|
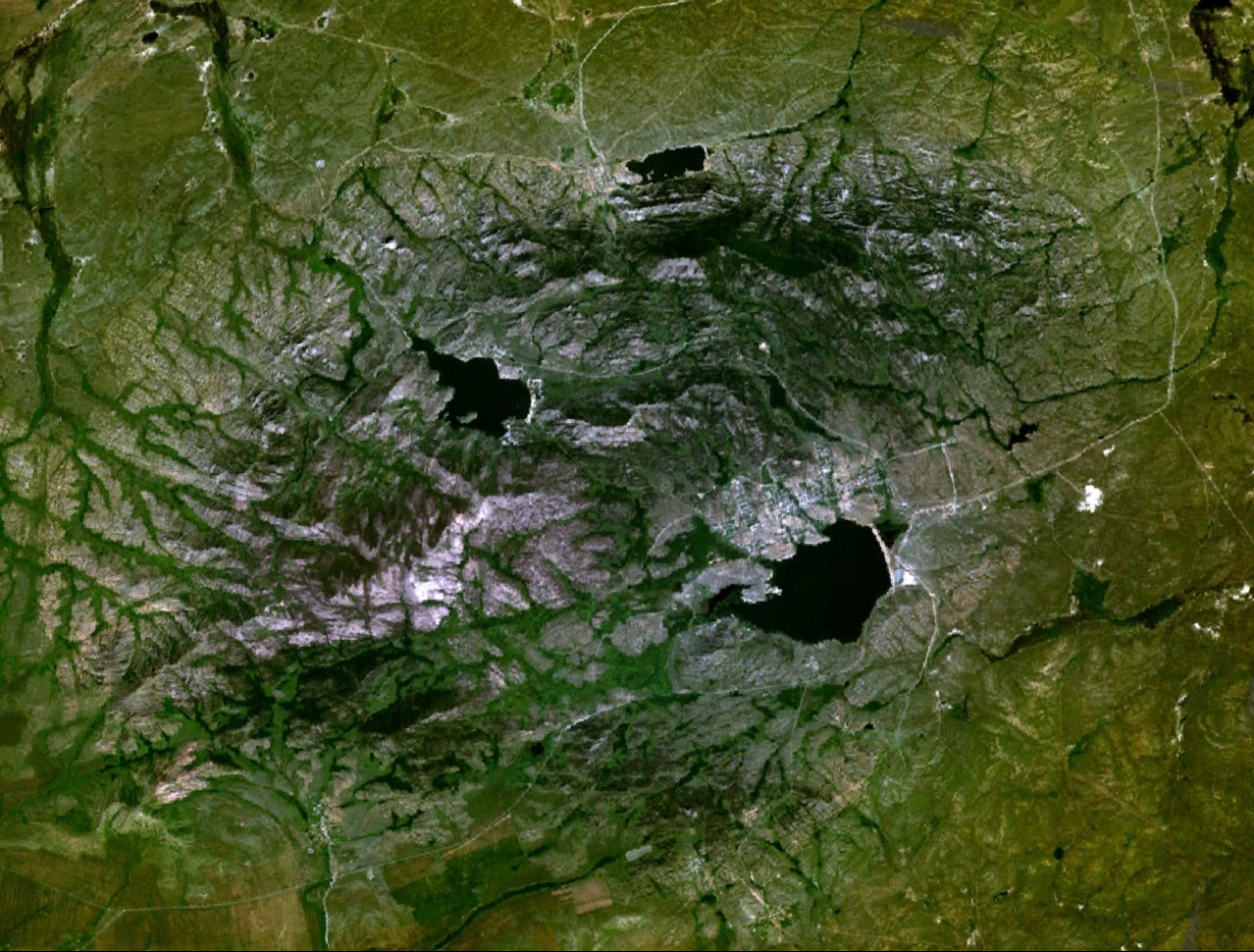
Tuzkol, Bayanaul District
Tuzkol ( kk, Тұзкөл) is a salt lake in Bayanaul District, Pavlodar Region, Kazakhstan. The lake lies southwest of the town of Bayanaul. Geography Tuzkol lies in a tectonic depression of the Kazakh Uplands to the southwest of the eastern part of the Bayanaul Range and to the east of the Ashchysu river. It is the largest of the lakes of the district. Zhanatilek village is located to the south of the southern shore. River Karasu, an intermittent stream, flows into the lake from the east. The water of the lake is saline, containing magnesium and sodium chloride. There is an to thick layer of mud at the bottom of the lake emitting a strong hydrogen sulfide smell. The mud is used locally for medicinal purposes.Google Earth See also *List of lakes of Kazakhstan Excluding the northernmost districts, Kazakhstan consists of endorheic basins, where rivers flow into one of the numerous lakes. The most important drainage system is known as Yedisu, meaning "seven rivers" in Tu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sentinel-2
Sentinel-2 is an Earth observation mission from the Copernicus Programme that systematically acquires optical imagery at high spatial resolution (10 m to 60 m) over land and coastal waters. The mission is currently a constellation with two satellites, Sentinel-2A and Sentinel-2B; a third satellite, Sentinel-2C, is currently undergoing testing in preparation for launch in 2024. The mission supports a broad range of services and applications such as agricultural monitoring, emergencies management, land cover classification or water quality. Sentinel-2 has been developed and is being operated by the European Space Agency, and the satellites were manufactured by a consortium led by Airbus Defence and Space in Friedrichshafen. Overview The Sentinel-2 mission has the following key characteristics: * Multi-spectral data with 13 bands in the visible, near infrared, and short wave infrared part of the spectrum * Systematic global coverage of land surfaces from 56° S to 84°&nb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bayanaul Range
Bayanaul Range ( kk, Баянауыл тауы; russian: Баянаульские горы) is a range of mountains in Bayanaul District, Pavlodar Region, Kazakhstan.Kanysh Satpaev. Encyclopedia / Editor-in-Chief B. O. Jakyp. — Almaty "Kazakh Encyclopedia", 2011. ISBN 9965-893-74-8 Bayanaul, the administrative center of Bayanaul District, lies at the feet of the eastern slopes of the mountains. A large sector of the range is part of the Bayanaul National Park, a protected area established in 1985. Geography The Bayanaul Range is one of the subranges of the Kazakh Upland system (Saryarka). It rises in the northeastern sector of the highlands. The Bayanaul stretches from east to west for about with mountaintops averaging between and . The highest point is Akbet, a high summit. The uppermost levels of the mountains are generally rocky and their slopes are deeply dissected by valleys and ravines. No major rivers have their sources in the range. Most flow into the surrounding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Lakes Of Kazakhstan ...
Excluding the northernmost districts, Kazakhstan consists of endorheic basins, where rivers flow into one of the numerous lakes. The most important drainage system is known as Yedisu, meaning "seven rivers" in Turkic languages. Below is the list of the more important lakes, some of which are shared (Caspian Sea, Lake Aral, Lake Aike, etc.) with the neighbouring countries. References {{Europe topic, List of lakes of * Lakes Kazakhstan Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country located mainly in Central Asia and partly in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the north and west, China to the east, Kyrgyzstan to the southeast, Uzbeki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Google Earth
