|
Type VI Collagen
Collagen VI (ColVI) is a type of collagen primarily associated with the extracellular matrix of skeletal muscle. ColVI maintains regularity in muscle function and stabilizes the cell membrane. It is synthesized by a complex, multistep pathway that leads to the formation of a unique network of linked microfilaments located in the extracellular matrix (ECM). ColVI plays a vital role in numerous cell types, including chondrocytes, neurons, myocytes, fibroblasts, and cardiomyocytes. ColVI molecules are made up of three alpha chains: α1(VI), α2(VI), and α3(VI). It is encoded by 6 genes: COL6A1, COL6A2, COL6A3, COL6A4, COL6A5, and COL6A6.Collagen VI at a glance Matilde Cescon, Francesca Gattazzo, Peiwen Chen, Paolo Bonaldo J Cell Sci 2015 128: 3525-3531; doi: 10.1242/jcs.169748 The chain lengths of α1(VI) and α2(VI) are about 1,000 amino acids. The chain length of α3(VI) is roughly a third larger than those of α1(VI) and α2(VI), and it consists of several spliced variants with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collagen
Collagen () is the main structural protein in the extracellular matrix found in the body's various connective tissues. As the main component of connective tissue, it is the most abundant protein in mammals, making up from 25% to 35% of the whole-body protein content. Collagen consists of amino acids bound together to form a triple helix of elongated fibril known as a collagen helix. It is mostly found in connective tissue such as cartilage, bones, tendons, ligaments, and skin. Depending upon the degree of mineralization, collagen tissues may be rigid (bone) or compliant (tendon) or have a gradient from rigid to compliant (cartilage). Collagen is also abundant in corneas, blood vessels, the gut, intervertebral discs, and the dentin in teeth. In muscle tissue, it serves as a major component of the endomysium. Collagen constitutes one to two percent of muscle tissue and accounts for 6% of the weight of the skeletal muscle tissue. The fibroblast is the most common cell that crea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
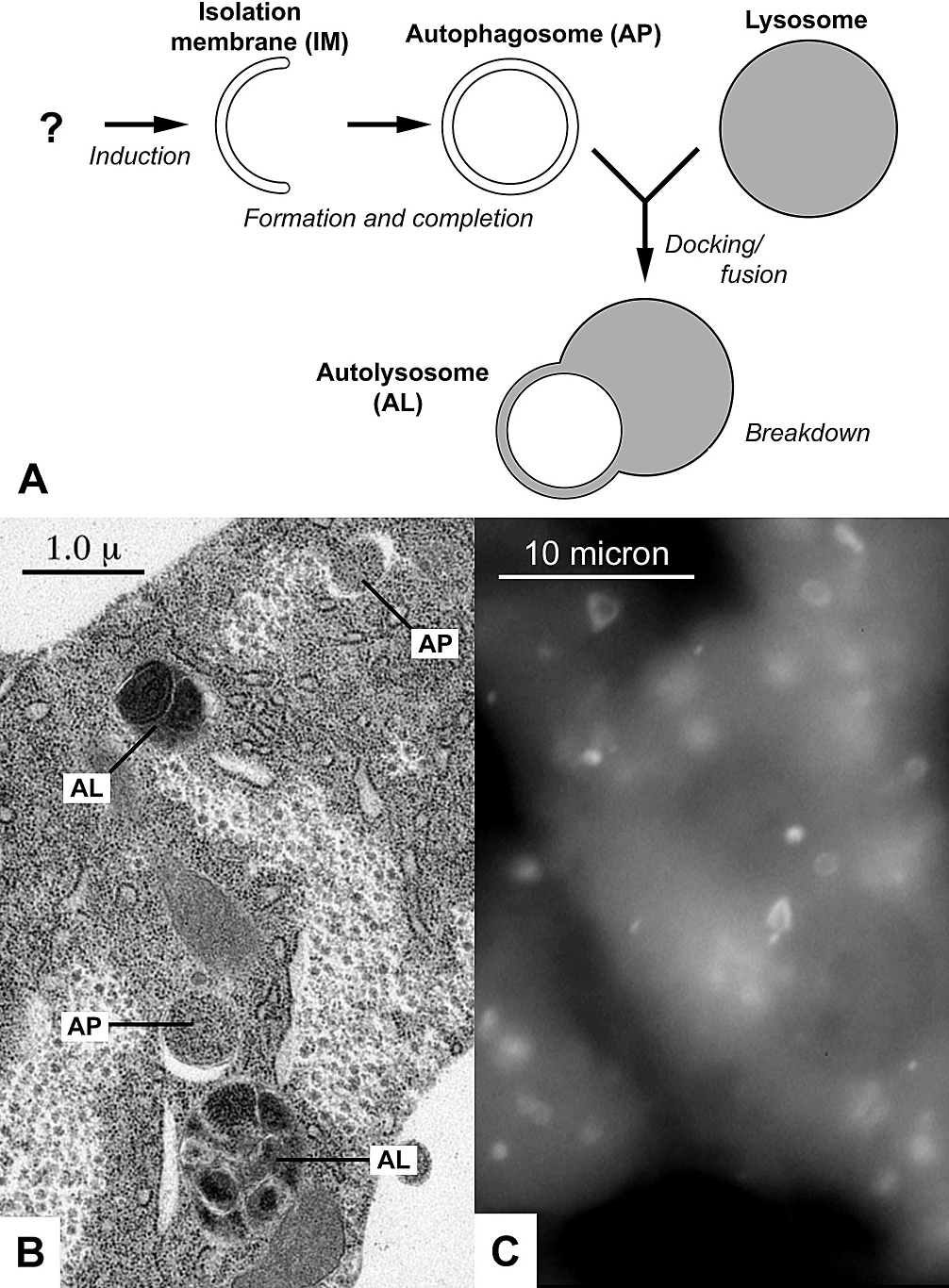
Autophagy
Autophagy (or autophagocytosis; from the Ancient Greek , , meaning "self-devouring" and , , meaning "hollow") is the natural, conserved degradation of the cell that removes unnecessary or dysfunctional components through a lysosome-dependent regulated mechanism. It allows the orderly degradation and recycling of cellular components. Although initially characterized as a primordial degradation pathway induced to protect against starvation, it has become increasingly clear that autophagy also plays a major role in the homeostasis of non-starved cells. Defects in autophagy have been linked to various human diseases, including neurodegeneration and cancer, and interest in modulating autophagy as a potential treatment for these diseases has grown rapidly. Four forms of autophagy have been identified: macroautophagy, microautophagy, chaperone-mediated autophagy (CMA), and crinophagy. In macroautophagy (the most thoroughly researched form of autophagy), cytoplasmic components (like mit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epineurium
The epineurium is the outermost layer of dense irregular connective tissue surrounding a peripheral nerve. It usually surrounds multiple nerve fascicles as well as blood vessels which supply the nerve. Smaller branches of these blood vessels penetrate into the perineurium. In addition to blood vessels which supply the nerve, lymphocytes and fibroblasts are also present and contribute to the production of collagen fibers that form the backbone of the epineurium. In addition to providing structural support, lymphocytes and fibroblasts also play a vital role in maintenance and repair of the surrounding tissues. When the spinal nerve leaves the vertebral canal via an intervertebral foramen, two layers of the spinal meninges, the arachnoid and the dura invaginate the nerve to form a dural sleeve of connective tissue, which is the epineurium. The outer portion of this sleeve comprises the external epineurium which permits longitudinal nerve excursion and absorption of longitudina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perineurium
The perineurium is a protective sheath that surrounds a nerve fascicle. This bundles together axons targeting the same anatomical location. The perineurium is composed from fibroblasts. In the peripheral nervous system, the myelin sheath of each axon in a nerve is wrapped in a delicate protective sheath known as the endoneurium. Fascicles, bundles of neurons, are surrounded by the perineurium. Several fascicles may be in turn bundled together with a blood supply and fatty tissue within yet another sheath, the epineurium. This grouping structure is analogous to the muscular organization system of epimysium, perimysium and endomysium. Structure The perineurium is composed of connective tissue, which has a distinctly lamellar arrangement consisting of one to several concentric layers. The perineurium is composed of perineurial cells, which are epithelioid myofibroblasts. Perineurial cells are sometimes referred to as myoepithelioid due to their epithelioid and myofibroblastoid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endoneurium
The endoneurium (also called endoneurial channel, endoneurial sheath, endoneurial tube, or Henle's sheath) is a layer of delicate connective tissue around the myelin sheath of each myelinated nerve fiber in the peripheral nervous system. Its component cells are called endoneurial cells. The endoneuria with their enclosed nerve fibers are bundled into groups called nerve fascicles, each fascicle within its own protective sheath called a perineurium. In sufficiently large nerves multiple fascicles, each with its blood supply and fatty tissue, may be bundled within yet another sheath, the epineurium. The endoneurium contains a liquid known as endoneurial fluid, which contains little protein. In the peripheral nervous system the endoneurial fluid is notionally equivalent to cerebrospinal fluid in the central nervous system. Peripheral nerve injuries commonly release increased amounts of endoneurial fluid into surrounding tissues; these can be detected by magnetic resonance neurography ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Connective Tissue
Connective tissue is one of the four primary types of animal tissue, along with epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. It develops from the mesenchyme derived from the mesoderm the middle embryonic germ layer. Connective tissue is found in between other tissues everywhere in the body, including the nervous system. The three meninges, membranes that envelop the brain and spinal cord are composed of connective tissue. Most types of connective tissue consists of three main components: elastic and collagen fibers, ground substance, and cells. Blood, and lymph are classed as specialized fluid connective tissues that do not contain fiber. All are immersed in the body water. The cells of connective tissue include fibroblasts, adipocytes, macrophages, mast cells and leucocytes. The term "connective tissue" (in German, ''Bindegewebe'') was introduced in 1830 by Johannes Peter Müller. The tissue was already recognized as a distinct class in the 18th century. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schwann Cell
Schwann cells or neurolemmocytes (named after German physiologist Theodor Schwann) are the principal glia of the peripheral nervous system (PNS). Glial cells function to support neurons and in the PNS, also include satellite cells, olfactory ensheathing cells, enteric glia and glia that reside at sensory nerve endings, such as the Pacinian corpuscle. The two types of Schwann cells are myelinating and nonmyelinating. Myelinating Schwann cells wrap around axons of motor and sensory neurons to form the myelin sheath. The Schwann cell promoter is present in the downstream region of the human dystrophin gene that gives shortened transcript that are again synthesized in a tissue-specific manner. During the development of the PNS, the regulatory mechanisms of myelination are controlled by feedforward interaction of specific genes, influencing transcriptional cascades and shaping the morphology of the myelinated nerve fibers. Schwann cells are involved in many important aspects of peri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UVB-induced Apoptosis
UV-induced apoptosis UV-induced apoptosis is an adequate (physiological) reaction of a cell damaged by UV radiation (UVR) in a sufficiently large (lethal) dose and it prevents the disordered destruction of UV damaged cells by help necrosis. Cell elimination by apoptosis occurs when UV-induced cell damage which cannot be repaired by the intracellular repair system exceeds at it certain limit (lethal damage). Through apoptosis, the cells are self-disassembled into compartments with their subsequent utilization (mainly by neighboring cells). The first time sign of the beginning of the apoptosis system is working in a UV damaged cell is the activation of restriction enzymes, which divide cell DNA into fragments convenient for utilization. But too large a dose of UVR can lead to breakdown (inactivation) of the energy-dependent mechanism of apoptosis (super lethal damage). In this case, cell destruction occurs randomly, not orderly, and during a significantly longer (compared with apopt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apoptosis
Apoptosis (from grc, ἀπόπτωσις, apóptōsis, 'falling off') is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (morphology) and death. These changes include blebbing, cell shrinkage, nuclear fragmentation, chromatin condensation, DNA fragmentation, and mRNA decay. The average adult human loses between 50 and 70 billion cells each day due to apoptosis. For an average human child between eight and fourteen years old, approximately twenty to thirty billion cells die per day. In contrast to necrosis, which is a form of traumatic cell death that results from acute cellular injury, apoptosis is a highly regulated and controlled process that confers advantages during an organism's life cycle. For example, the separation of fingers and toes in a developing human embryo occurs because cells between the digits undergo apoptosis. Unlike necrosis, apoptosis produces cell fragments called apoptotic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peptide
Peptides (, ) are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. Long chains of amino acids are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty amino acids are called oligopeptides, and include dipeptides, tripeptides, and tetrapeptides. A polypeptide is a longer, continuous, unbranched peptide chain. Hence, peptides fall under the broad chemical classes of biological polymers and oligomers, alongside nucleic acids, oligosaccharides, polysaccharides, and others. A polypeptide that contains more than approximately 50 amino acids is known as a protein. Proteins consist of one or more polypeptides arranged in a biologically functional way, often bound to ligands such as coenzymes and cofactors, or to another protein or other macromolecule such as DNA or RNA, or to complex macromolecular assemblies. Amino acids that have been incorporated into peptides are termed residues. A water molecule is released during formation of each amide bond.. All peptides except cyclic pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dena Dubal
Dena Dubal is the David A. Coulter Endowed Chair in Ageing and Neurodegenerative Disease at University of California, San Francisco. Dubal has demonstrated that the hormone Klotho can enhance cognition and protect the brain from neurodegenerative decline. Early life and education Dubal is from Houston. She attended Episcopal High School and graduated in 1992. She was an undergraduate student at the University of California, Berkeley, where she studied neuroscience with a minor in anthropology. During her undergraduate physiology classes she recognised that the process of ageing still presented many mysteries to the scientific community. After earning her bachelor's degree, Dubal studied medicine at the University of Kentucky College of Medicine. She worked with Phyllis Wise on the impact of hormones on brain injury caused by stroke. She was a neurological resident at the University of California, San Francisco, where she was elected Chief Resident and continued to research age ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alzheimer's Disease
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegeneration, neurodegenerative disease that usually starts slowly and progressively worsens. It is the cause of 60–70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in short-term memory, remembering recent events. As the disease advances, symptoms can include primary progressive aphasia, problems with language, Orientation (mental), disorientation (including easily getting lost), mood swings, loss of motivation, self-neglect, and challenging behaviour, behavioral issues. As a person's condition declines, they often withdraw from family and society. Gradually, bodily functions are lost, ultimately leading to death. Although the speed of progression can vary, the typical life expectancy following diagnosis is three to nine years. The cause of Alzheimer's disease is poorly understood. There are many environmental and genetic risk factors associated with its development. The strongest genetic risk factor is from an alle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |