|
Turtle Dove Shoal
Turtle Dove Shoal is a dangerous shoal about three kilometres wide, located at , in the Indian Ocean about fifty kilometres south of the Houtman Abrolhos, off the coast of Western Australia. The shoal was first charted on a 1627 map by Hessel Gerritsz, where it was labelled as the "Tortelduyff" rocks. The name is thought to signify that the shoal was first discovered by the ship ''Tortelduif'', which is recorded as having arrived at Batavia, Dutch East Indies on 21 June 1623. It was originally laid down in latitude 29° 11' S, and as a result later voyages failed to locate it. In his 1825 '' Narrative of a survey of the intertropical and western coasts of Australia'', Phillip Parker King suggested that they were merely the southernmost reef of the Houtman Abrolhos. In 1846, John Lort Stokes Admiral John Lort Stokes, RN (1 August 1811 – 11 June 1885)Although 1812 is frequently given as Stokes's year of birth, it has been argued by author Marsden Hordern that Stokes was born ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
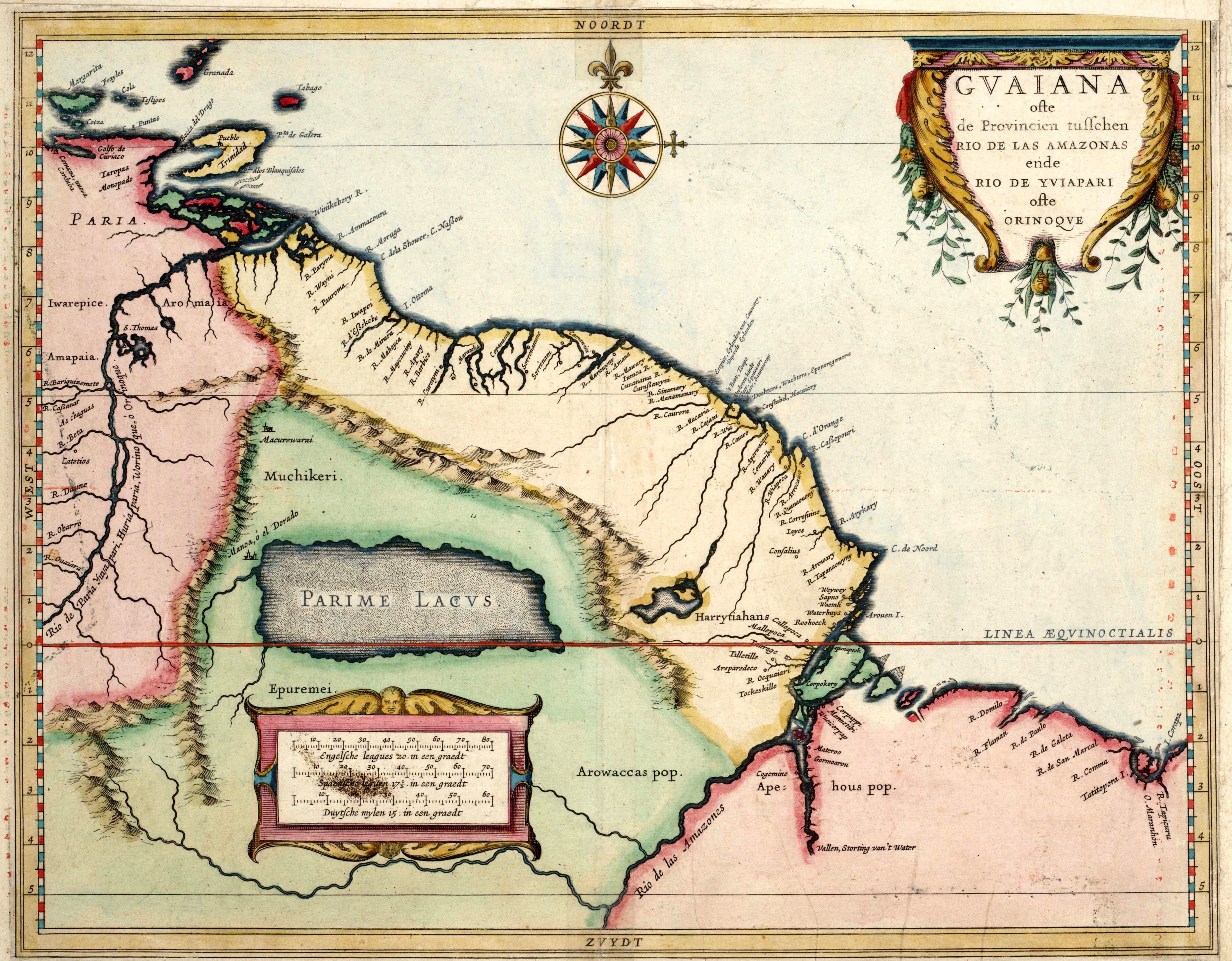
Caert Van't Landt Van D'Eendracht (NLA Balanced)
''Caert van't Landt van d'Eendracht'' ("Chart of the Land of Eendracht") is a 1627 map by Hessel Gerritsz. One of the earliest maps of Australia, it shows what little was then known of the west coast, based on a number of voyages beginning with the 1616 voyage of Dirk Hartog, when he named Eendrachtsland after his ship. The map is oriented with north to the left and shows lines of latitude from 20th parallel south to the 35th parallel south and also shows the Tropic of Capricorn. The top left of the map shows a river labelled ''Willems revier, besocht by 't volck van 't Schip Mauritius in Iulius A° 1618'' ("Willem's River, visited by the crew of the ship Mauritius in July 1618"). The identity of this river, now referred to as ''Willem River'', is unknown; it is possibly the Ashburton River. In the bottom left corner is a feature labelled ''Hier ist Engels schip de Trial vergaen in Iunias, A° 1622'' ("Here the English ship ''Trial'' was wrecked in June 1622"). This is poss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caert Van't Landt Van D'Eendracht (detail Showing Houtman Abrolhos And Turtle Dove Shoal)
''Caert van't Landt van d'Eendracht'' ("Chart of the Land of Eendracht") is a 1627 map by Hessel Gerritsz. One of the earliest maps of Australia, it shows what little was then known of the west coast, based on a number of voyages beginning with the 1616 voyage of Dirk Hartog, when he named Eendrachtsland after his ship. The map is oriented with north to the left and shows lines of latitude from 20th parallel south to the 35th parallel south and also shows the Tropic of Capricorn. The top left of the map shows a river labelled ''Willems revier, besocht by 't volck van 't Schip Mauritius in Iulius A° 1618'' ("Willem's River, visited by the crew of the ship Mauritius in July 1618"). The identity of this river, now referred to as ''Willem River'', is unknown; it is possibly the Ashburton River. In the bottom left corner is a feature labelled ''Hier ist Engels schip de Trial vergaen in Iunias, A° 1622'' ("Here the English ship ''Trial'' was wrecked in June 1622"). This is po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shoal
In oceanography, geomorphology, and geoscience, a shoal is a natural submerged ridge, bank, or bar that consists of, or is covered by, sand or other unconsolidated material and rises from the bed of a body of water to near the surface. It often refers to those submerged ridges, banks, or bars that rise near enough to the surface of a body of water as to constitute a danger to navigation. Shoals are also known as sandbanks, sandbars, or gravelbars. Two or more shoals that are either separated by shared troughs or interconnected by past or present sedimentary and hydrographic processes are referred to as a shoal complex.Neuendorf, K.K.E., J.P. Mehl Jr., and J.A. Jackson, eds. (2005) ''Glossary of Geology'' (5th ed.). Alexandria, Virginia, American Geological Institute. 779 pp. The term ''shoal'' is also used in a number of ways that can be either similar or quite different from how it is used in geologic, geomorphic, and oceanographic literature. Sometimes, this term refer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by the Southern Ocean or Antarctica, depending on the definition in use. Along its core, the Indian Ocean has some large marginal or regional seas such as the Arabian Sea, Laccadive Sea, Bay of Bengal, and Andaman Sea. Etymology The Indian Ocean has been known by its present name since at least 1515 when the Latin form ''Oceanus Orientalis Indicus'' ("Indian Eastern Ocean") is attested, named after Indian subcontinent, India, which projects into it. It was earlier known as the ''Eastern Ocean'', a term that was still in use during the mid-18th century (see map), as opposed to the ''Western Ocean'' (Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic) before the Pacific Ocean, Pacific was surmised. Conversely, Ming treasure voyages, Chinese explorers in the Indian Oce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Houtman Abrolhos
The Houtman Abrolhos (often called the Abrolhos Islands) is a chain of 122 islands and associated coral reefs, in the Indian Ocean off the west coast of Australia, about west of Geraldton, Western Australia. It is the southernmost true coral reef in the Indian Ocean, and one of the highest latitude reef systems in the world. It is one of the world's most important seabird breeding sites, and is the centre of Western Australia's largest single-species fishery, the western rock lobster fishery. It has a small seasonal population of fishermen, and a limited number of tourists are permitted for day trips, but most of the land area is off limits as conservation habitat. It is well known as the site of numerous shipwrecks, the most famous being the Dutch ships , which was wrecked in 1629, and , wrecked in 1727. The islands are an unincorporated area with no municipal government, subject to direct administration of the Government of Western Australia. In July 2019, the Houtman Abro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Australia