Google Earth is a computer program that renders a 3D computer graphics, 3D representation of Earth based primarily on satellite imagery. The program maps the Earth by superimposition, superimposing satellite images, aerial photography, and geographic information system, GIS data onto a 3D globe, allowing users to see cities and landscapes from various angles. Users can explore the globe by entering addresses and coordinates, or by using a Computer keyboard, keyboard or computer mouse, mouse. The program can also be downloaded on a smartphone or Tablet computer, tablet, using a touch screen or stylus to navigate. Users may use the program to add their own data using Keyhole Markup Language and upload them through various sources, such as forums or blogs. Google Earth is able to show various kinds of images overlaid on the surface of the earth and is also a Web Map Service client. In 2019, Google has revealed that Google Earth now covers more than 97 percent of the world, and has c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Sulfide
Hydrogen sulfide is a chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless chalcogen-hydride gas, and is poisonous, corrosive, and flammable, with trace amounts in ambient atmosphere having a characteristic foul odor of rotten eggs. The underground mine gas term for foul-smelling hydrogen sulfide-rich gas mixtures is ''stinkdamp''. Swedish chemist Carl Wilhelm Scheele is credited with having discovered the chemical composition of purified hydrogen sulfide in 1777. The British English spelling of this compound is hydrogen sulphide, a spelling no longer recommended by the Royal Society of Chemistry or the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry. Hydrogen sulfide is toxic to humans and most other animals by inhibiting cellular respiration in a manner similar to hydrogen cyanide. When it is inhaled or it or its salts are ingested in high amounts, damage to organs occurs rapidly with symptoms ranging from breathing difficulties to convulsions and death. Despite this, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnesium Chloride
Magnesium chloride is the family of inorganic compounds with the formula , where x can range from 0 to 12. These salts are colorless or white solids that are highly soluble in water. These compounds and their solutions, both of which occur in nature, have a variety of practical uses. Anhydrous magnesium chloride is the principal precursor to magnesium metal, which is produced on a large scale. Hydrated magnesium chloride is the form most readily available. Production Magnesium chloride can be extracted from brine or sea water. In North America, it is produced primarily from Great Salt Lake brine. In the Jordan Valley, it is obtained from the Dead Sea. The mineral bischofite () is extracted (by solution mining) out of ancient seabeds, for example, the Zechstein seabed in northwest Europe. Some deposits result from high content of magnesium chloride in the primordial ocean. Some magnesium chloride is made from evaporation of seawater. In the Dow process, magnesium chloride is regen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saline Water
Saline water (more commonly known as salt water) is water that contains a high concentration of dissolved salts (mainly sodium chloride). On the United States Geological Survey (USGS) salinity scale, saline water is saltier than brackish water, but less salty than brine. The salt concentration is usually expressed in parts per thousand (permille, ‰) and parts per million (ppm). The USGS salinity scale defines three levels of saline water. The salt concentration in slightly saline water is 1,000 to 3,000 ppm (0.1–0.3%); in moderately saline water is 3,000 to 10,000 ppm (0.3–1%); and in highly saline water is 10,000 to 35,000 ppm (1–3.5%). Seawater has a salinity of roughly 35,000 ppm, equivalent to 35 grams of salt per one liter (or kilogram) of water. The saturation level is only nominally dependent on the temperature of the water. At one liter of water can dissolve about 357 grams of salt, a concentration of 26.3% w/w. At boiling () the amount that can be dissolved in o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ashchysu (Ayr)
The Ashchysu ( kk, Ащысу; russian: Ащысу) is a river in the Bukhar-Zhyrau District, Karaganda Region, and May District, Pavlodar Region, Kazakhstan. It is long and has a catchment area of . The area of the basin is a seasonal grazing ground for local cattle and the Ashchysu is used for watering livestock. The river is frozen between November and April. Course The Ashchysu has its sources in the northwest-facing slopes of the Ayr Mountains of the Kazakh Uplands. It heads first northwards, then it bends when it reaches the highland plain and flows roughly northeastwards at the feet of the range along its northern slopes. Further downstream it describes a wide bend and heads roughly northwestwards, leaving the Kyzyltau to the east near Zhanatilek and Tuzkol. When it reaches Musa Shormanov village (former Tendik), the river bends and heads northeastwards within a wide valley. Further downstream it bends and flows eastwards north of the Bayanaul Range, past a number ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pavlodar Region
Pavlodar Region ( kk, Павлодар облысы, translit=Pavlodar oblysy; russian: Павлодарская область, translit=Pavlodarskaya oblast) is a region of Kazakhstan. The population of the region was and ; the latest official estimate (as at the start of 2018) was 754,739. Its capital is the city of Pavlodar, which had a population of 360,014 at the start of 2018. Many people, especially Ukrainians, migrated to Pavlodar in Nikita Khrushchev's Virgin Lands Campaign. The Bayanaul National Park, a protected area of the Kazakh Uplands, is located in the Bayanaul Range, within 100 km of Ekibastuz. Geography Pavlodar borders Russia (Altai Krai, Omsk Oblast and Novosibirsk Oblast) to the north, and also borders the following Kazakh regions: Akmola (to the west), East Kazakhstan (to the south-east), North Kazakhstan (to the north-west), and Karaganda (to the south). The Irtysh River flows from the Altay Mountains in China to Russia through the region; the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kazakh Uplands
The Kazakh Uplands ( kk, Сарыарқа, ''Saryarqa'' - "Yellow Ridge", russian: Казахский мелкосопочник, Kazakhskiy Melkosopochnik), also known as the Kazakh Hummocks, is a large peneplain formation extending throughout the central and eastern regions of Kazakhstan.Казахский мелкосопочник (Kazakh Uplands) '''' in 30 vols. — Ch. ed. . - 3rd ed. - M. Soviet Encyclopedia, 1969-1978. (in Russian) Administratively the Kazakh Uplands stretch acros ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bayanaul District
Bayanaul ( kk, Баянауыл ауданы, ) is a district of Pavlodar Region in northern Kazakhstan. The administrative center of the district is the selo of Bayanaul. Population: Geography Bayanaul District lies in the Kazakh Uplands. high mount Akbet in the Bayanaul Range is the highest point in the district and Tuzkol is the largest lake.Google Earth Google Earth is a computer program that renders a 3D computer graphics, 3D representation of Earth based primarily on satellite imagery. The program maps the Earth by superimposition, superimposing satellite images, aerial photography, and geog ... References Districts of Kazakhstan Pavlodar Region {{Kazakhstan-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salt Lake
A salt lake or saline lake is a landlocked body of water that has a concentration of salts (typically sodium chloride) and other dissolved minerals significantly higher than most lakes (often defined as at least three grams of salt per litre). In some cases, salt lakes have a higher concentration of salt than sea water; such lakes can also be termed hypersaline lakes, and may also be pink lakes on account of their colour. An alkalic salt lake that has a high content of carbonate is sometimes termed a soda lake. One saline lake classification differentiates between: *subsaline: 0.5–3‰ (0.05-0.3%) *hyposaline: 3–20‰ (0.3-2%) *mesosaline: 20–50‰ (2-5%) *hypersaline: greater than 50‰ (5%) Properties Salt lakes form when the water flowing into the lake, containing salt or minerals, cannot leave because the lake is endorheic (terminal). The water then evaporates, leaving behind any dissolved salts and thus increasing its salinity, making a salt lake an excellent place ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |