yellowknife Bay near the outlet of the Yellowknife River. Yellowknife and its surrounding water bodies were named after a local Dene tribe, who were known as the "Copper Indians" or "Yellowknife Indians", today incorporated as the Yellowknives Dene First Nation. They traded tools made from copper deposits near the Arctic Coast. Its population, which is ethnically mixed, was 19,569 per the 2016 Canadian Census. Of the eleven official languages of the Northwest Territories, five are spoken in significant numbers in Yellowknife: Dene Suline, Dogrib, South and North Slavey, English, and French. In the Dogrib language, the city is known as ''Sǫǫ̀mbak’è'' (, "where the money is"). Modern Yellowknives members can be found in the adjoining, primarily Indigenous c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cree Language
Cree (also known as Cree– Montagnais–Naskapi) is a dialect continuum of Algonquian languages spoken by approximately 117,000 people across Canada, from the Northwest Territories to Alberta to Labrador. If considered one language, it is the aboriginal language with the highest number of speakers in Canada. The only region where Cree has any official status is in the Northwest Territories, alongside eight other aboriginal languages. There, Cree is spoken mainly in Fort Smith and Hay River. Names Endonyms are: * (Plains Cree) * (Woods Cree) * (Western Swampy Cree) * (Eastern Swampy Cree) * (Moose Cree) * (Southern East Cree) * (Northern East Cree) * (Atikamekw) * (Western Montagnais, Piyekwâkamî dialect) * (Western Montagnais, Betsiamites dialect) * (Eastern Montagnais) Origin and diffusion Cree is believed to have begun as a dialect of the Proto-Algonquian language spoken between 2,500 and 3,000 years ago in the original Algonquian homeland, an u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
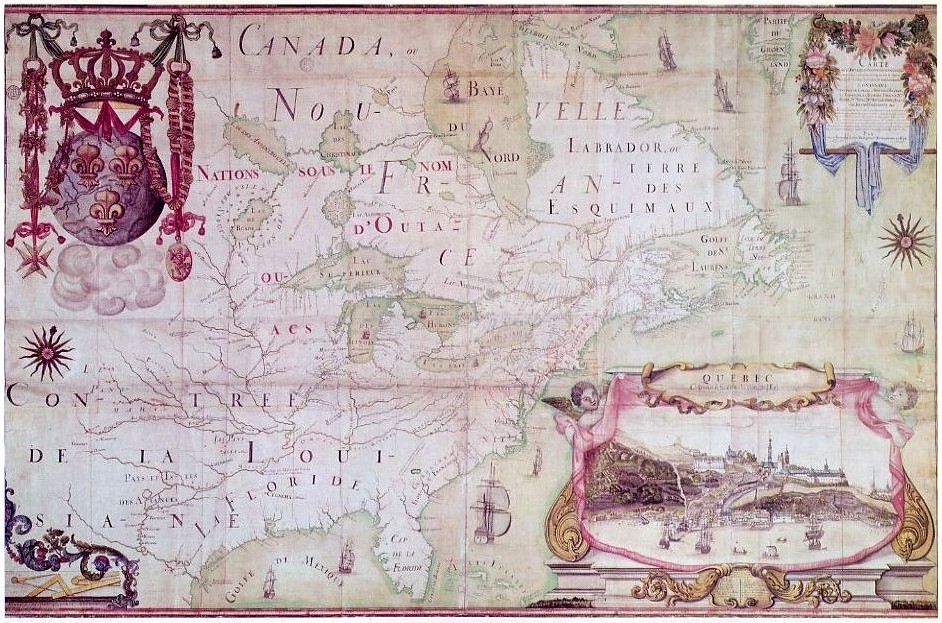
Jean-Baptiste-Louis Franquelin
Jean-Baptiste-Louis Franquelin (1650-c.1712) was a French trader who was appointed in the early 1670s as the first cartographer in '' Nouvelle France'' (Canada) by the colony's governor. He was appointed in 1688 as royal hydrographer by Louis XIV. Franquelin was born in the commune of Pallauau-sur-Indre in central France. He migrated to New France in 1671 where he was soon appointed as the colony's cartographer. He documented a decade of Louis Jolliet and René-Robert Cavelier de La Salle's explorations in North America. He also completed other projects for the Crown and served the king's military engineer. After returning to France in 1692, he never lived in Canada again. Biography Born at Saint-Michel de Villebernin, he grew up in the village in the small commune of Palluau-sur-Indre in central France. Having developed drawing and mapmaking skills, Franquelin migrated in 1671 from Indre department to ''Nouvelle France'' (Quebec) to work as a trader. New France Governor L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)