Western Australia (commonly abbreviated as WA) is a state of Australia occupying the western percent of the land area of Australia excluding external territories. It is bounded by the Indian Ocean to the north and west, the Southern Ocean to the south, the Northern Territory to the north-east, and South Australia to the south-east. Western Australia is Australia's largest state, with a total land area of . It is the second-largest country subdivision in the world, surpassed only by Russia's Sakha Republic. the state has 2.76 million inhabitants percent of the national total. The vast majority (92 percent) live in the south-west corner; 79 percent of the population lives in the Perth area, leaving the remainder of the state sparsely populated. The first Europeans to visit Western Australia belonged to the Dutch Dirk Hartog expedition, who visited the Western Australian coast in 1616. The first permanent European colony of Western Australia occurred following the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hessel Gerritsz
Hessel Gerritsz ( – buried 4 September 1632) was a Dutch engraver, cartographer, and publisher. He was one of the notable figures in the Golden Age of Netherlandish cartography. Despite strong competition, he is considered by some "unquestionably the chief Dutch cartographer of the 17th century". Early career He started in Alkmaar as an apprentice to Willem Jansz Blaeu, who was ten years his elder. Gerritsz moved with Blaeu’s workshop to Amsterdam, where he married Geertje Gijsberts of Alkmaar in 1607. They had eight children. Geertje would die before 1624, when Hessel remarried. By 1610 he had a printing workshop on his own. Many of his engravings and maps made it into the atlases of Blaeu, Jan Janssonius, and others. Career Printer Gerritsz produced a world map in 1612 that included the discoveries of Queirós and specifically indicated "Austrialia del Espiritu Santo", now known to be Vanuatu, but for long thought to be part of the "South land". The map w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Batavia, Dutch East Indies
Batavia was the capital of the Dutch East Indies. The area corresponds to present-day Jakarta, Indonesia. Batavia can refer to the city proper or its suburbs and hinterland, the Ommelanden, which included the much-larger area of the Residency of Batavia in the present-day Indonesian provinces of Jakarta, Banten and West Java. The founding of Batavia by the Dutch in 1619, on the site of the ruins of Jayakarta, led to the establishment of a Dutch colony; Batavia became the center of the Dutch East India Company's trading network in Asia. Monopolies on local produce were augmented by non-indigenous cash crops. To safeguard their commercial interests, the company and the colonial administration absorbed surrounding territory. Batavia is on the north coast of Java, in a sheltered bay, on a land of marshland and hills crisscrossed with canals. The city had two centers: Oud Batavia (the oldest part of the city) and the relatively-newer city, on higher ground to the south. It was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Narrative Of A Survey Of The Intertropical And Western Coasts Of Australia
A narrative, story, or tale is any account of a series of related events or experiences, whether nonfictional ( memoir, biography, news report, documentary, travelogue, etc.) or fictional (fairy tale, fable, legend, thriller, novel, etc.). Narratives can be presented through a sequence of written or spoken words, through still or moving images, or through any combination of these. The word derives from the Latin verb ''narrare'' (to tell), which is derived from the adjective ''gnarus'' (knowing or skilled). Narration (i.e., the process of presenting a narrative) is a rhetorical mode of discourse, broadly defined (and paralleling argumentation, description, and exposition), is one of four rhetorical modes of discourse. More narrowly defined, it is the fiction-writing mode in which a narrator communicates directly to an audience. The school of literary criticism known as Russian formalism has applied methods that are more often used to analyse narrative fiction, to non-ficti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phillip Parker King
Rear Admiral Phillip Parker King, FRS, RN (13 December 1791 – 26 February 1856) was an early explorer of the Australian and Patagonian coasts. Early life and education King was born on Norfolk Island, to Philip Gidley King and Anna Josepha King ''née'' Coombe, and named after his father's mentor, Admiral Arthur Phillip (1738–1814), (first governor of New South Wales and founder of the British penal colony which later became the city of Sydney in Australia), which explains the difference in spelling of his and his father's first names. King was sent to England for education in 1796, and he joined the Royal Naval Academy, at Portsmouth, in county Hampshire, England in 1802. King entered the Royal Navy in 1807, where he was commissioned lieutenant in 1814. Expeditions in Australia King was assigned to survey the parts of the Australian coast not already examined by Royal Navy officer, Matthew Flinders, (who had already made three earlier exploratory voyages between 17 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Lort Stokes
Admiral John Lort Stokes, RN (1 August 1811 – 11 June 1885)Although 1812 is frequently given as Stokes's year of birth, it has been argued by author Marsden Hordern that Stokes was born in 1811, citing a letter by fellow naval officer Crawford Pasco congratulating him on his birthday in 1852. was an officer in the Royal Navy who travelled on for close to eighteen years. Biography Born on 1 August 1811, son of Henry Stokes, of Scotchwell, near Haverfordwest, Pembrokeshire, and Anne, daughter of Dr George Phillips, Stokes joined the Royal Navy on 20 September 1824. The first ship he served on was , and then in October 1825 he joined the crew of ''Beagle'' under Captain Phillip Parker King. ''Beagle'' was involved in a survey of the waters of South America. In 1828 the commander of HMS ''Beagle'', Pringle Stokes (not related to John Lort Stokes), committed suicide and Robert FitzRoy assumed command; the ship returned to England in 1830 and was recommissioned. From 1831 to 1836 S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Champion (schooner)
H.M. Colonial Schooner Champion was in service with the Colony of Western Australia from 1836 until 1852. Champion Bay, Geraldton, Western Australia was named after her by Lieutenant John Lort Stokes of , who surveyed the area in April 1840. George Fletcher Moore had travelled in ''Champion'' to the region and first located the bay in January of that year. See also *Henry Bull (settler) Lieutenant Henry Bull (1799) was an early settler in the Swan River Colony. He entered the Royal Navy in December 1813, and served in the West Indies and South America. He retired as a Lieutenant in 1829, and the following year he arrived in ..., captain of ''Champion'' in 1836 References {{reflist Schooners of Australia 1788–1850 ships of Australia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)

_photo_2.jpg)