|
Twat (other)
''Twat'' is an English-language vulgarism which means the vulva or vagina, and is used figuratively as a derogatory epithet. In British English, and Irish English it is a common insult referring to an obnoxious or stupid person regardless of gender; in American English, it is rarer and usually used to insult a woman. In Britain and Ireland, the usual pronunciation rhymes with "hat", while Americans most often use the older pronunciation that rhymes with "squat". This is reflected in the former variant spelling of "twot". The literal sense is first attested in 1656, the epithet in the 1930s. The word's etymology is uncertain. The '' American Heritage Dictionary'' suggests a conjectural Old English word "thwāt", meaning "a cut", cognate with the Old Norse "þveit" ("thveit"). Jonathon Green suggests a connection with "twitchel", a dialect term for a narrow passage. The twentieth-century British slang verb ''twat'', meaning 'to hit, whack', is probably an unrelated homonym of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vulgarism
In the study of language and literary style, a vulgarism is an expression or usage considered standard language, non-standard or characteristic of uneducated speech or writing. In colloquial or Lexical definition, lexical English, "vulgarism" or "vulgarity" may be synonymous with profanity or obscenity, but a linguistic or literary vulgarism encompasses a broader category of perceived fault not confined to scatology, scatological or sexual offensiveness. These faults may include Received Pronunciation, errors of pronunciation, orthography, misspellings, word malformations,Johannes Tromp, ''The Assumption of Moses: A Critical Edition with Commentary'', ''Studia in Veteris Testamenti Pseudepigrapha'' (Brill, 1993), pp. 27, 39–40, 243. and malapropisms. "wikt:vulgarity, Vulgarity" is generally used in the more restricted sense. In regular and mostly informal conversations, the presence of vulgarity, if any, are mostly for intensifying, exclaiming or scolding. In modern times, vulgaris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twatt Road Sign
Twatt may refer to: * Twatt, Orkney, Scotland * Twatt, Shetland Twatt is a settlement in the Shetland Islands of Scotland. It is located on the Shetland Mainland on a minor road that leads from the A971 road to Clousta, north of Bixter. The settlement is within the parish of Sandsting. The settlement name ..., Scotland See also * Twat (other) {{geodis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William James Rolfe
William James Rolfe, Litt.D. (December 10, 1827 – July 7, 1910) was an American educator and Shakespearean scholar. Early life and education Rolfe was born in Newburyport, Massachusetts on December 10, 1827. He attended Amherst College from 1845 through 1848, but left without graduating after three years due to financial hardship. Amherst, though, nonetheless later awarded him an honorary degree. Career Between 1852 and 1868, he served as headmaster of high schools at Dorchester, Lawrence, Salem, and Cambridge, Massachusetts. From 1882 to 1887, he served as president of Martha's Vineyard Summer Institute Martha's Vineyard Summer Institute was the first summer school for teachers in the United States. The school was started in the summer of 1878 and closed in June 1906. It was situated in Oak Bluffs, Massachusetts, Cottage City, Massachusetts, Cotta .... Early in his career, he edited selections from Ovid and Virgil and (in collaboration) the ''Cambridge Course of Physics' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Country English
West Country English is a group of English language varieties and accents used by much of the native population of South West England, the area sometimes popularly known as the West Country. The West Country is often defined as encompassing the counties of Cornwall, Devon, Dorset, Somerset, Wiltshire, the City of Bristol, and Gloucestershire. However, the northern and eastern boundaries of the area are hard to define. In the adjacent counties of Herefordshire, Worcestershire, Berkshire, Hampshire, the Isle of Wight and Oxfordshire it is possible to encounter similar accents and, indeed, much the same distinct dialect but with some similarities to others in neighbouring regions. Although natives of such locations, especially in rural parts, can still have West Country influences in their speech, the increased mobility and urbanisation of the population has meant that in the more populous counties of Worcestershire, Berkshire, Hampshire (including the Isle of Wight), and Oxfo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Notes And Queries
''Notes and Queries'', also styled ''Notes & Queries'', is a long-running quarterly scholarly journal that publishes short articles related to " English language and literature, lexicography, history, and scholarly antiquarianism".From the inner sleeve of all modern issues of ''Notes and Queries''. Its emphasis is on "the factual rather than the speculative". The journal has a long history, having been established in 1849 in London;''Notes and Queries'', Series 1, Volume 1, Nov 1849 - May 1850 via it is now published by |
Victorian Era
In the history of the United Kingdom and the British Empire, the Victorian era was the period of Queen Victoria's reign, from 20 June 1837 until her death on 22 January 1901. The era followed the Georgian period and preceded the Edwardian period, and its later half overlaps with the first part of the '' Belle Époque'' era of Continental Europe. There was a strong religious drive for higher moral standards led by the nonconformist churches, such as the Methodists and the evangelical wing of the established Church of England. Ideologically, the Victorian era witnessed resistance to the rationalism that defined the Georgian period, and an increasing turn towards romanticism and even mysticism in religion, social values, and arts. This era saw a staggering amount of technological innovations that proved key to Britain's power and prosperity. Doctors started moving away from tradition and mysticism towards a science-based approach; medicine advanced thanks to the adoption ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardinal's Hat
A (plural: ; from la, galērum, originally connotating a helmet made of skins; cf. '' galea'') is a broad-brimmed hat with tasselated strings which was worn by clergy in the Catholic Church. Over the centuries, the red ''galero'' was restricted to use by individual cardinals while such other colors as black, green and violet were reserved to clergy of other ranks and styles. Description When creating a cardinal, the pope used to place a scarlet ''galero'' on the new cardinal's head in consistory, the practice giving rise to the phrase "receiving the red hat." In 1969, Pope Paul VI issued a decree ending the use of the ''galero''. Since that time, only the scarlet ''zucchetto'' and ''biretta'' are placed over the heads of cardinals during the papal consistory. Some cardinals continue to obtain a ''galero'' privately so that the custom of suspending it over their tombs may be observed. Raymond Cardinal Burke has been known to publicly wear the ''galero'' on occasion in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EEBO
The Text Creation Partnership (TCP) is a not-for-profit organization based in the library of the University of Michigan . Its purpose is to produce large-scale full-text electronic resources (especially in the humanities) on behalf of both member institutions (particularly academic libraries) and scholarly publishers, under an arrangement calculated to serve the needs of both, and in so doing to demonstrate the value of a business model that sees corporate and non-profit information-providers as potentially amicable collaborators rather than as antagonistic vendors and customers respectively. Projects TCP has sponsored four text-creation projects to date. The first and the largest is "EEBO-TCP (Phase I)" (2001–2009), an effort to produce structurally marked-up full-text transcriptions of 25,000+ of the roughly 125,000 books to be found either in the Pollard and Redgrave and Wing short-title catalogues of early English printed books, or among the Thomason Tracts, that is, from amon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-Catholicism In The United Kingdom
Anti-Catholicism in the United Kingdom dates back to the English and Irish Reformations which were launched by King Henry VIII and the Scottish Reformation which was led by John Knox. Within England, the Act of Supremacy 1534 declared the English crown to be "the only supreme head on earth of the Church in England" in place of the pope. Any act of allegiance to the latter was considered treasonous because the papacy claimed both spiritual and political power over its followers. Ireland was brought under direct English control starting in 1536 during the Tudor conquest of Ireland. The Scottish Reformation in 1560 abolished Catholic ecclesiastical structures and rendered Catholic practice illegal in Scotland. Today, anti-Catholicism remains common in the United Kingdom, with particular relevance in Scotland and Northern Ireland. Anti-Catholicism among many of the English was grounded in the fear that the pope sought to reimpose not just religio-spiritual authority over England bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Vane The Younger
Sir Henry Vane (baptised 26 March 161314 June 1662), often referred to as Harry Vane and Henry Vane the Younger to distinguish him from his father, Henry Vane the Elder, was an English politician, statesman, and colonial governor. He was briefly present in North America, serving one term as the governor of the Massachusetts Bay Colony, and supported the creation of Roger Williams' Rhode Island Colony and Harvard College. A proponent of religious tolerance, as governor, he defended Anne HutchinsonMoore, p. 318 and her right to teach religious topics in her home which put him in direct conflict with the Puritan leaders in the Massachusetts Colony. He returned to England after losing re-election and eventually, Mrs. Hutchinson was banned from the colony. He was a leading Parliamentarian during the English Civil War and worked closely with Oliver Cromwell. He played no part in the execution of King Charles I, and refused to take oaths that expressed approval of the act. Vane se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wimple
A wimple is a medieval form of female headcovering, formed of a large piece of cloth worn draped around the neck and chin, covering the top of the head; it was usually made from white linen or silk. Its use developed in early medieval Europe; in medieval Christianity it was unseemly for a married woman to show her hair. A wimple might be elaborately starched, creased and folded in prescribed ways. Later elaborate versions were supported on wire or wicker framing, such as the cornette. Italian women abandoned their head coverings in the 15th century or replaced them with transparent gauze, showing their braids. Elaborate braiding and elaborately laundered clothes demonstrated status, because such grooming was performed by others. Today a plain wimple is worn by the nuns of certain orders who retain a traditional habit. In literature The Wife of Bath and the Prioress are depicted wearing wimples in the ''Canterbury Tales'' of Geoffrey Chaucer (c. 1343–1400). The King James ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
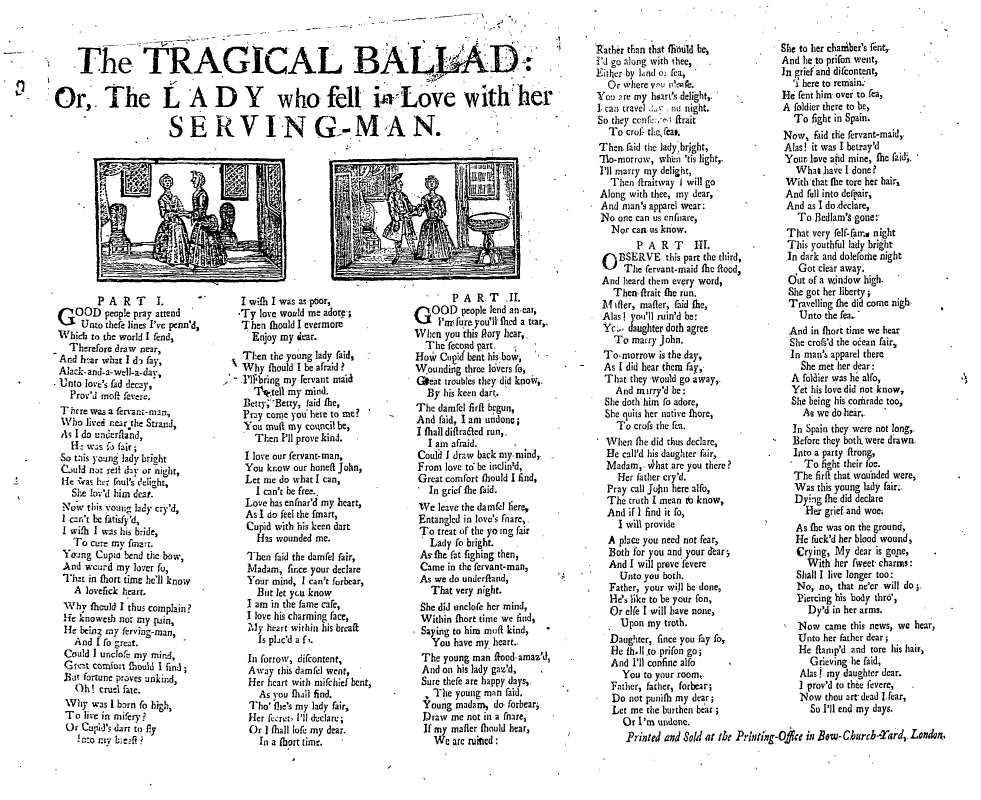
Broadside Ballad
A broadside (also known as a broadsheet) is a single sheet of inexpensive paper printed on one side, often with a ballad, rhyme, news and sometimes with woodcut illustrations. They were one of the most common forms of printed material between the sixteenth and nineteenth centuries, particularly in Britain, Ireland and North America because they are easy to produce and are often associated with one of the most important forms of traditional music from these countries, the ballad. Development of broadsides Ballads developed out of minstrelsy from the fourteenth and fifteenth century. These were narrative poems that had combined with French courtly romances and Germanic legends that were popular at the King’s court, as well as in the halls of lords of the realm. By the seventeenth century, minstrelsy had evolved into ballads whose authors wrote on a variety of topics. The authors could then have their ballads printed and distributed. Printers used a single piece of paper known as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |