|
Tuʻi-tā-tui
Tui-tā-tui ''(translation: The king who strikes the knee)'' was the 11th king of the Tuʻi Tonga, a dynasty in Tonga, who lived during the 12th century AD. Heketā Tuitātui had, like his father Momo, his court in Heketā ''(meaning: cripple hit)'', near the village of Niutōua on Tongatapu. It was there that he built, as an impressive gateway to the royal compound, the Haamonga-a-Maui. From the Haamonga a path proceeded about 50 m to the slightly elevated esi maka fākinanga, ''(stone to lean against)'' where the king sat against with his back, safe from any assassin from that direction. He was a huge, strong man, and easily handled a large stick as whether it was nothing. He hit everybody against the knees who would approach him too closely from the front. At par with this was his introduction of a new kava circle layout (a formal gathering of the chiefs of the country under him), in which the king sat more apart from the others (including supposed assassins) than before. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuʻi Tonga
The Tuʻi Tonga is a line of Tongan kings, which originated in the tenth century with the mythical ʻAhoʻeitu, and withdrew from political power in the fifteenth century by yielding to the ''Tuʻi Haʻatakalaua''. The title ended with the death of the last ''Tuʻi Tonga'', Sanualio Fatafehi Laufilitonga, in 1865, who bequeathed the ancient title and its ''mana'' to his nephew, Fatafehi Tu'i Pelehake, who was the ''Tu'i Faleua'', or Lord of the Second House (traditionally supposed to succeed to the office of the ''Tuʻi Tonga'' should the original line of kings perish without a natural successor). Tu'i Pelehake surrendered the title and its privileges to his father-in-law, King George Tupou I, who united its power and prestige with that of the ''Tu'i Kanokupolu'', '' Tu'i Vava'u'', and '' Tu'i Ha'apai'' titles to establish the modern-day institution of the Tongan Crown. Though the title is no longer conferred, the ancient line remains unbroken and is represented by the noble titl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Windward
Windward () and leeward () are terms used to describe the direction of the wind. Windward is ''upwind'' from the point of reference, i.e. towards the direction from which the wind is coming; leeward is ''downwind'' from the point of reference, i.e. along the direction towards which the wind is going. The side of a ship that is towards the leeward is its "lee side". If the vessel is heeling under the pressure of crosswind, the lee side will be the "lower side". During the Age of Sail, the term ''weather'' was used as a synonym for ''windward'' in some contexts, as in the ''weather gage''. Because it captures rain, the windward side of a mountain tends to be wet compared to the leeward it blocks. Origin The term "lee" comes from the middle-low German word // meaning "where the sea is not exposed to the wind" or "mild". The terms Luv and Lee (engl. Windward and Leeward) have been in use since the 17th century. Usage Windward and leeward directions (and the points o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Tonga
The history of Tonga is recorded since the ninth century BC, when seafarers associated with the Lapita diaspora first settled the islands which now make up the Kingdom of Tonga. Along with Fiji and Samoa, the area served as a gateway into the rest of the Pacific region known as Polynesia. Ancient Tongan mythologies recorded by early European explorers report the islands of 'Ata and Tongatapu as the first islands having been hauled to the surface from the deep ocean by Maui. Pre-contact The dates of the initial settlement of Tonga are still subject to debate; nonetheless, one of the oldest occupied sites is found in the village of Pea on Tongatapu. Radiocarbon dating of a shell found at the site reportedly dates the occupation at 3180 ± 100 BP (Before Present). Some of the oldest sites pertaining to the first occupants of the Tongan Islands are found on Tongatapu which is also where the first Lapita ceramics were found by WC McKern in 1921. Nonetheless, reaching the Tongan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tongan Monarchs
Tongan may refer to: * Something of, from, or related to the country of Tonga *Tongans, people from Tonga *Tongan language, the national language of Tonga *Tong'an District, a district in Xiamen, Fujian, China See also *Tonga (other) *Tonga language (other) *Tonga people (Malawi) *Tonga people (Zambia and Zimbabwe) The Tonga people of Zambia and Zimbabwe (also called 'Batonga') are a Bantu ethnic group of southern Zambia and neighbouring northern Zimbabwe, and to a lesser extent, in Mozambique. They are related to the Batoka who are part of the Tokaleya peo ... {{disambig Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Talatama
Talatama is named as the oldest son of Tuitātui and succeeded him as the 12th Tuʻi Tonga ''(king of Tonga)'' somewhere in the middle of the 12th century AD. They lived at Heketā, along the northcoast of Tongatapu Tongatapu is the main island of Tonga and the site of its capital, Nukualofa. It is located in Tonga's southern island group, to which it gives its name, and is the country's most populous island, with 74,611 residents (2016), 70.5% of the nation ..., with its rocky shore. Launching and landing canoes was difficult and the surf of the sea was always noisy. The nearby village of Kolonga, nowadays is nicknamed Utulongoaa ''(noisy coast)'', because that was what Talatama's sister Fatafehi said. Either to please her or just to find a better harbour for themselves Talatama and his younger brother Talaihaapepe decided to move the royal court to Mua ''(meaning: first'', because as the new capital, the village would be the first to receive honours). Indeed, the coast there ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
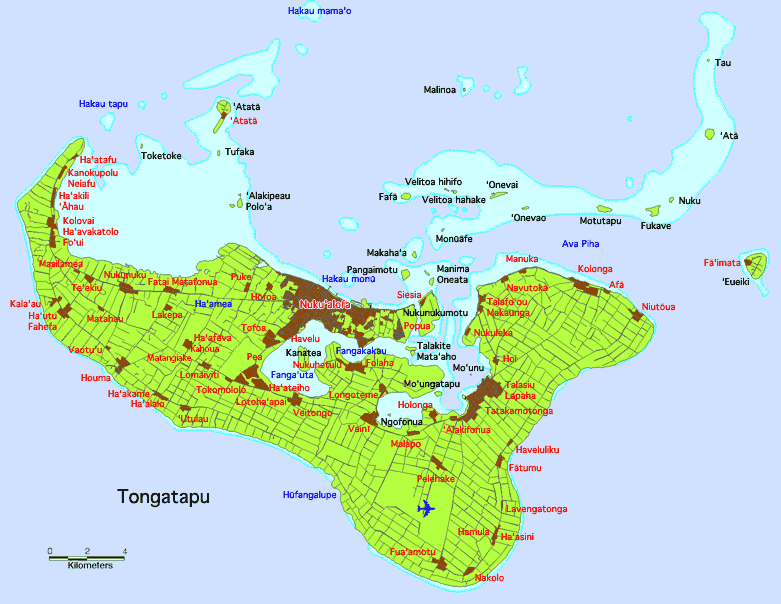
Folaha
Tongatapu is the main island of Tonga and the site of its capital, Nukualofa. It is located in Tonga's southern island group, to which it gives its name, and is the country's most populous island, with 74,611 residents (2016), 70.5% of the national population, on . Based on Google Earth Pro, its maximum elevation is at least above sea level along Liku Road at 21 degrees 15 minutes and 55.7 seconds south 175 degrees 08 minutes 06.4 seconds west, but could be even higher somewhere else. Tongatapu is Tonga's centre of government and the seat of its monarchy. Tongatapu has experienced more rapid economic development than the other islands of Tonga, and has thus attracted many internal migrants from them. Geography The island is (or including neighbouring islands) and rather flat, as it is built of coral limestone. The island is covered with thick fertile soil consisting of volcanic ash from neighbouring volcanoes. At the steep coast of the south, heights reach an average of , an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malapo
Malapo is a small village in the eastern district of Tongatapu in the kingdom of Tonga Tonga (, ; ), officially the Kingdom of Tonga ( to, Puleʻanga Fakatuʻi ʻo Tonga), is a Polynesian country and archipelago. The country has 171 islands – of which 45 are inhabited. Its total surface area is about , scattered over in .... It is located in the fork of the road junction, where the main road to Nukualofa splits into the road to Mua and beyond and the road to the airport near Fuaamotu. It is near to the neighbouring village of Holonga. The population is 647. Overview The village is located on (chief) Luani's estate, and the main hall is called after him: Tāufatoutai. The famous '' faikava'' singers, the Afoeteau (100 chords) hail from Malapo. There is a huge mound in Malapo, which may contain the remnants of king Tuitātui, but no one knows for sure, and the government is unwilling to have archeologists start digging. References Populated places in Tonga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motutapu
Motutapu Island (otherwise known as ''Motutapu'') is a island in the Hauraki Gulf to the northeast of the city of Auckland, New Zealand New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island count .... The island is part of the Hauraki Gulf#National significance, Hauraki Gulf Maritime Park. Its full name, rarely used, is ''Te Motutapu a Taikehu'', "The sacred island of Taikehu", Taikehu having been a tohunga (tribal priest) of the Tainui iwi. 'Motutapu', meaning "sacred" or "sanctuary" island, is a term used for various islands in a number of Polynesian culture, Polynesian cultures. The island can be accessed via regular ferry services departing from Auckland City. Geography Approximately 18,000 years ago during the Last Glacial Maximum when sea levels were over 100 metres lower than present d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fiji
Fiji ( , ,; fj, Viti, ; Fiji Hindi: फ़िजी, ''Fijī''), officially the Republic of Fiji, is an island country in Melanesia, part of Oceania in the South Pacific Ocean. It lies about north-northeast of New Zealand. Fiji consists of an archipelago of more than 330 islands—of which about 110 are permanently inhabited—and more than 500 islets, amounting to a total land area of about . The most outlying island group is Ono-i-Lau. About 87% of the total population of live on the two major islands, Viti Levu and Vanua Levu. About three-quarters of Fijians live on Viti Levu's coasts: either in the capital city of Suva; or in smaller urban centres such as Nadi—where tourism is the major local industry; or in Lautoka, where the Sugarcane, sugar-cane industry is dominant. The interior of Viti Levu is sparsely inhabited because of its terrain. The majority of Fiji's islands were formed by Volcano, volcanic activity starting around 150 million years ago. Some geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |